It’s now easier for scientists to create gene-edited insects thanks to a new technique called “direct parental CRISPR.”


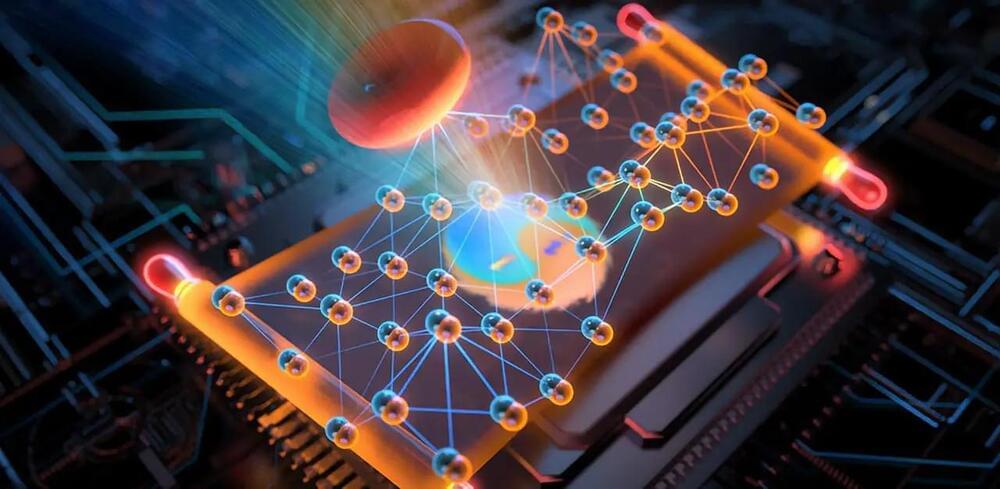
Computational imaging holds the promise of revolutionizing optical imaging with its wide field of view and high-resolution capabilities. Through the joint reconstruction of amplitude and phase — a technique known as “coherent imaging or holographic imaging” — the throughput of an optical system can expand to billions of optically resolvable spots. This breakthrough empowers researchers to gain crucial insights into cellular and molecular structures, making a significant impact on biomedical research.
Despite the potential, existing large-scale coherent imaging techniques face challenges hindering their widespread clinical use. Many of these techniques require multiple scanning or modulation processes, resulting in long data collection times to achieve a high resolution and signal-to-noise ratio. This slows down imaging and limits its feasibility in clinical settings due to tradeoffs between speed, resolution, and quality.
A makeshift lab in Fresno, California was illegally storing over 1,000 bioengineered mice and disease samples. Ana Kasparian and Wosney Lambre discuss on The Young Turks. https://shoptyt.com/collections/justice-is-coming.
Watch TYT LIVE on weekdays 6–8 pm ET. http://youtube.com/theyoungturks/live.
“An illegal lab in California containing nearly 1,000 bioengineered mice has officials concerned after improperly stored tissue samples were tested and discovered to contain infectious diseases including HIV and Hepatitis.
“This is an unusual situation. I’ve been in government for 25 years. I’ve never seen anything like this,” Reedley City Manager Nicole Zieba said, per local news outlet KRON4.”
The largest online progressive news show in the world. Hosted by Cenk Uygur and Ana Kasparian. LIVE weekdays 6–8 pm ET.
Help support our mission and get perks. Membership protects TYT’s independence from corporate ownership and allows us to provide free live shows that speak truth to power for people around the world. See Perks: ▶ https://www.youtube.com/TheYoungTurks/join.

Still a big maybe but it gives them other ideas/possibilities. Hopefully they succeed soon! My mother has glaucoma. It’ll probably be decades before this cure happens though. Unless it can be accelerated which is predicted by Ray Kurzweil in his book The Singularity is Near. I think other futurists have said similar things though I’m not familiar with all of them, I saw a talk by one for NASA.
In efforts to tackle the leading cause of blindness in developed countries, researchers have recruited nanotechnology to help regrow retinal cells.
Macular degeneration is a form of central vision loss, which has massive social, mobility, and mental consequences. It impacts hundreds of millions of people globally and is increasing in prevalence.
The degeneration is the consequence of damaged retinal pigment cells. Our bodies are unable to grow and replace these cells once they start dying, so scientists have been exploring alternative methods to replace them and the membrane within which they sit.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links:
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
Use Code: ConquerAging At Checkout.
Epigenetic Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
At-Home Blood Testing: https://getquantify.io/mlustgarten.
Oral Microbiome: https://www.bristlehealth.com/?ref=michaellustgarten.
Now fast forward 10 more years. That same man and his peers will have counted 70 circles round the sun. But John will remain biologically 60. At the same time, someone who is 30 years old in the year 2033 could theoretically begin the therapy at age 30, and stick at a biological age of 30 for the next 30 years, when their calendar would call them 60. That’s what gene therapies for longevity could do.
Longevity startups are riding high as a wave of gene therapies advance through clinical trials. Can they actually turn back the clock?
So far, gene therapy has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for only a couple of applications like rare inherited diseases and blood cancer. That said, more than 2,000 clinical trials are taking place in 2023, with 200 of them having already reached phase 3 clinical trials. A slew of upcoming gene therapies could be approved—possibly in the months to come—in the United States and Europe, targeting everything from sickle cell disease and hemophilia to metastatic skin cancer. In this future, gene therapy will be approved for everything we can imagine—and many things we can’t.
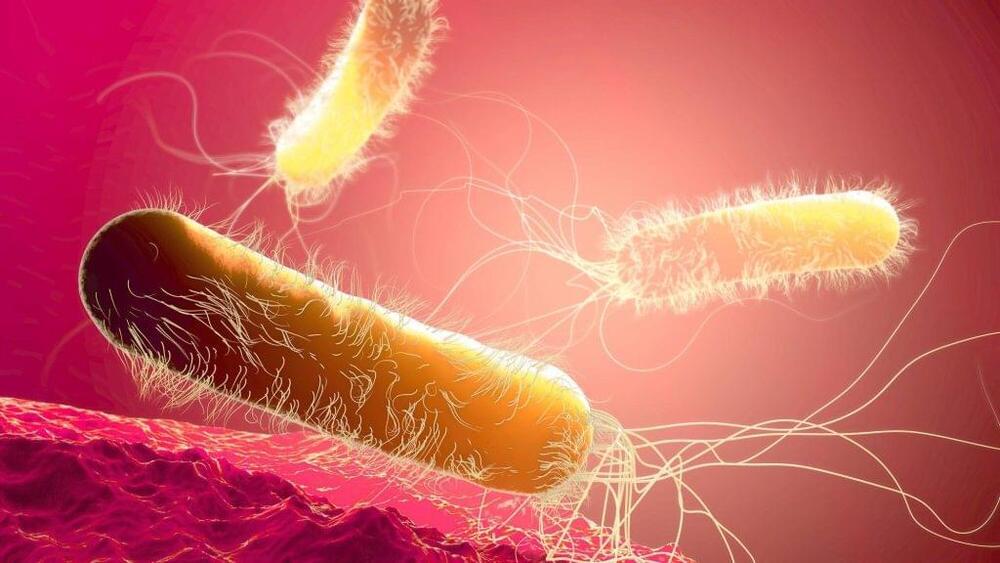
Mayo Clinic scientists are building an expansive library of DNA blueprints of disease-causing bacterial species. The unique collection of genomic sequences is serving as a reference database to help doctors provide rapid and precise diagnoses and pinpoint targeted treatments to potentially improve patient outcomes.
The vast data set is also being studied by researchers in an effort to develop new individualized treatments to combat bacteria-related diseases.
Bacterial infections were linked to more than 7 million global deaths in 2019. Of those, nearly 1.3 million were the direct result of drug-resistant bacteria, according to the National Institutes of Health.

Head over to our on-demand library to view sessions from VB Transform 2023. Register Here
The recent Ant-Man movie did a great job of putting quantum up in lights, but the future of quantum science shines even brighter than fiction. One application, quantum sensors, is already the basis of some of the most important systems and technologies in our world — global positioning systems (GPS) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners are prime examples.
Quantum sensors and quantum AI are just the beginning: Robots are now getting the quantum sensor treatment too. Quantum sensors will supercharge the way robots work and how we apply them to important 21st-century challenges.

Assessments of the health impacts of the non-sugar sweetener aspartame are released today by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Citing “limited evidence” for carcinogenicity in humans, IARC classified aspartame as possibly carcinogenic to humans (IARC Group 2B) and JECFA reaffirmed the acceptable daily intake of 40 mg/kg body weight. Aspartame is an artificial (chemical) sweetener widely used in various food and beverage products since the 1980s, including diet drinks, chewing gum, gelatin, ice cream, dairy products such as yogurt, breakfast cereal, toothpaste and medications such as cough drops and chewable vitamins.
https://www.who.int/news/item/14-07-2023-aspartame-h…s-released
An expert panel found a potential association with liver cancer, but too little research exists to assume a causal connection. For now, the WHO left current consumption guidelines unchanged.