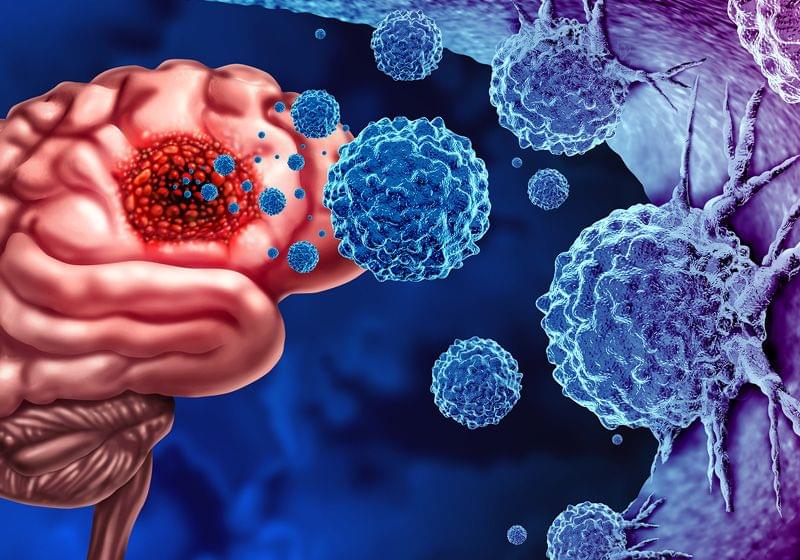
Scientists established an epigenetic mouse model for glioma, providing insight into how epigenetics can initiate cancer.

A study in the journal Cell sheds new light on the evolution of neurons, focusing on the placozoans, a millimeter-sized marine animal. Researchers at the Center for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona find evidence that specialized secretory cells found in these unique and ancient creatures may have given rise to neurons in more complex animals.
Placozoans are tiny animals, around the size of a large grain of sand, which graze on algae and microbes living on the surface of rocks and other substrates found in shallow, warm seas. The blob-like and pancake-shaped creatures are so simple that they live without any body parts or organs.
These animals, thought to have first appeared on Earth around 800 million years ago, are one of the five main lineages of animals alongside Ctenophora (comb jellies), Porifera (sponges), Cnidaria (corals, sea anemones and jellyfish) and Bilateria (all other animals).
The intricate interplay of gene expression within living cells is akin to a well-orchestrated symphony, with each gene playing its part in perfect harmony to ensure cells function as they should. At the heart of this symphony are transcription factors (TFs), molecular maestros that regulate the expression of genes by binding to specific DNA sequences known as promoters.
Unlocking the secrets of these genome-scale regulatory networks requires a comprehensive collection of gene expression profiles, but measuring gene expression responses for every TF and promoter pair has posed a formidable challenge due to the sheer number of potential combinations, even in relatively simple organisms such as bacteria.
To tackle this challenge, researchers led by Fuzhong Zhang, professor of energy, environmental & chemical engineering in the McKelvey School of Engineering at Washington University in St. Louis, developed a technique called pooled promoter responses to TF perturbation sequencing (PPTP-seq).
Studying genes in families with a propensity for certain diseases has led to many critical advances in medicine, including the discovery of statins in family members who suffered heart attacks at an early age.
Now, a team of researchers at Case Western Reserve University has identified an inherited mutation in a gene linked to a highly lethal cancer called esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC).
“With this discovery, we will be able to identify early those at a high risk of developing EAC in their lifetime, and accordingly tailor screening, lifestyle and treatment strategies to prevent cancer development,” said Kishore Guda, an associate professor at the Case Western Reserve School of Medicine and member of the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center.
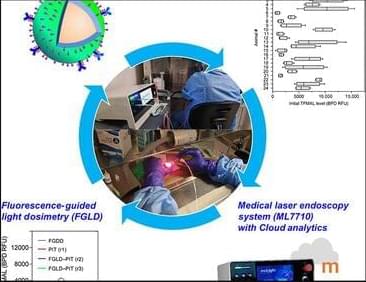
Abstract of full article w/ downloadable pdf:
Fluorescence-guided intervention can bolster standard therapies by detecting and treating microscopic tumors before lethal recurrence. Tremendous progress in photoimmunotherapy and nanotechnology has been made to treat metastasis. However, many are lost in translation due to heterogeneous treatment effects. Here, we integrate three technological advances in targeted photo-activable multi-agent liposome (TPMAL), fluorescence-guided intervention, and laser endoscopy (ML7710) to improve photoimmunotherapy. TPMAL consists of a nanoliposome chemotherapy labeled with fluorophores for tracking and photosensitizer immunoconjugates for photoimmunotherapy… More.
Fluorescence-guided photoimmunotherapy using nanotechnology and ML7710 reduces heterogeneous therapy effects and tumor metastasis.

Chemotherapy as a treatment for cancer is one of the major medical success stories of the 20th century, but it’s far from perfect. Anyone who has been through chemotherapy or who has had a friend or loved one go through it will be familiar with its many side effects: hair loss, nausea, weakened immune system, and even infertility and nerve damage.
This is because chemotherapy drugs are toxic. They’re meant to kill cancer cells by poisoning them, but since cancer cells derive from healthy cells and are substantially similar to them, it is difficult to create a drug that kills them without also harming healthy tissue.
But now a pair of Caltech research teams have created an entirely new kind of drug delivery system, one that they say may finally give doctors the ability to treat cancer in a more targeted way. The system employs drugs that are activated by ultrasound —and only right where they are needed in the body.

NIH-funded study suggests need to reevaluate opioid addiction treatment recommendations in the era of fentanyl.
Individuals with opioid use disorder who were prescribed a lower buprenorphine dose were 20% more likely to discontinue treatment than those on a higher dose, according to a study of patients prescribed buprenorphine in Rhode Island from 2016 to 2020, as fentanyl became widely available. The study, published today in JAMA Network Open, was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, and conducted by researchers at Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island; NIDA and the Rhode Island Department of Health.
Among patients newly initiating buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder, 59% of those prescribed the target daily dose of 16 milligrams recommended by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and 53% of those prescribed the higher 24 mg daily dose discontinued treatment within 180 days. A statistical analysis that allowed for multivariable comparison of these two dose groups showed patients prescribed the recommended dose (16 mg) were significantly more likely to discontinue treatment over 180 days compared to those prescribed 24 mg.

At Science4Seniors we strive to take rigorous research published in Scientific Journals and make the core information accessible to all. If you want to support us please like and follow us on Facebook. In recent years, the intersection of medical science and technology has unfurled fascinating possibilities, especially in diagnostics. Among the many marvels we’ve been introduced to, medical artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping how we detect and diagnose a plethora of health conditions. One area that stands out significantly in this transformation is the potential of AI in the analysis of retinal images.
In response to the increasing demand for medical services amid labor shortages and a rapidly aging population, Shanghai-based Fourier Intelligence is developing an innovative humanoid robot. The GR-1, as it is called, promises to transform healthcare facilities and offer vital assistance to the elderly.
Like many countries, China is confronting the challenge of an aging population. The number of individuals aged 60 and over is projected to rise from 280 million to over 400 million by 2035, according to estimates from the country’s National Health Commission. That’s more than the entire population of the United States projected for that year.
It’s not the sheer number of the elderly that is a problem, but rather their share of the overall population. By 2040, nearly 30% of China’s population will be 60 or older.