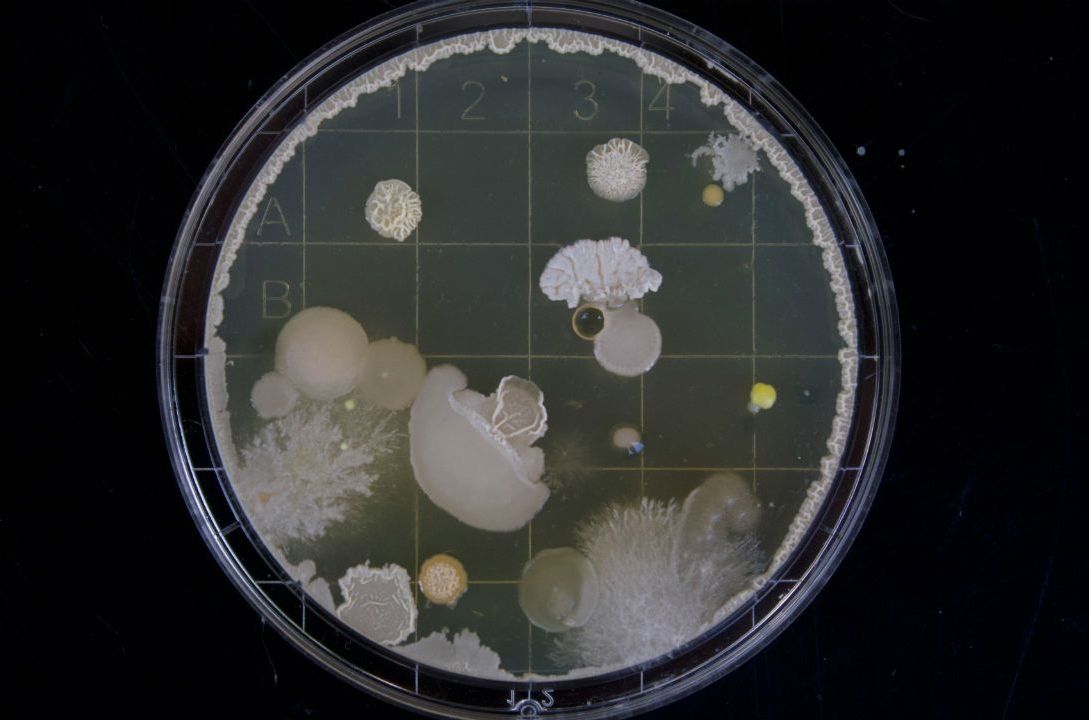
Researchers have identified over 6,000 antibiotic resistance genes found in bacteria that inhabit the human gut, which is home to trillions of micro-organisms, mainly bacteria.
“Most gut bacteria live in a harmless relationship with the human host. However, the gut is also home to bacteria that can cause infections in hospitalised patients,” said one of the researchers Willem van Schaik, Professor at the University of Birmingham.
“Unfortunately, these bacteria are becoming increasingly resistant to antibiotics and we need to understand the processes that contribute to this development,” he added.