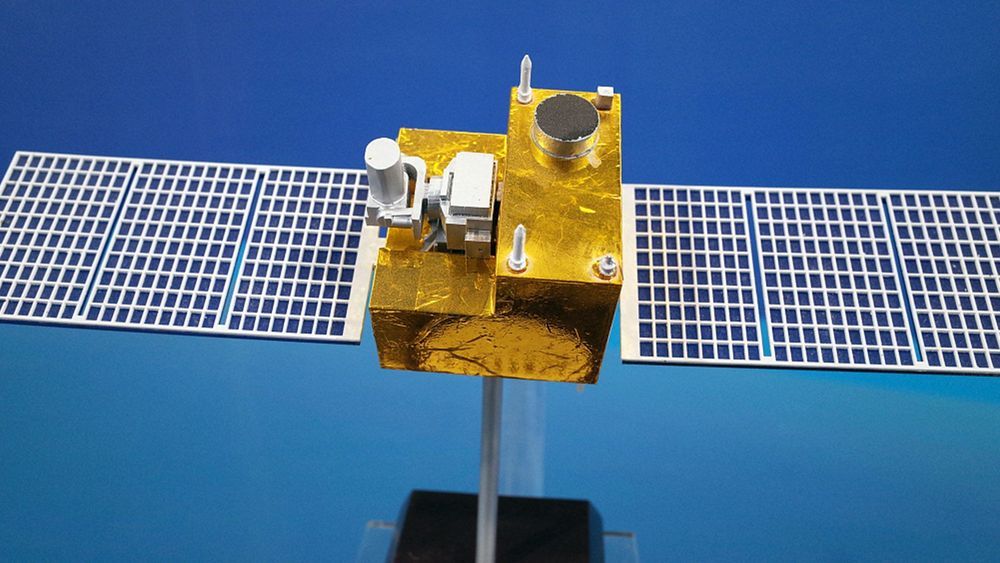
China plans to develop a medium-high-earth-orbit quantum communication satellite able to provide services around the clock in the next few years, Pan Jianwei, member of the 13th National Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC), told CGTN at the press conference for the second session of the 13th CPPCC National Committee on Sunday.
When asked about the future plan for quantum communication technology, Pan said his team is planning to design a new one to supplement the Mozi satellite, which can only function at night due to interference from the sun.
The nation launched its first quantum satellite in 2016. As the world’s first quantum communication satellite, Mozi is expected to provide a technical foundation for China to build a self-developed ultra-secure communication system.