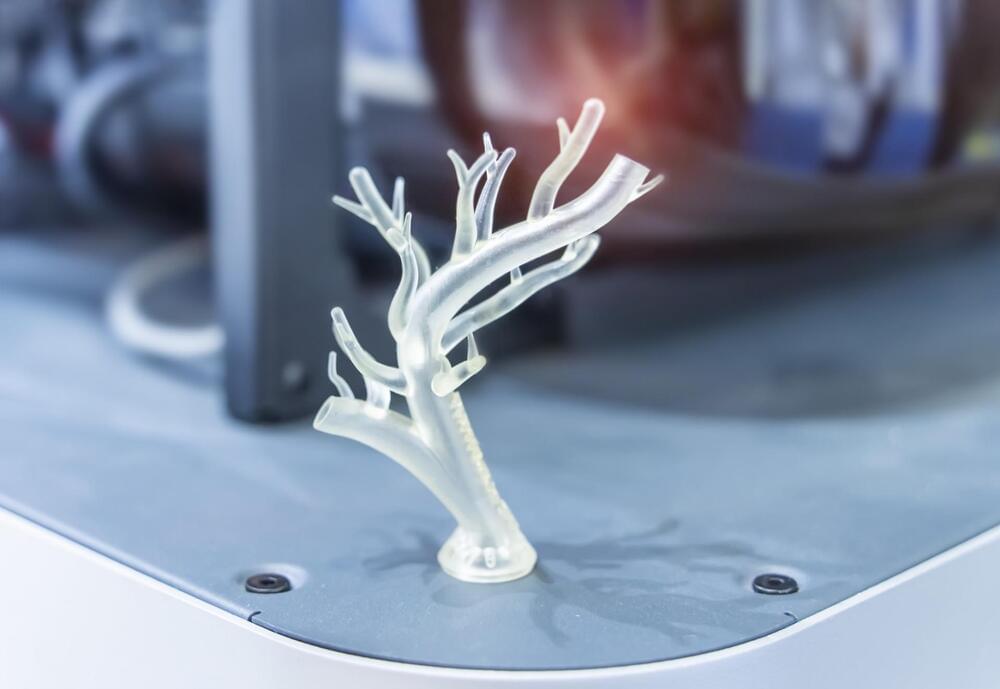
In the United States, the shortage of available organs for transplantation remains a critical issue, with over 100,000 individuals currently on the waiting list. The demand for organs, including hearts, kidneys, and livers, significantly outweighs the available supply, leading to prolonged waiting times and often, devastating consequences.
It is estimated that approximately 6,000 Americans lose their lives while waiting for a suitable donor organ every year.
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University have developed a novel tissue engineering technique that aims to potentially bridge the gap between organ demand and availability, offering a beacon of hope.