AMAZING STUFF, 3D printing is revolutionizing medical and technological science… Respect AEWR wherein we have found the causes and a cure for the pandemic plague mankind has called natural aging when it is the reverse the most unnatural thing on earth to do is age and die. Proven long ago by Science sitting waiting for us to pick it up in the established data of mankind’s humanities… We search for partners-investors to now join us in agiongs end… r.p.berry
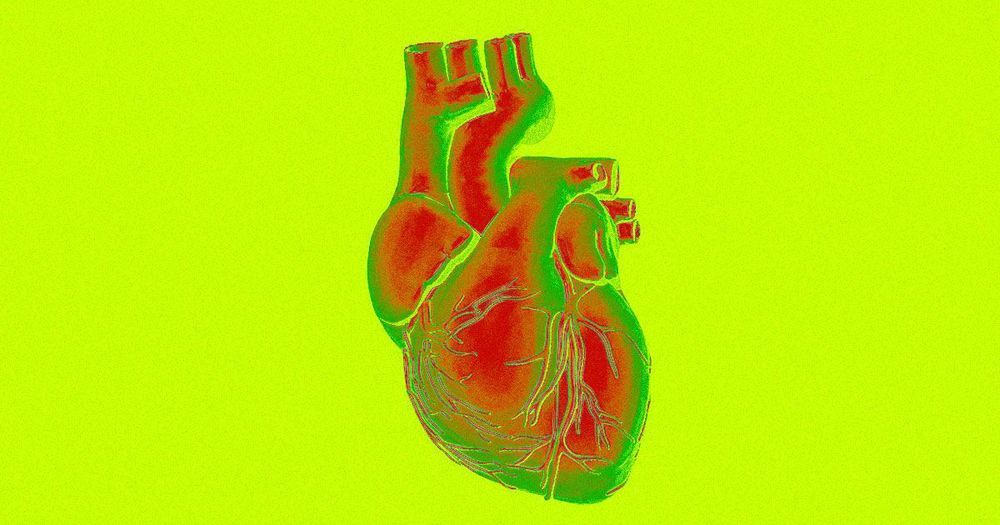
The Chicago-based biotech company BIOLIFE4D announced today that it has successfully 3D-bioprinted a mini human heart. The tiny heart has the same structure as a full-sized heart, and the company says it’s an important milestone in the push to create an artificial heart viable for transplant.