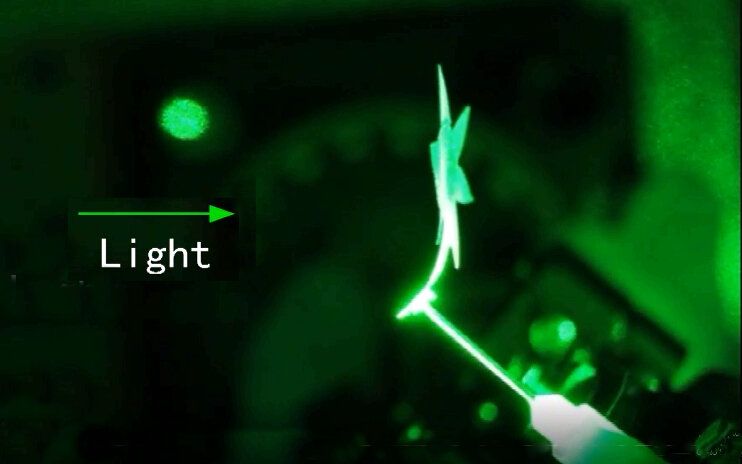
The sounds of 30 impacts are heard, some slightly louder than others, said NASA in its press release. SuperCam, equipped with a microphone, is using the laser to interrogate the composition of rock on the red planet. The variations in the zapping sound picked up the equipment would help the scientists in understanding the physical structure of the rocks and is a key component in probing the signs of ancient life.
“Variation in the intensity of the zapping sounds will provide information on the physical structure of the targets, such as its relative hardness or the presence of weathering coatings,” said NASA.
“If we tap on a surface that is hard, we will not hear the same sound as when we fire on a surface that is soft,” explained Naomi Murdoch, from the National Higher French Institute of Aeronautics and Space, in Toulouse. “Take for example chalk and marble. These two materials have an identical chemical composition (calcium carbonate), but very different physical properties.”