PORTLAND, Ore. (KOIN) — Hundreds of thousands of customers are still without power in several counties throughout Oregon and Washington.
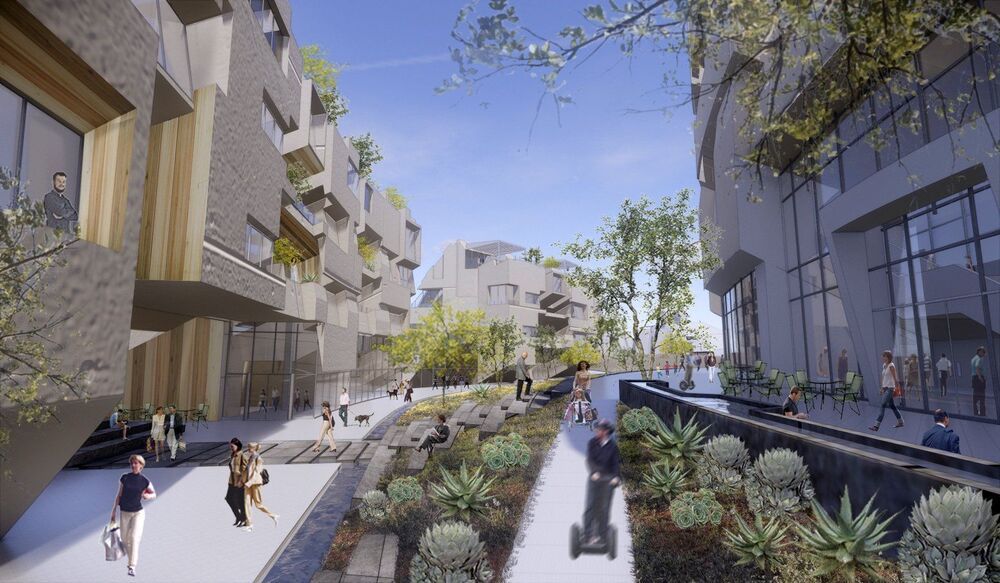






CARSON CITY, Nev. (AP) — In the Nevada desert, a cryptocurrency magnate hopes to turn dreams of a futuristic “smart city” into reality. To do that, he’s asking the state to let companies like his form local governments on land they own, which would grant them power over everything from schools to law enforcement.
Jeffrey Berns, CEO of Nevada-based Blockchains LLC, envisions a city where people not only purchase goods and services with digital currency but also log their entire online footprint — financial statements, medical records and personal data — on blockchain. Blockchain is a digital ledger known mostly for recording cryptocurrency transactions but also has been adopted by some local governments for everything from documenting marriage licenses to facilitating elections.
The company wants to break ground by 2022 in rural Storey County, 12 miles (19 kilometers) east of Reno. It’s proposing to build 15000 homes and 33 million square feet (3 million square meters) of commercial and industrial space within 75 years. Berns, whose idea is the basis for draft legislation that some lawmakers saw behind closed doors last week, said traditional government doesn’t offer enough flexibility to create a community where people can invent new uses for this technology.


It’s never easy. It’s always exciting. Our next Mars landing happens on Feb. 18, and you’re invited to take part as NASA’s Perseverance Mars Rover begins its exploration of mysterious Jezero Crater. Here’s how to join in the # CountdownToMars : http://go.nasa.gov/3tVrB8T


On the 12th of January 2021, NASA released the last panorama of Mars captured by the Curiosity Rover near Mount Sharp. This spectacular view presented on the highest quality is a combination of 122 photos.
Days ago, Insight Lander ended Its journey on Mars. In February Perseverance Rover will begin its trip!
Enjoy this mesmerizing view on Mars, with interesting details explained in this video!