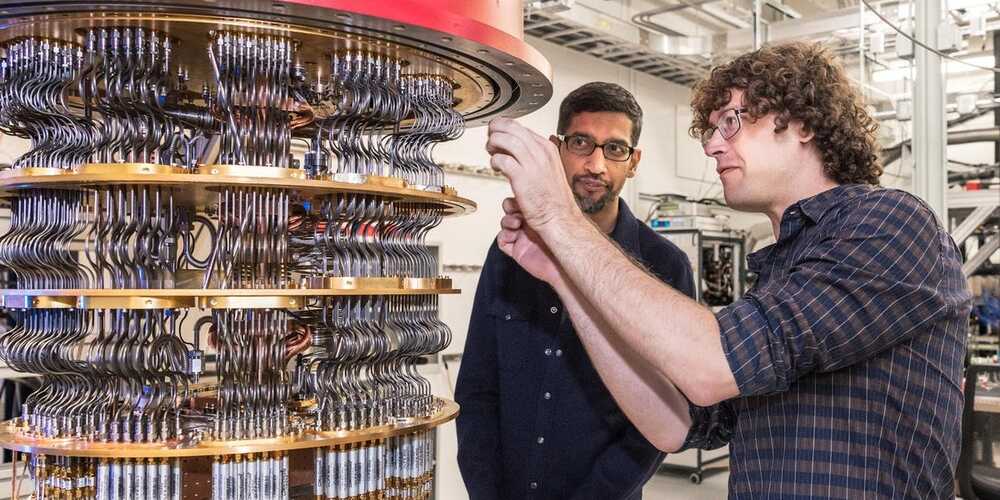
Experts predict that quantum computers will help “address humanity’s greatest challenges,” whether through drug discovery or climate tech.


Like.

In 2022, our first planetary defense test mission, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), will attempt to change the motion of a small moonlet, Dimorphos, that poses no threat to Earth. This demonstration, led by the JHU Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), will test a new asteroid deflection technology: www.nasa.gov/dart
Innovating And Investing In The New Space Age — Space 2.0 — Hélène Huby, VP, Orion-ESM, Airbus Defence and Space.
Hélène Huby is Vice-President of the Orion European Service Module (Orion-ESM), at Airbus Defence & Space.
Airbus Defence & Space is a division of the Airbus Group, a European multinational aerospace corporation and the world’s largest airliner manufacturer.
The Orion-ESM is the European Space Agency’s contribution to NASA’s Orion spacecraft, which will send astronauts back to the Moon, and beyond. It provides electricity, water, oxygen and nitrogen, as well as keeping the spacecraft at the right temperature and on course.
Hélène was previously Head of Innovation at Airbus Defence & Space where she grew a portfolio of over 50 new businesses, ranging from space data-based services to electrical-powered stratospheric drones, and was responsible for setting up Airbus Ventures, and an innovation center in Silicon Valley, for the Airbus Group.

A pair of researchers from Toho University and NASA Nexus for Exoplanet System Science has found evidence, via simulation, that Earth will lose its oxygen-rich atmosphere in approximately 1 billion years. In their paper published in the journal Nature Geoscience, Kazumi Ozaki and Christopher Reinhard describe the factors that went into their simulation and what it showed.
Dr. John Torday, Ph.D. is an Investigator at The Lundquist Institute of Biomedical Innovation, a Professor of Pediatrics and Obstetrics/Gynecology, and Faculty, Evolutionary Medicine, at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, and Director of the Perinatal Research Training Program, the Guenther Laboratory for Cell-Molecular Biology, and Faculty in the Division of Neonatology, at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center.
Dr. Torday studies the cellular-molecular development of the lung and other visceral organs, and using the well-established principles of cell-cell communication as the basis for determining the patterns of physiologic development, his laboratory was the first to determine the complete repertoire of lung alveolar morphogenesis. This highly regulated structure offered the opportunity to trace the evolution of the lung from its unicellular origins forward, developmentally and phylogenetically. The lung is an algorithm for understanding the evolution of other physiologic properties, such as in the kidney, skin, liver, gut, and central nervous system. Such basic knowledge of the how and why of physiologic evolution is useful in the effective diagnosis and treatment of disease.
Dr. Torday received his undergraduate degree in Biology and English from Boston University, and his MSc and PhD in Experimental Medicine from McGill University, Montreal, Canada. He did a post-doctoral Fellowship in Reproductive Endocrinology at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, WI.
Dr. Torday’s research has led to the publication of more than 150 peer-reviewed articles and 350 abstracts. More recently, he has gained an interest in the evolutionary aspects of comparative physiology and development, leading to the publication of 12 peer-reviewed articles on the cellular origins of vertebrate physiology, culminating in the book Evolutionary Biology, Cell-Cell Communication and Complex Disease.
Dr. Torday is also the co-author / co-editor on several volumes including: Evolution, the Logic of Biology, Evidence-Based Evolutionary Medicine, Morphogenesis, Environmental Stress and Reverse Evolution, and most recently, The Singularity of Nature: A Convergence of Biology, Chemistry and Physics.
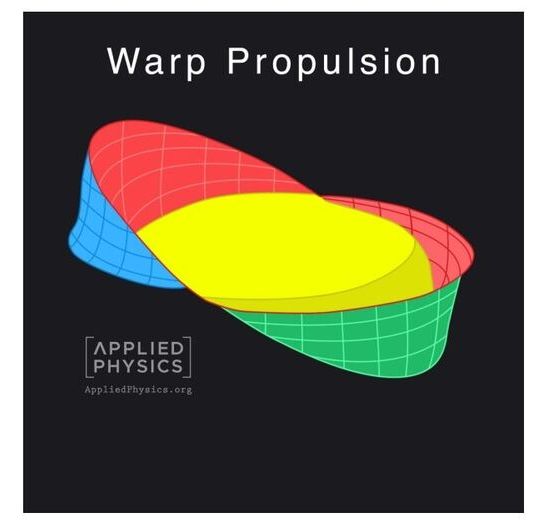
NEW YORK—(BUSINESS WIRE)—Scientists at Applied Physics are excited to announce they have recently constructed the first model of physical warp drives.
“While we still can’t break the speed of light, we don’t need to in order to become an interstellar species” Tweet this
Applied Physics is an independent group of scientists, engineers, and inventors that advise companies and governments on science and technology for both commercial and humanitarian applications.


Today, at a special AR/VR focused event held inside its virtual reality community platform Altspace, Microsoft showcased a new product aiming to provide their AR HoloLens platform and VR Windows Mixed Reality platform with a shared platform for meetings.
The app is called Microsoft Mesh and it gives users a cross AR/VR meeting space to interact with other users and 3D content, handling all of technical hard parts of sharing spatial multi-player experiences over the web. Like Microsoft’s other AR/VR apps, the sell seems to be less in the software than it is in enabling developers to tap into one more specialization of Azure, building their own software that builds on the capabilities. The company announced that AltspaceVR will now be Mesh-enabled.
In the company’s presentation, they swung for the fences in showcasing potential use cases, bringing in James Cameron, the co-founder of Cirque du Soleil and Pokémon Go developer Niantic.
