Just four months after the groundbreaking surgery, the patient was able to feel the touch of his sister’s hand.


In a recent article published in Scientific Reports, researchers describe the symptom profiles of respiratory viral infections from the Flu Watch Community and the Virus Watch cohort studies to compare the frequency of the range of symptoms experienced during influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), rhinovirus, seasonal coronaviruses (CoVs) infections, and infections from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) wild-type (wt) strain and variants of concerns (VOCs), including Alpha, Delta, Omicron BA1/BA2/BA5.
Study: Symptom profiles of community cases infected by influenza, RSV, rhinovirus, seasonal coronavirus, and SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Image Credit: KitjaKitja/Shutterstock.com.


In a recent review published in BJC reports, researchers investigated the complex relationship between gut bacteria, diet, and patient nutrition, aiming to discern how these combined elements impact responses to immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) cancer treatment and identify patients most likely to benefit from such therapy.
Study: Gut microbiome and nutrition-related predictors of response to immunotherapy in cancer: making sense of the puzzle. Image Credit: SewCreamStudio/Shutterstock.com.



The skin is the largest organ of the body, comprising several compartments and about 20 different cell types that are involved in various skin functions – complexity that is more than skin deep! [1] Skin aging is a multifactorial process that is impacted by several intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Constant exposure of the human skin to such stimuli impacts its function and accelerates aging resulting in dry skin, wrinkling, thinning of the epidermis, and reduced barrier integrity. While we notice most of those changes by looking in a mirror – something the cosmetics industry has leveraged to multi-billion dollar effect – older skin is more at risk of injury, less able to sense touch, heat and cold, slower to heal and more prone to cellulitis and other skin infections.
Aging is a complex and gradual process characterized by a reduction in function and reproducibility along with an increase in the incidence of degenerative diseases. Skin aging has been reported to be associated with the presence and accumulation of senescent cells. “A number of diseases that increase in older people may have a unifying underlying mechanism having to do with senescence,” says Ruth Montgomery, PhD, professor of medicine and epidemiology (microbial diseases) at Yale School of Medicine [2].
Senescent cells are those that have lost their proliferative capacity, are resistant to apoptosis, and secrete factors that can cause tissue deterioration and inflammation [3]. These factors are termed senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) and can lead to extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition, impact epidermal stem cell renewal and worsen melanin synthesis.
Each cell in the body stores its genetic information in DNA in a stable and protected form that is readily accessible for the cell to carry on its activities. Nevertheless, mutations—changes in genetic information—occur throughout the human genome and can have a powerful influence on human health and evolution.
“Our team is interested in a classical question about mutation—why do mutation rates in the genome vary so tremendously from one DNA location to another? We just do not have a clear understanding of why this occurs,” said Dr. Md. Abul Hassan Samee, assistant professor of integrative physiology at Baylor College of Medicine and corresponding author of the work.
Previous studies have shown that the DNA sequences flanking a mutated position—the sequence context—play a strong role in the mutation rate. “But this explanation still leaves unanswered questions,” Samee said. “For example, one type of mutation occurs frequently in a specific sequence context while a different type of mutation occurs infrequently in that same sequence context. So, we think that a different mechanism could explain how mutation rates vary in the genome. We know that each building block or base that makes up a DNA sequence has its own 3D chemical shape. We proposed, therefore, that there is a connection between DNA shape and mutations rates, and this paper shows that our idea was correct.”
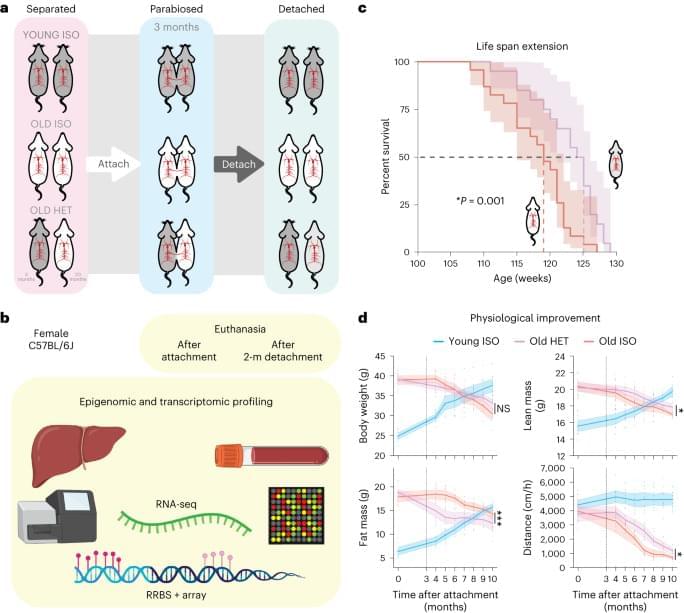
Heterochronic parabiosis ameliorates age-related diseases in mice, but how it affects epigenetic aging and long-term health was not known. Here, the authors show that in mice exposure to young circulation leads to reduced epigenetic aging, an effect that persists for several months after removing the youthful circulation.