Basically many have theorized that these seeds coming from meteorites mean that essentially perhaps that life started from seeds like this. Going much deeper down the rabbit hole we actually are starting to see a grand design possibly by actually organisms that evolved into what we have now over millions of years which is actually weird because all earth would have been just a rock but this could be a grand architecture genetically even from the first seed to the biological singularity. This could Basically prove the existence of some entity that may have created humans and all life most like from this seed which means whether it is alien gods or God there will be so much more discover due to this complexity which can benefit all medicine and also genetic engineering 🤔 😉 😀
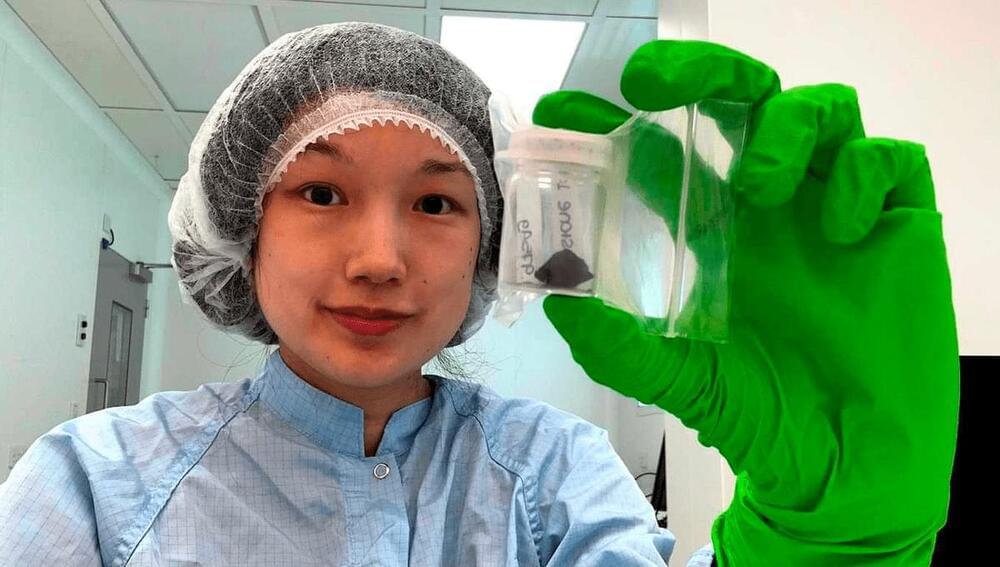
The fact the first of four surviving pieces was collected within 12 hours of landing, allowing little time for contamination, added to the meteorite’s value. Indeed, because the abundance of organic material in the meteorite was ten times lower than in other carbonaceous chondrites, they might not have been distinguishable from Earthly contamination had it not been retrieved so quickly. As it is, some of the amino acids found are quite rare on Earth, confirming their extraterrestrial origins.
The Winchcombe stones had a number of features never previously seen in meteorites, including low amino acid abundance for a carbonaceous chondrite but unusual ratios among the amino acids and PAHs that are present. Combined with the incomplete conversion of Winchcombe’s components into solid rock, this led the authors to speculate Winchcombe could represent a new class of meteorite that has not been studied before.
Perhaps in part because of its weak structure, very little of the Winchcombe meteorite made it to the ground. Just 600 grams (1.3 pounds) have been recovered, compared to a 27-kilogram (60-pound) carbonaceous chondrite that landed in Costa Rica in 2019. This prevented certain forms of analysis that require bulk samples.