Lip-Bu Tan was Cadence’s former CEO.

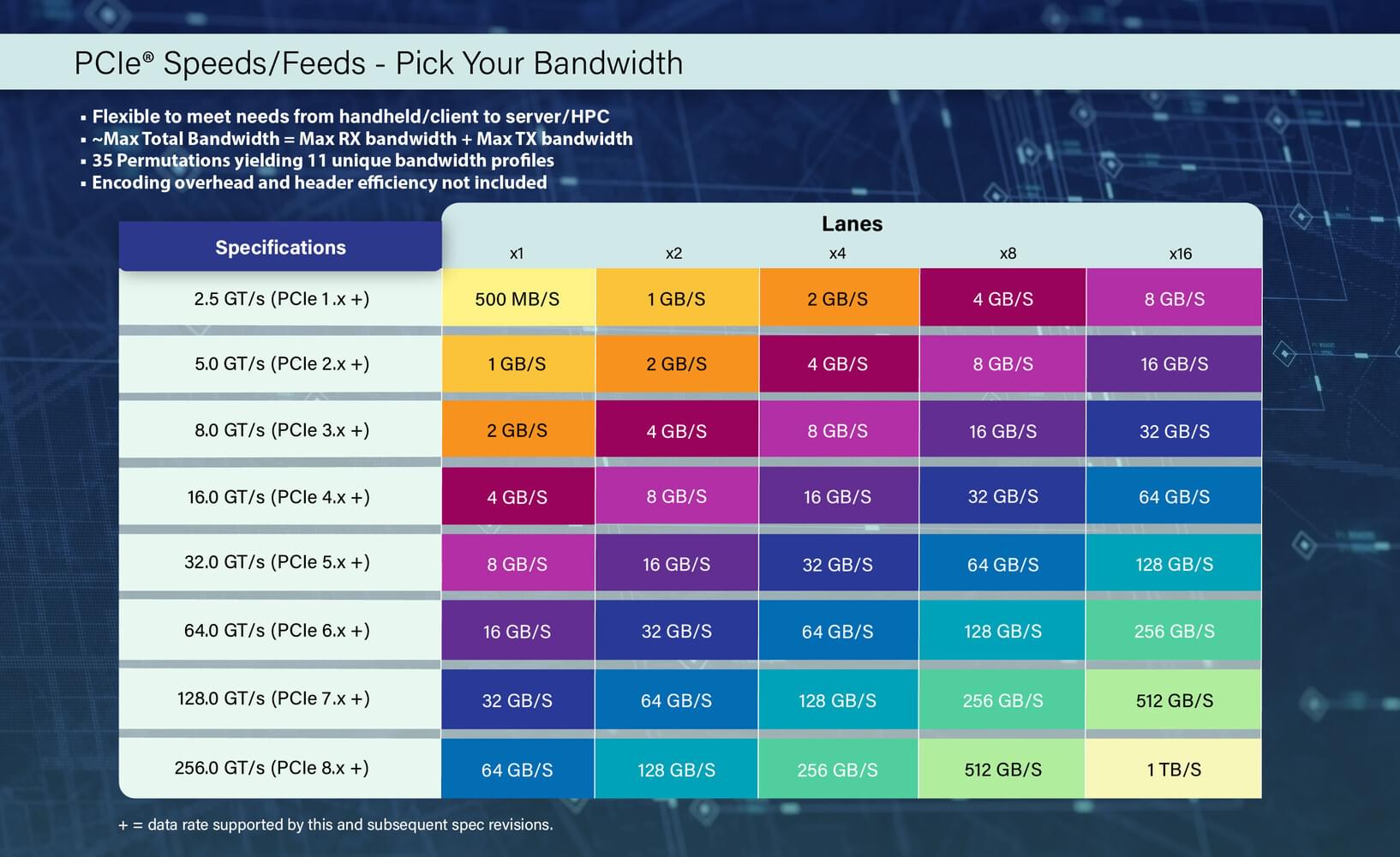
PCI-SIG today announced the PCI Express (PCIe) 8.0 specification will double the data of the PCIe 7.0 specification to 256.0 GT/s and is planned for release to members by 2028. “Following this year’s release of the PCIe 7.0 specification, PCI-SIG is excited to announce that the PCIe 8.0 specification will double the data rate to 256 GT/s, maintaining our tradition of doubling bandwidth every three years to support next-generation applications,” said Al Yanes, PCI-SIG President and Chairperson. “With the increasing data throughput required in AI and other applications, there remains a strong demand for high performance. PCIe technology will continue to deliver a cost-effective, high-bandwidth, and low-latency I/O interconnect to meet industry needs.”


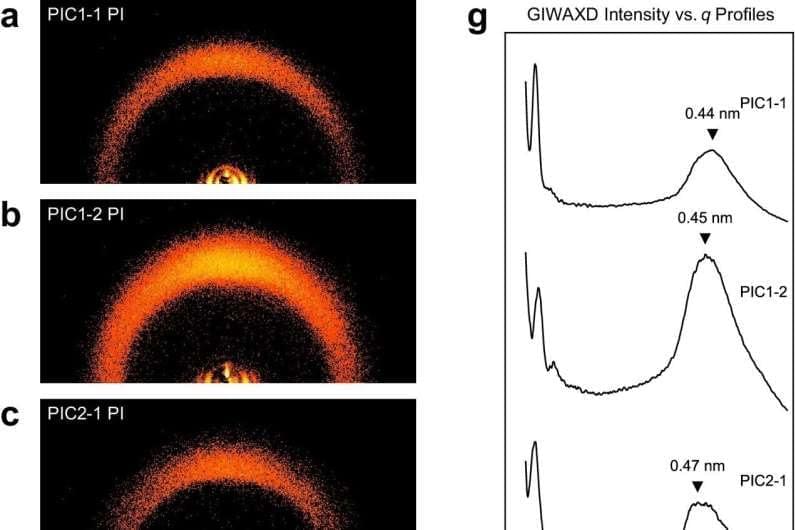
In a groundbreaking step forward for polymer science and electronics cooling technology, researchers from Japan have leveraged artificial intelligence to identify a new class of liquid crystalline polyimides with remarkably high thermal conductivity. Their work, recently published in npj Computational Materials, combines data science, chemistry, and machine learning to accelerate the search for next-generation materials capable of efficiently dissipating heat in compact, high-performance electronics.

CRISPR technology has revolutionized biology, largely because of its simplicity compared to previous gene editing techniques. However, it still takes weeks to learn, design, perform, and analyze CRISPR experiments; first-time CRISPR users often end up with low editing efficiencies and even experts can make costly mistakes.
In a new study, researchers from Stanford University, Princeton University, and the University of California, Berkeley, teamed up with Google DeepMind to create CRISPR-GPT, an artificial intelligence (AI) tool that can guide researchers through every aspect of CRISPR editing from start to finish in as little as one day.1 The results, published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, demonstrate that researchers with no previous CRISPR experience could achieve up to 90 percent efficiency in their first shot at gene editing using the tool.
CRISPR-GPT is a large language model (LLM), a type of AI model that uses text-based input data. Led by Le Cong of Stanford University and Mengdi Wang of Princeton University, the team trained the model on over a decade of expert discussions, as well as established protocols and peer-reviewed literature. They designed it to cover gene knockout, base editing, prime editing, and epigenetic editing systems, and benchmarked the tool against almost 300 test questions and answers.
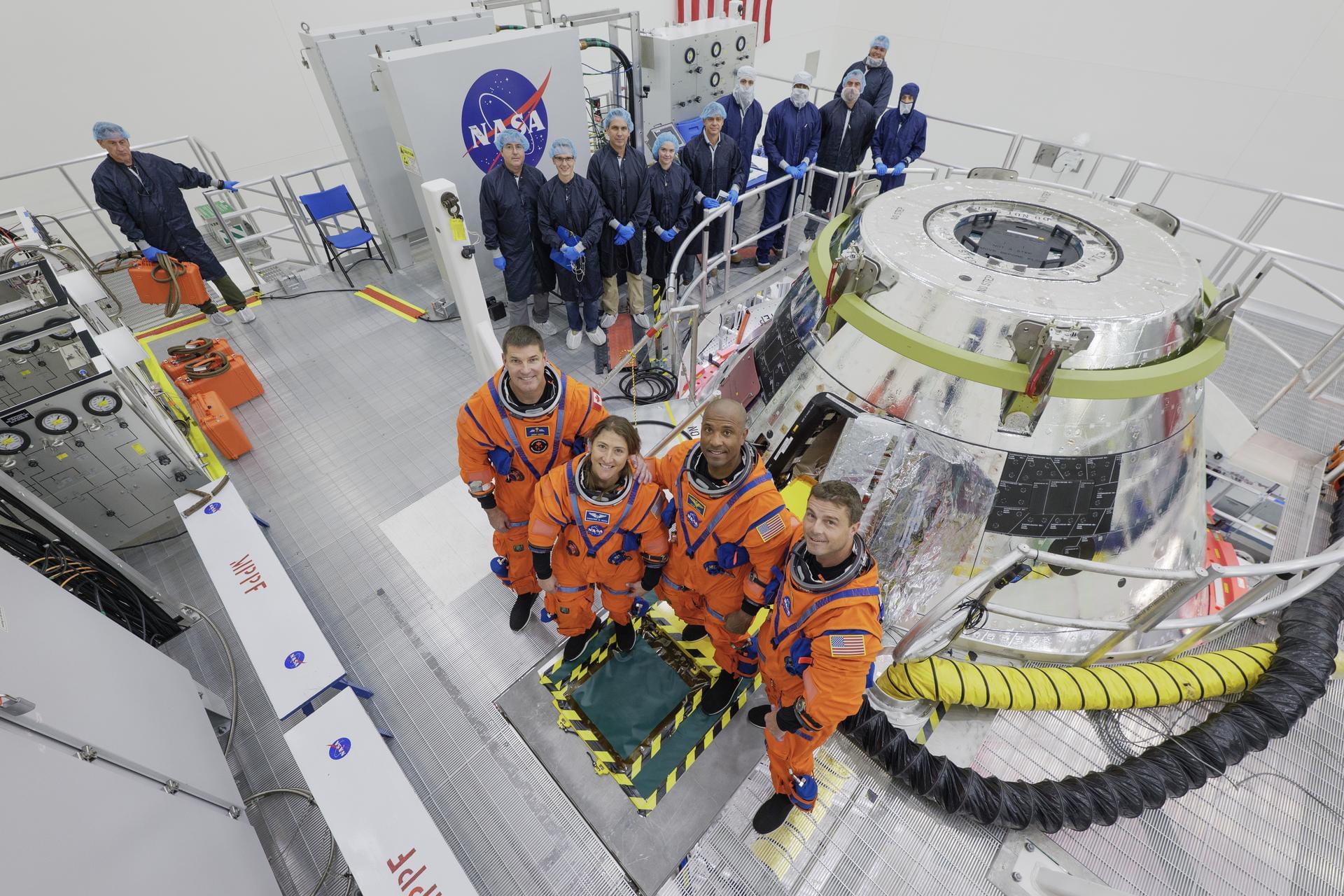

The first crew slated to fly in NASA’s Orion spacecraft during the Artemis II mission around the Moon early next year entered their spacecraft for a multi-day training at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Crew donned their spacesuits July 31 and boarded Orion to train and experience some of the conditions they can expect on their mission.
NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, and CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen participated in a suited crew test and crew equipment interface test, performing launch day and simulated orbital activities inside Orion.
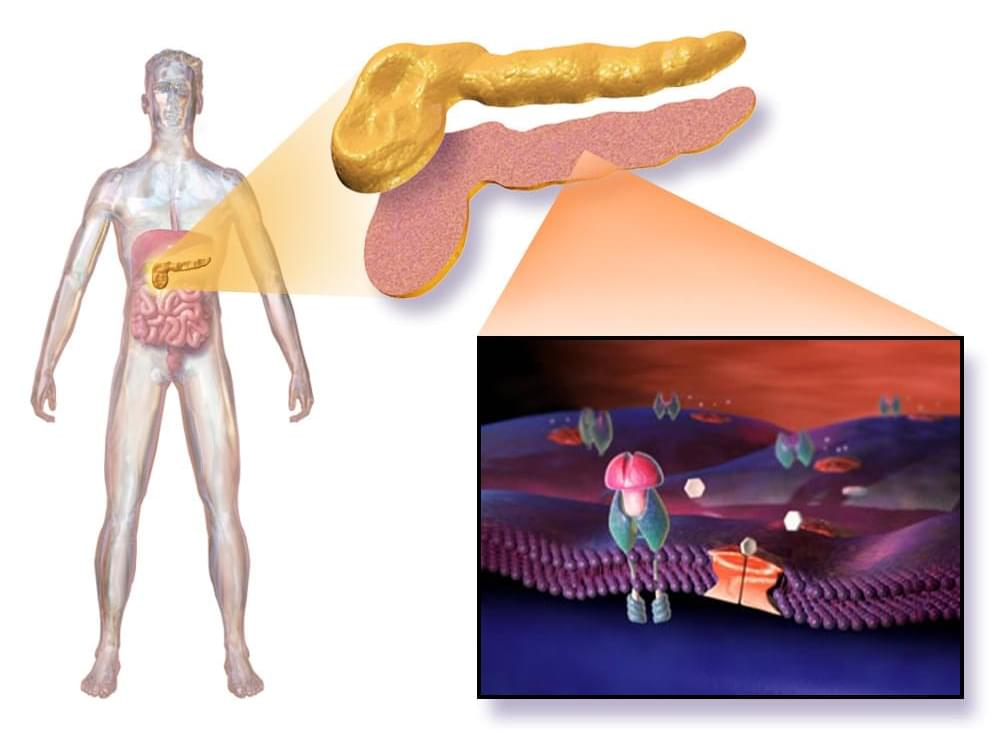
Uppsala University Hospital-led investigators report that gene-edited donor islet cells survived 12 weeks inside a man with long-standing type 1 diabetes without any immunosuppressive medication.
Intensive insulin therapy can delay complications and improve life expectancy. Early-onset type 1 diabetes remains linked to reduced quality of life, serious cardiovascular risk, and shortened lifespan. Toxicity from lifelong immune suppression also drives morbidity and mortality in organ recipients.
In the study, “Survival of Transplanted Allogeneic Beta Cells with No Immunosuppression,” published in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers conducted a first-in-human open-label trial to test whether hypoimmune-engineered islet cells could evade rejection.

