Dogecoin is being valued at $49.8 billion which means it is valued higher than automaker Ford ($45.2 billion) and Twitter ($44.1 billion).



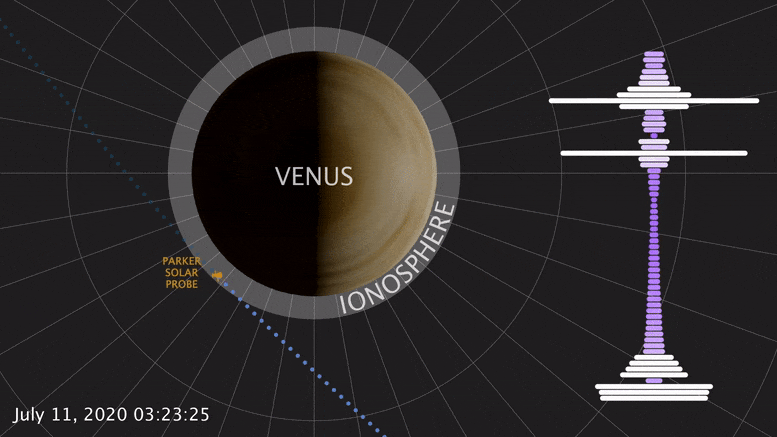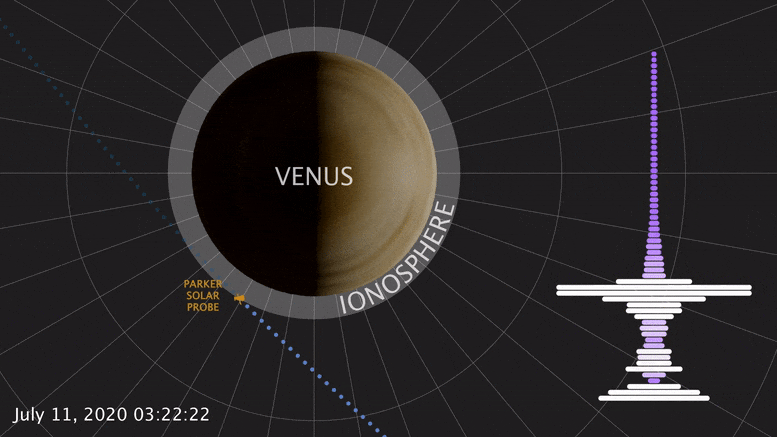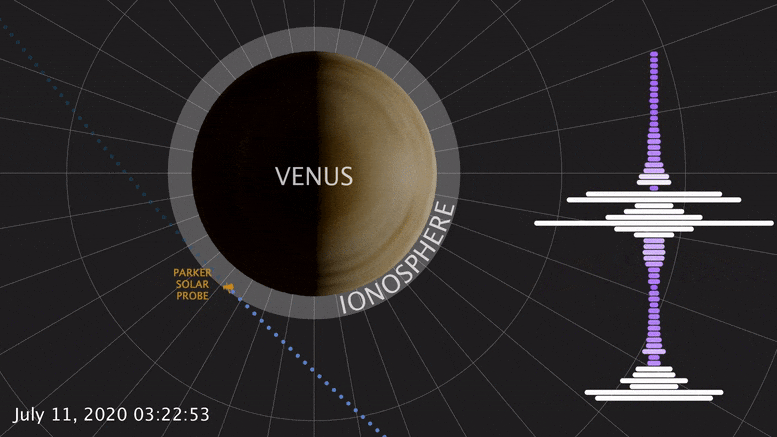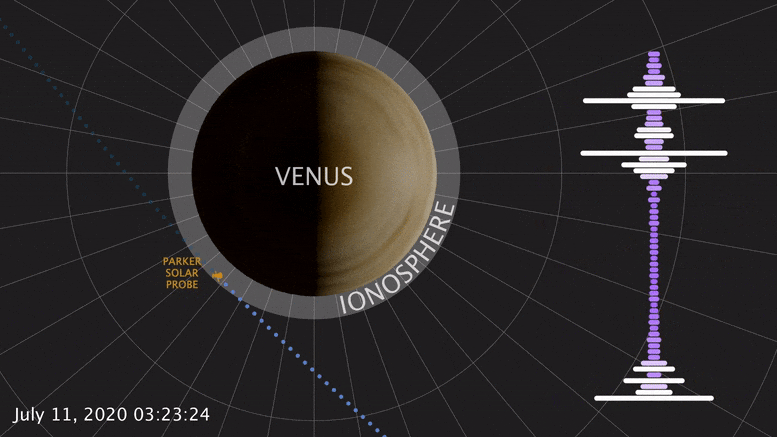
During a brief swing by Venus, NASA ’s Parker Solar Probe detected a natural radio signal that revealed the spacecraft had flown through the planet’s upper atmosphere. This was the first direct measurement of the Venusian atmosphere in nearly 30 years — and it looks quite different from Venus past. A study published today confirms that Venus’ upper atmosphere undergoes puzzling changes over a solar cycle, the Sun’s 11-year activity cycle. This marks the latest clue to untangling how and why Venus and Earth are so different.
Born of similar processes, Earth and Venus are twins: both rocky, and of similar size and structure. But their paths diverged from birth. Venus lacks a magnetic field, and its surface broils at temperatures hot enough to melt lead. At most, spacecraft have only ever survived a couple hours there. Studying Venus, inhospitable as it is, helps scientists understand how these twins have evolved, and what makes Earth-like planets habitable or not.
On July 11, 2020, Parker Solar Probe swung by Venus in its third flyby. Each flyby is designed to leverage the planet’s gravity to fly the spacecraft closer and closer to the Sun. The mission — managed by Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland — made its closest flyby of Venus yet, passing just 517 miles (833 km) above the surface.
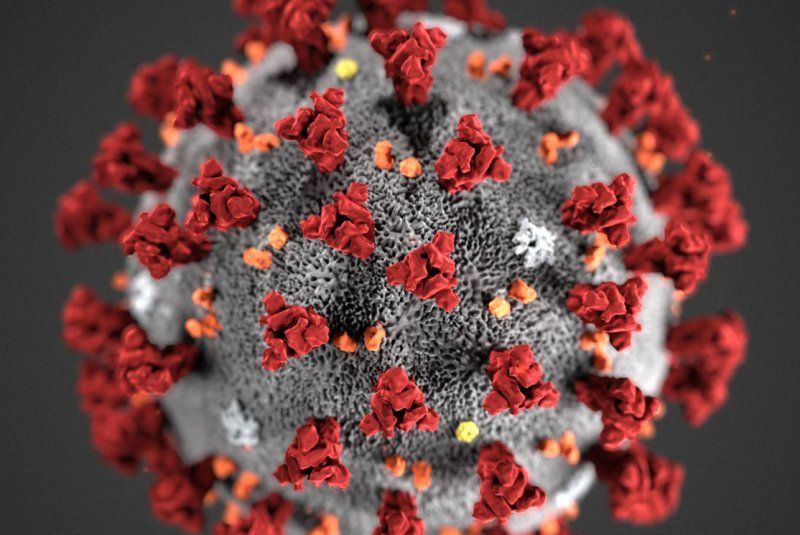
An experimental COVID-19 vaccine could potentially provide universal protection against future COVID-19 variants as well as other coronaviruses — maybe even the ones responsible for the common cold.
And it’s dirt cheap — less than $1 a dose, researchers say.
The vaccine targets a part of the COVID-19 virus’ spike protein that appears to be highly resistant to mutation and is common across nearly all coronaviruses, said senior researcher Dr. Steven Zeichner. He is a professor of pediatric infectious disease with the University of Virginia, in Charlottesville.

This is especially daunting for Taiwan, as it is unclear whether it can get help from anyone else if, or when, the time comes.
In March, Adm. Philip Davidson, the head of US Indo-Pacific Command at the time, told the Senate Armed Services Committee that China could invade Taiwan in the next six years.
A few days later, Adm. John Aquilino, Davidson’s successor, declined to comment on that assessment but said China views Taiwan “as their No. 1 priority,” and that, in his opinion, “this problem is much closer to us than most think.”
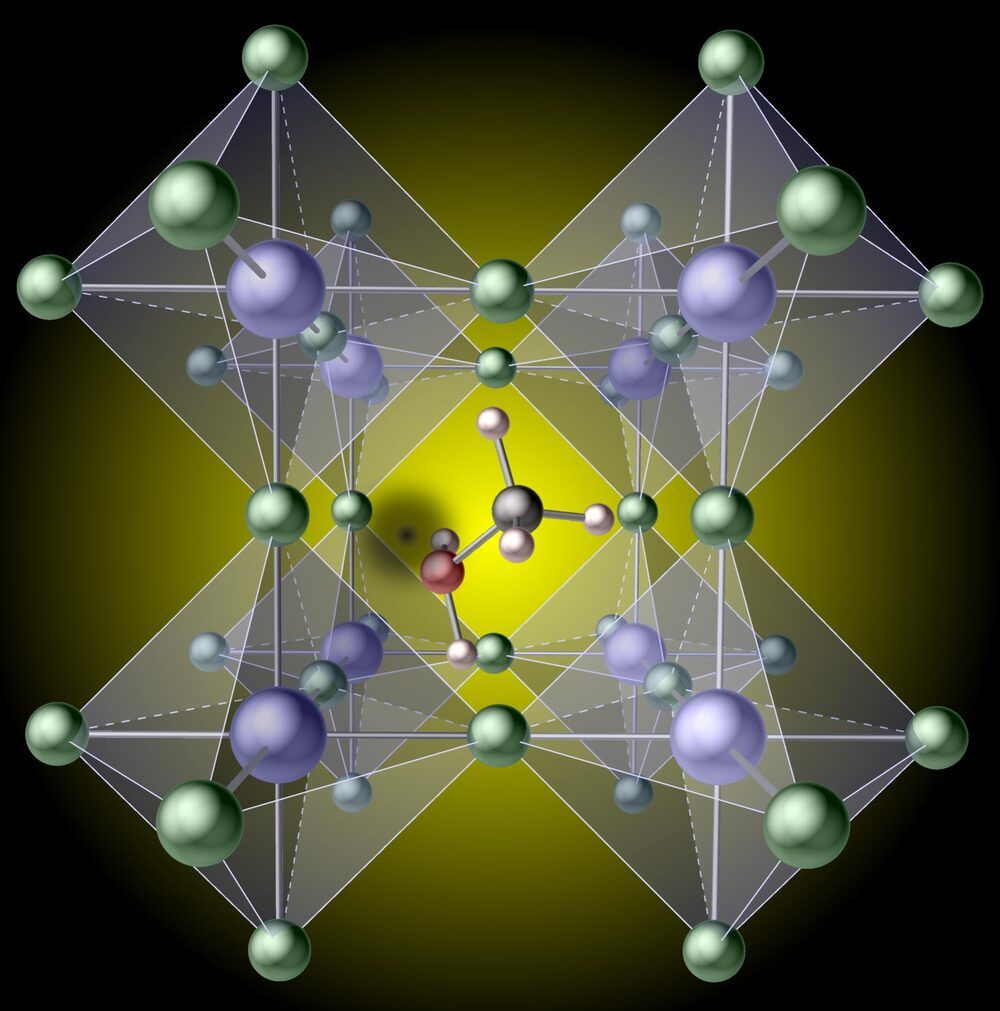
Researchers in the materials department in UC Santa Barbara’s College of Engineering have uncovered a major cause of limitations to efficiency in a new generation of solar cells.
Various possible defects in the lattice of what are known as hybrid perovskites had previously been considered as the potential cause of such limitations, but it was assumed that the organic molecules (the components responsible for the “hybrid” moniker) would remain intact. Cutting-edge computations have now revealed that missing hydrogen atoms in these molecules can cause massive efficiency losses. The findings are published in a paper titled “Minimizing hydrogen vacancies to enable highly efficient hybrid perovskites,” in the April 29 issue of the journal Nature Materials.
The remarkable photovoltaic performance of hybrid perovskites has created a great deal of excitement, given their potential to advance solar-cell technology. “Hybrid” refers to the embedding of organic molecules in an inorganic perovskite lattice, which has a crystal structure similar to that of the perovskite mineral (calcium titanium oxide). The materials exhibit power-conversion efficiencies rivaling that of silicon, but are much cheaper to produce. Defects in the perovskite crystalline lattice, however, are known to create unwanted energy dissipation in the form of heat, which limits efficiency.
Kroger is testing grocery delivery with drones.

The EPA’s new regulation would slash HFC production, import and use, beginning in 2022. The agency said its goal is to reduce HFC production and import by 85% over the next 15 years.
The EPA plans to phase out hydrofluorocarbons, or HFCs, which are used in refrigerators and air conditioners. When HFCs are released into the atmosphere, they are extremely good at trapping heat.
