Extraterrestrial life in the universe might be rarer than scientists thought; here’s why.
Follow Elements for more!
Extraterrestrial life in the universe might be rarer than scientists thought; here’s why.
Follow Elements for more!

Scientists have identified a group of planets outside our solar system where the same chemical conditions that may have led to life on Earth exist.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge and the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology (MRC LMB), found that the chances for life to develop on the surface of a rocky planet like Earth are connected to the type and strength of light given off by its host star.
Their study, published in the journal Science Advances, proposes that stars which give off sufficient ultraviolet (UV) light could kick-start life on their orbiting planets in the same way it likely developed on Earth, where the UV light powers a series of chemical reactions that produce the building blocks of life.
Scientists say they’ve found a huge lake of salty water buried deep beneath Mars’s surface.
Could there be life on Mars?
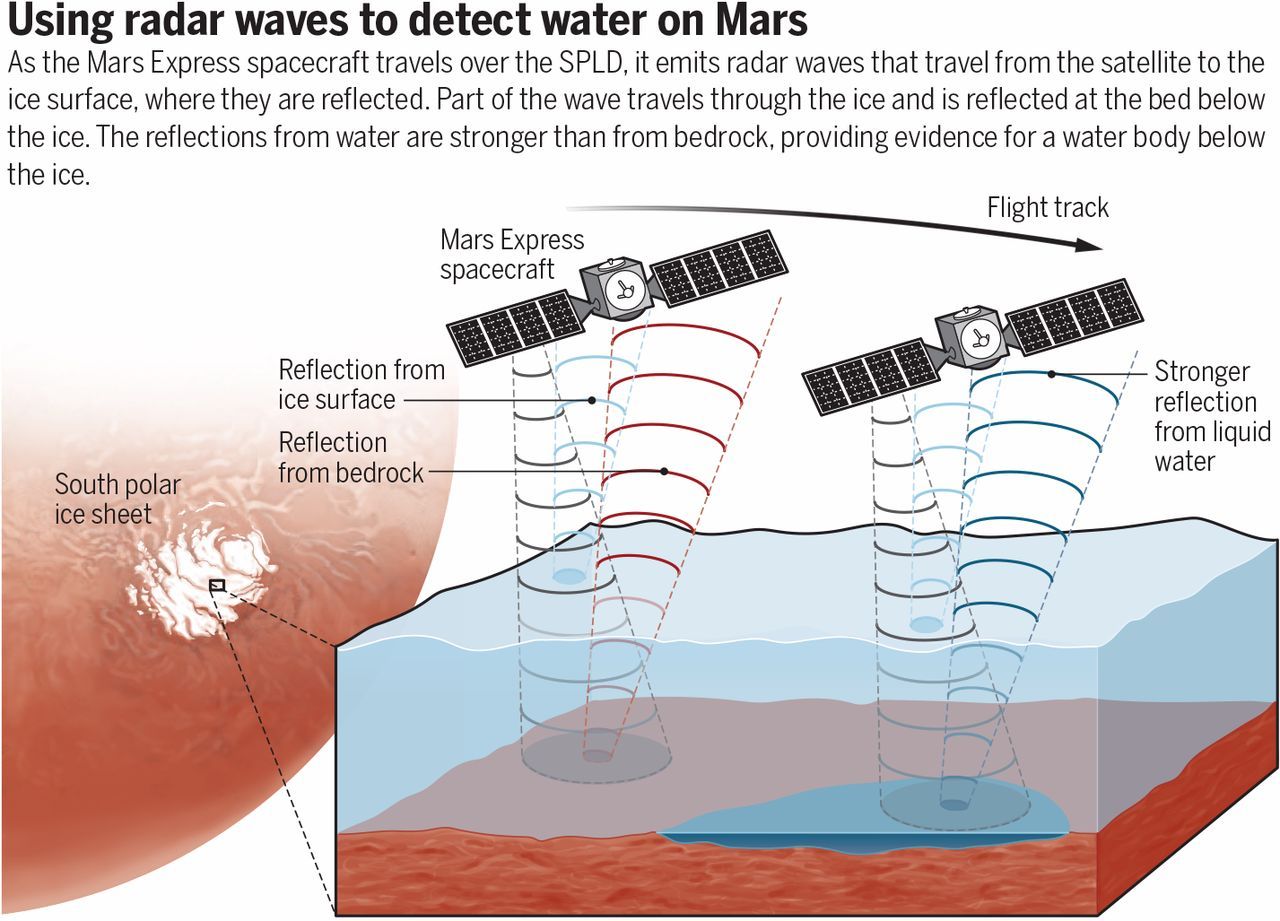
A water body exists below the Martian south polar ice cap.
Without water, no form of life as we know it could exist. There is therefore great interest in detecting liquid water on other planets of our Solar System. Landforms such as dry river valleys and lakes show that liquid water must have been present on Mars in the past (1). Nowadays, small amounts of gaseous water exist in the Martian atmosphere, and some water ice is found on the planet’s surface. Water droplets were seen condensing onto the Phoenix lander (2), and there may be reoccurring water activity on slopes during the Martian summer (3). However, stable bodies of liquid water have not been found on Mars. Published in Science’s First Release this week, Orosei et al. (4) report an analysis of radar data from the Mars Express mission that shows the existence of stable liquid water below 1.5 km of ice, close to the Martian south pole.
Ice caps similar to those on Earth exist at the Martian north and south poles, known as the North and South Polar Layered Deposits (NPLD and SPLD, respectively). More than 30 years ago, Clifford hypothesized that liquid water might be present below the Martian polar ice caps (5). Despite mean annual air temperatures of around −60°C, lakes exist below Earth’s Antarctic ice sheet (6). Glacier ice insulates the bed from the cold surface. Thus, temperatures at the base of the Antarctic ice sheet, which may be as thick as 4.8 km, can reach the pressure melting point of water; the melting point is reduced owing to the pressure of the ice layer above. Water at the ice base reduces basal friction, leading to increased flow speeds. Finding liquid water below the Martian ice caps might solve ongoing debates about whether the NPLD ice flow is due to ice deformation, deformation of the bed, or gliding over the bed or whether it is not flowing at all (7).
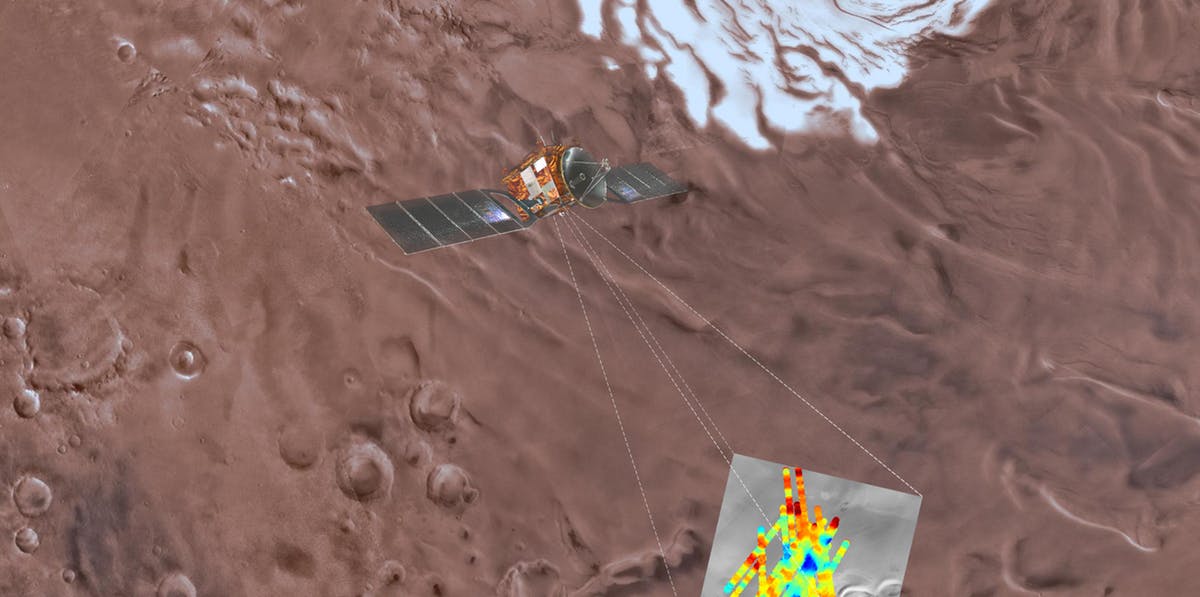

Scientists announced Wednesday that they’ve found evidence of a large body of water beneath the surface of Mars. It may not be little green men, but it’s pretty darn cool.
The announcement, which comes less than two months after the Curiosity Rover found evidence of organic molecules on Mars, adds one more piece to the puzzle for scientists searching the planet for signs that it could support life — or at least could have in the past. And while scientists have long known that Mars used to have liquid water billions of years ago, the fact that it could still have water is a big deal since there’s a possibility that this water may host living organisms.
The researchers involved in the discovery, a team of Italian astronomers and physicists, published their findings in a paper in the journal Science. In the paper, the team presents evidence collected from May 2012 to December 2015 by the MARSIS (Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionosphere Sounding) experiment aboard the Mars Express spacecraft that shows evidence of a large body of liquid water.
For as long as she can remember, she’s puzzled over what’s out there. As a kid drifting off to sleep on a trampoline outside her family’s home near Portland, Ore., she would track the International Space Station. She remembers cobbling together a preteen version of the Drake Equation on those nights and realizing that the likelihood of intelligent alien life was something greater than zero. Star Trek marathons with her father catalyzed her cosmic thinking, as did her mother’s unexpected death when Bailey was 8. The house lost some of its order—some of its gravity—which led to more nights gazing skyward on the trampoline.
In college, Bailey got a hard-won paid internship at the now-merged aerospace giant Hamilton Sundstrand and joined a team repairing turbine engines. She hated it. “It was the opposite of pushing the envelope,” she says. “Nothing new ever went into that building. Nothing new ever left that building.”
By the time she set off to get a master’s degree in mechanical engineering at Duke University, the idea of logging 30 years at a place like Boeing Cor NASA had lost all appeal. She tried her hand at finance and later law, and was unlucky enough to excel at both. “I made it pretty far down that path, but then I thought, Wait, if I become a lawyer, then I’m a lawyer and that’s what I do,” she recalls. “What if I don’t want to do that on Tuesdays?”

Interstellar travel one of the most moral projects? “one of the most moral projects might be to prepare for interstellar travel. After all, if the Earth becomes inhabitable—whether in 200 years or in 200,000 years—the only known civilization in the history of the solar system will suddenly go extinct. But if the human species has already spread to other planets, we will escape this permanent eradication, thus saving millions—possibly trillions—of lives that can come into existence after the demise of our first planet.”
The Red Planet is a freezing, faraway, uninhabitable desert. But protecting the human species from the end of life on Earth could save trillions of lives.

Life on Mars will continue after all. After three seasons on cable television, the Syfy space war drama The Expanse was given the axe on May 10. Since then, support from the show’s fans has helped it find new life: The series has officially been renewed by Amazon for Season 4, which will be streamable. That’s right — not only will the sci-fi favorite return, but it is now marathon material. So, when is The Expanse Season 4? A premiere date has not yet been announced, but one thing is for sure — fans and The Expanse cast members alike can’t get enough of the show’s revival.
The Expanse, based on the New York Times bestselling eight-part book series co-written by Daniel Abraham and Ty Franck under the pen name James S. A. Corey, is set in a fully colonized solar system on the brink of war. There are three main parties that make up this narrative — Earth, Mars, and the asteroid belt — and their biggest mission is universal peace. Just like Rome wasn’t built in a day, though, universal peace wasn’t achieved in three seasons, so it only makes sense that Amazon picked up the story for continuation on a new platform.
It helps that Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos is a big fan of the books on which the show is based, according to the Hollywood Reporter, and he wasn’t ready to see the TV series go. He made the public announcement on May 25 at a National Space Society panel where the show’s cast and crew were in attendance.