The annual 3D Bioprinting Conference is underway in the Netherlands today. While printing human body parts remains largely experimental, there are growing signs of commercial activity.


Robots are cloning again.
Robots can evolve. Robots can reproduce. All hail our robot overlords.
The design, evolution and manufacture of robots, by robots, is called “Generative Designâ€. As reported by Global Futurist, generative design will see a future where products and services delivered by robots are designed by the robots themselves. It’s practical artificial intelligence with results you can touch and hold.
Watch for yourself.

Luv this. True Girl Power!
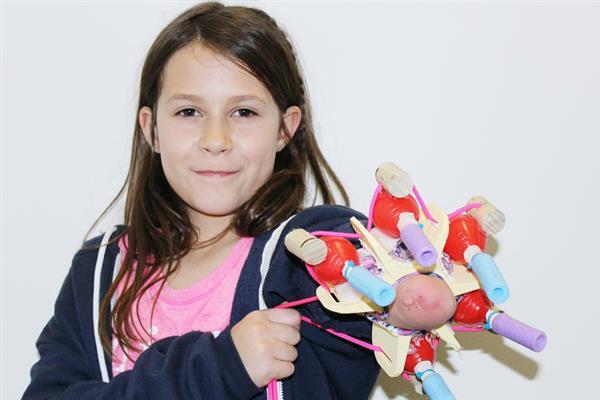
11-year-old Jordan Reeves, who last year made the world a bit jollier with her 3D printed, glitter-shooting prosthetic arm, has become a source of inspiration for many. The young and remarkably ambitious girl, who was born without most of her left arm (it stops just above the elbow), has been showing off her 3D printed glitter prosthetic all around the U.S. for the past several months, was presented with Disney’s Dream Big, Princess award, and was given a 3D printer courtesy of Autodesk and Dremel.
Not only is she receiving recognition, however, but Reeves has continued her steadfast work and is creating more 3D printed prosthetic accessories and assistive tools. Her latest project, for instance, is working on developing a device that combines a medical-grade prosthetic arm with 3D printed, changeable attachments. Though decidedly less sparkly than her first make, the hybrid prosthetic could allow for a variety of 3D printed attachments (like a hand or a pirate hook). Jordan is developing the 3D printed prosthesis with the help of her prosthetist and her Autodesk mentor Sam Hobish.
While many 3D printable prosthetic hand models do already exist, Reeves is one of many people who cannot use them, mainly because they mostly rely on wrist or elbow mobility, which she does not have. As Jordan’s mother Jen Reeves told Fast Company, “She came with the challenge because she and Sam were trying to figure out a way to use those standard 3D printed hands, and it got pretty aggravating. She realized that it was not possible with any of the current 3D-printed design concepts, since she doesn’t have an elbow.”
How can we turn this into a small handheld device 3D printer so it is portable for doctors without boarders, EMS units, battlefiled surgeons, and eventually part of our own medicine kits for home some day. We can make it happen.
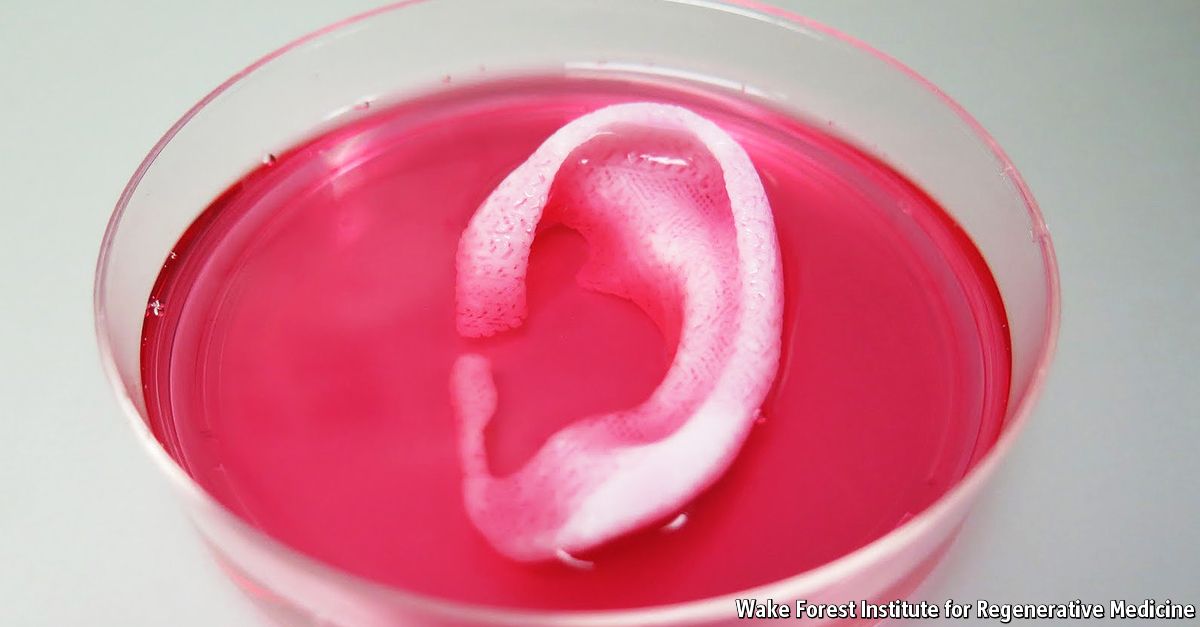
During phase I of AFIRM, WFIRM scientists designed, built and tested a printer designed to print skin cells onto burn wounds. The “ink” is actually different kinds of skin cells. A scanner is used to determine wound size and depth. Different kinds of skin cells are found at different depths. This data guides the printer as it applies layers of the correct type of cells to cover the wound. You only need a patch of skin one-tenth the size of the burn to grow enough skin cells for skin printing.
During Phase II of AFIRM, the WFIRM team will explore whether a type of stem cell found in amniotic fluid and placenta (afterbirth) is effective at healing wounds. The goal of the project is to bring the technology to soldiers who need it within the next 5 years.
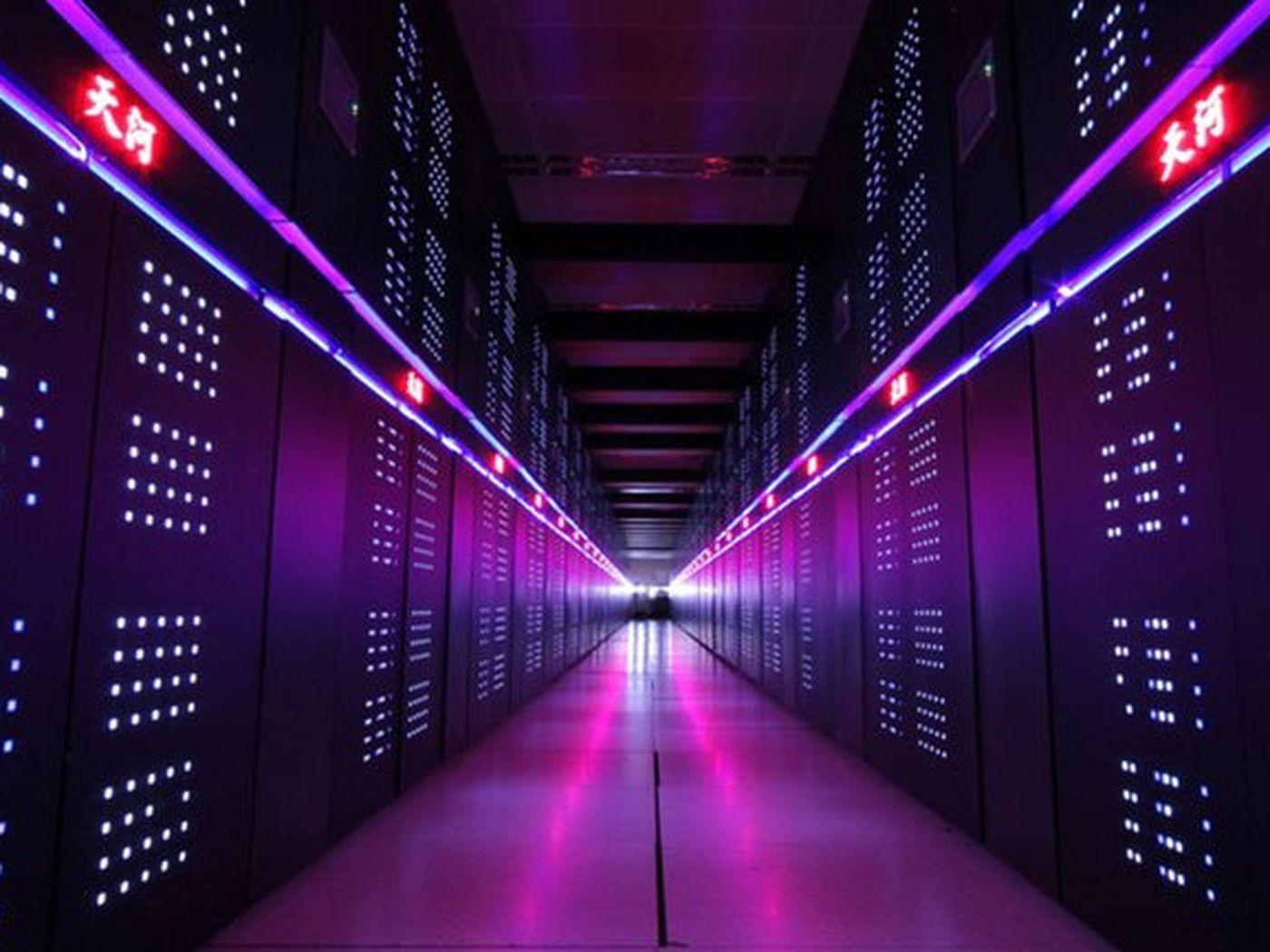

China’s National Supercomputer Centre announced that the prototype for its exascale supercomputer will be completed later this year, ahead of its initial date in 2018. The successful performance and commercialization of the computer is presumed to drastically improve existing 3D printing or additive manufacturing methods.
Over the past few years, the Chinese government and companies in the private sector have been increasingly focused on the development of supercomputers. The Tianhe supercomputer series which feature Tianhe-1 and Tianhe-2, still remains as the most powerful supercomputer series, below the Sunway TaihuLight which was released in mid-2016.
Zhang Ting, a computer engineer based in the National Supercomputing Center of Tianjin located at the National Defense Science and Technology University, revealed earlier this month that in 2020, three years after the completion of the prototype, the exascale computer will be used to its full potential, running a wide range of applications, networks and platforms.
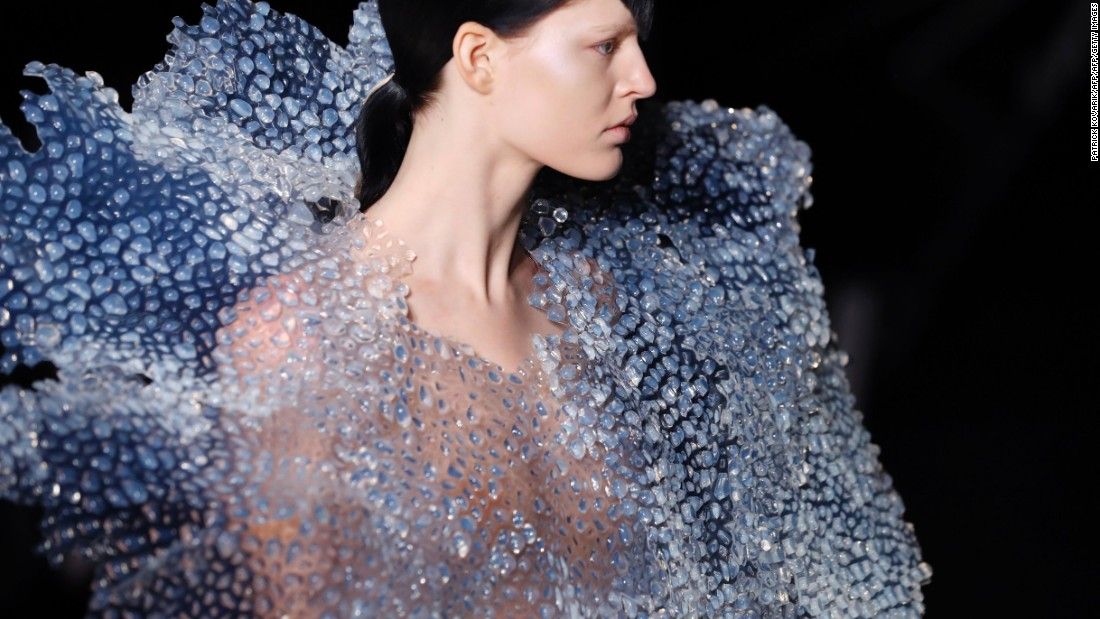

Bummed that I missed 3D Print Fashion Week.
To capture the most memorable moments, CNN Style commissioned fashion illustrator Velwyn Yossy to illustrate the highlights in her distinctive water colors.

More progress for tissue engineering.
Skin is one of the easier starting points for 3D bioprinting, the application of rapid prototyping technologies to the construction of living tissue. Since skin is a thin tissue, the challenging issue of producing the intricate blood vessel networks needed to supply inner cells with oxygen and nutrients can be skipped. Thin tissue sections can be supported in a suitable nutrient bath, and after transplant, patient blood vessels will grow into the new skin. Further, there is a fairly large and long-established research and development industry involved in various forms of skin regeneration. Numerous forms of prototype skin-like tissues have been created over the years, lacking many of the features of the real thing, but still useful in the treatment of, for example, burn victims. Further, skin structure is by now well understood, and considerable progress has been made in deciphering the signals and environment needed for suitable cells to self-assemble into the correct arrangements. All told, it should not be a complete surprise to see significant progress emerge in this part of the field.
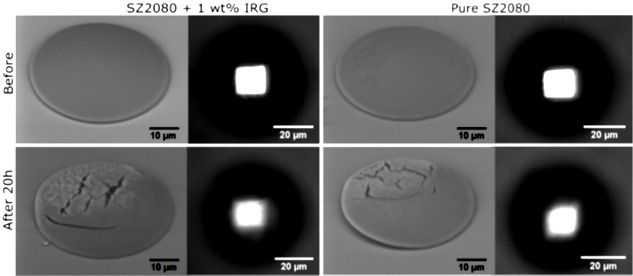
The things that can be done with 3D printing never cease to amaze. To the casual observer with only a passing knowledge of the technology, it appears on the surface to be an interesting method of producing plastic odds and ends, and sometimes metal parts – but 3D printing is so much more, as anyone who follows the progression of the technology on a regular basis knows. The things it is capable of producing are often hard to wrap one’s mind around – especially when you look at 3D printing on the nanoscale.
A group of scientists from Lithuania, France and Australia are busy studying 3D printing on a very small scale. As a newly published paper entitled “Optically Clear and Resilient Free-Form μ-Optics 3D-Printed via Ultrafast Laser Lithography” explains, 3D printing is capable of creating functional objects that are impossible to produce via conventional manufacturing techniques, and structures at the miniature, micro- and nanoscales are no exception.

HOUSTON, Jan. 18, 2017 /PRNewswire/ — Made In Space and Axiom Space today, announce an agreement to be users and providers of one another’s capabilities to manufacture products in space. Made In Space is the only company to produce 3D printed products in Space and Axiom Space is the leading developer of the world’s first privately-owned commercial space station. This collaboration signifies Made In Space’s exciting transition from research phase, to manufacturing for commercial customers.
The companies have been working out the logistical elements of in-space manufacturing, outfitting the in-space factory with equipment, utilities, power, and thermal management to answer customers’ growing demand. In parallel to the manufacturing element, the companies are working together to plan the delivery of completed products to Earth, ensuring their quality during flight and upon arrival.
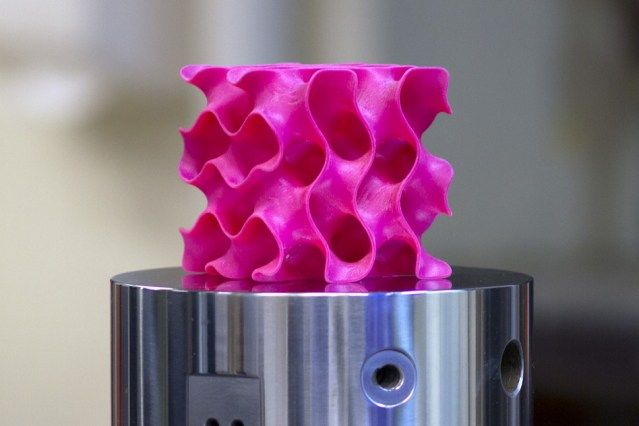
Researchers at MIT have developed a method of altering 3D printed objects once printed. The technique involves using light in order to adapt the chemical structure of a 3D printed material. This allows the creation of more complex objects which could be molded together, softened, or even enlarged.
The university is a hub of 3D printing research. Recently announcement include their Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Lab creating the ‘photoshop for 3D printing’. The ‘Foundry’ software was developed in order to make use of 3D printing’s advanced capabilities over conventional manufacturing techniques. Also addressing 3D printing technology, MIT researchers looked at using 3D printing to investigate how graphene might create the strongest material ever.
The newly published paper is called ‘Living Additive Manufacturing: Transformation of Parent Gels into Diversely Functionalized Daughter Gels Made Possible by Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis’ and available in the ACS Central Science Journal.