Nearly one year ago to the day, we first revealed Curtiss Motorcycle’s upcoming Zeus V8 electric motorcycle. And now we’re learning that the innovative electric motorcycle has already begun production, thanks to a recently announced partnership.
Category: 3D printing – Page 75
Electronic Alchemy develops multi-material electronics 3D printer for NASA
3D printer manufacturer Electronic Alchemy has developed a system capable of additive manufacturing fully functional electronics. Named eForge, NASA intends to use the system during planetary space missions to 3D print chemical sensors on demand. Following the launch of eForge, the company is also now designing a device to recycle 3D printed electronics, further reducing NASA’s need for resupply missions.
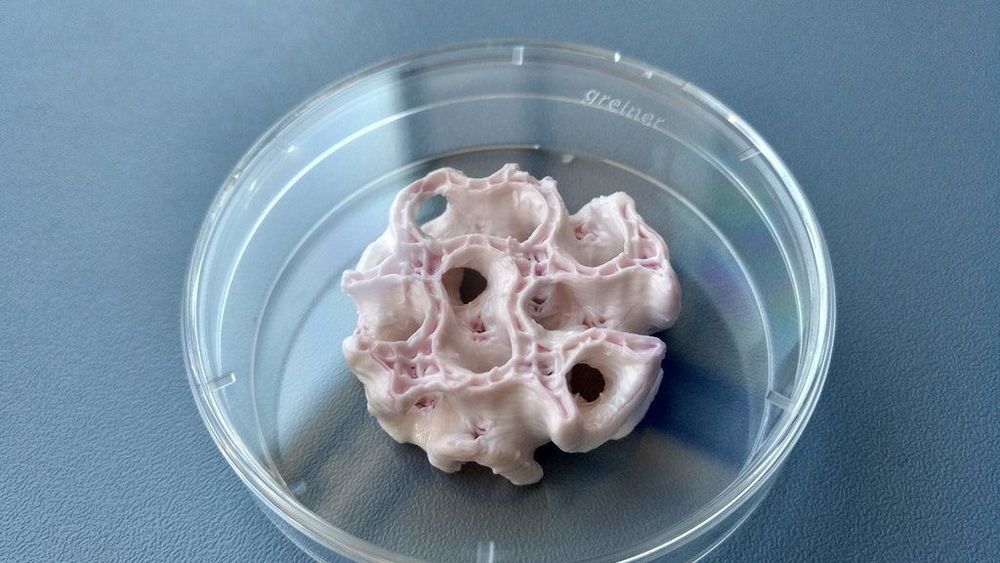
Luxembourg company builds 3D printers to create human skin in space
A Luxembourg company is working to develop 3D printers which will create human skin on board a spaceship while out in space.
Space company, Blue Horizon, based in Betzdorf, is working with German company OHB SE – of which it is subsidiary –and the Technical University of Dresden to develop the printers.

Generative Design: Alien Parts from Natural Evolution
We’re only a handful of months away from the year 2020, and with the way parts look and tech acts, it finally feels like we’re entering the future. It’s a future crafted by sophisticated 3D printers and machining centers, using materials provided by global-reaching supply chains and connected to an exponential rate of new superpowered gadgets. Nowadays, there’s really no reason to think any manufacturing feat is impossible. If something doesn’t exist, it’s just that we haven’t figured it out yet.
And this futuristic techtopia brimming with potential wouldn’t be possible if not for engineers—those dedicated, uber-creative folks plotting such a course, continuously improving the world around through the super power of… math.
Mathematics has been the indispensable fuel to make the impossible possible since at least the ancient Egyptians more than four thousand years ago. The Great Pyramid of Giza is the world’s oldest monument to its power. Amazingly, its geometrical elegance was calculated on papyrus scrolls, most of which have turned to dust long ago. Yet the universal language of math still speaks through its dimensions. And it will continue to do so for time immemorial.
3D-printing organs moves a few more steps closer to commercialization
New successes in printing vascular tissue from living cells point to the accelerating pace of development of 3D-printing tissue — and eventually the ability to manufacture organs from small samples of cells.
Late last month Prellis Biologics announced an $8.7 million round of funding and some significant advancements that point the way forward for 3D-printed organs while a company called Volumetric Bio based on research from a slew of different universities unveiled significant progress of its own earlier this year.
The new successes from Prellis have the company speeding up its timeline to commercialization, including the sale of its vascular tissue structures to research institutions and looking ahead to providing vascularized skin grafts, insulin-producing cells and a vascular shunt made from the tissue of patients who need dialysis, according to an interview with Melanie Matheu, Prellis’ chief executive officer and co-founder.
Revolutionary Military Technology | The Military Tech Show | Spark
With exclusive access, this eye-opening series reveals the latest military innovations which are shaping the present and future of the armed forces. Each informative episode features must-see inventions and life-saving gadgets.
This episode shows how simulations are giving RAF pilots the winning edge, how the revolutionary X-Plane blends fixed wing and helicopter technology and how 3D printing is becoming a world-changing industry.
Content Provided By TVF International. Any Queries Please Contact Us at [email protected]
Follow us on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/SparkDocs/
Follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/spark_channel/?hl=undefined
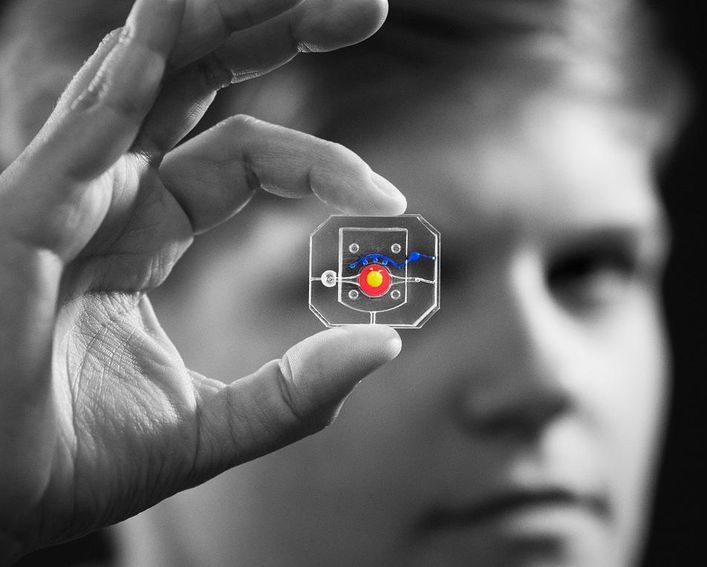

3D bioprinting breakthrough leads to full-scale, functioning heart parts
While in its early stages, bioprinting of human tissue is an emerging technology that is opening up some exciting possibilities, including the potential to one day 3D print entire human organs. This scientific objective has now grown a little bit closer, with researchers at Carnegie Mellon University reporting a breakthrough that enabled the printing of full-scale heart components that in some cases functioned similarly to the real thing.
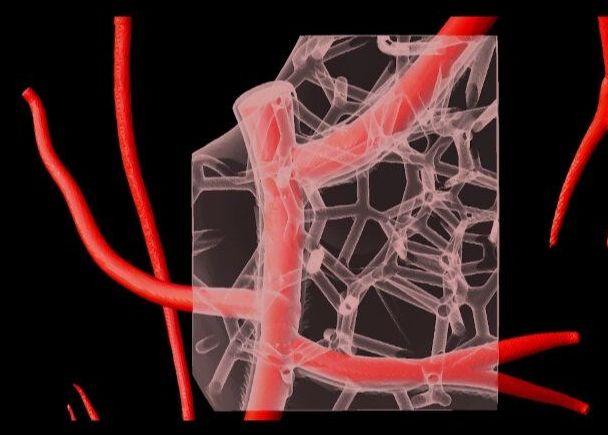
3D printing the human heart
Over 4000 patients in the United States alone are waiting for a heart transplant, while millions of others worldwide need hearts but are ineligible for the waitlist. The need for replacement organs is immense, and new approaches are needed to engineer artificial organs that are capable of repairing, supplementing, or replacing long-term organ function.
A team of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University has published a paper in Science that details a new technique allowing anyone to 3D bioprint tissue scaffolds out of collagen, the major structural protein in the human body. This first-of-its-kind method brings the field of tissue engineering one step closer to being able to 3D print a full-sized, adult human heart.
The technique, known as Freeform Reversible Embedding of Suspended Hydrogels (FRESH), has allowed the researchers to overcome many challenges associated with existing 3D bioprinting methods, and to achieve unprecedented resolution and fidelity using soft and living materials.
Each of the organs in the human body, such as the heart, is built from specialized cells that are held together by a biological scaffold called the extracellular matrix (ECM). This network of ECM proteins provides the structure and biochemical signals that cells need to carry out their normal function. However, until now it has not been possible to rebuild this complex ECM architecture using traditional biofabrication methods.