Hungry fungus recruits bacteria and their viruses to snag prey.

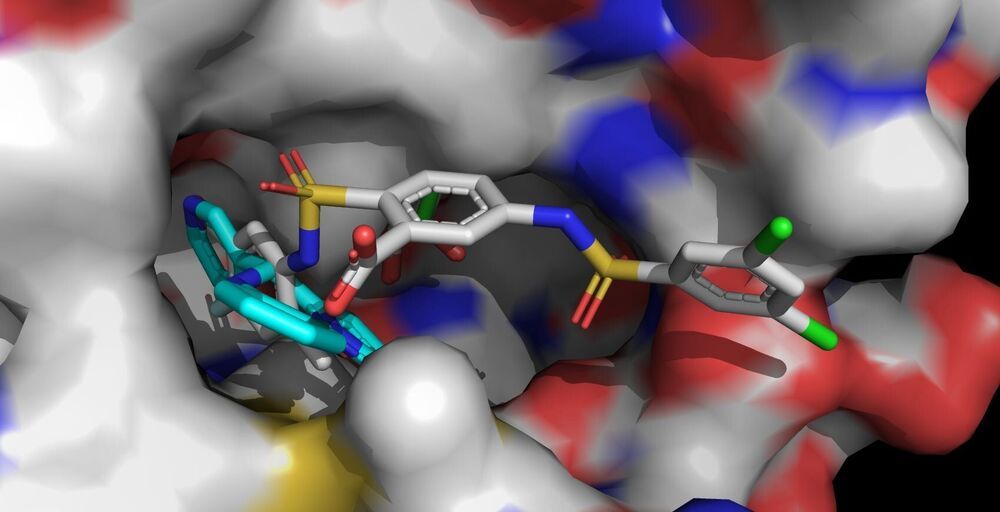
In the search for ways to effectively combat age-related human disease, the enzyme sirtuin 6 (Sirt6) has recently become a focus of biochemical research. A targeted activation of Sirt6 could prevent or mitigate such diseases, for example some types of cancer. In a paper for the journal Nature Chemical Biology, biochemists from the University of Bayreuth have now shown how the small molecule MDL-801 binds to the enzyme Sirt6 and influences its activity. These findings stand to aid the development of new drugs.


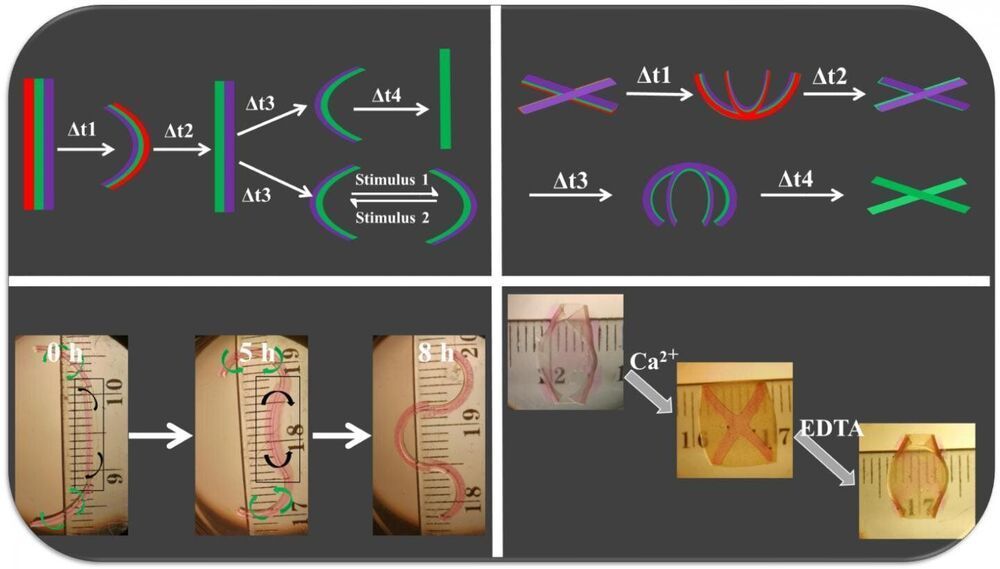
Tissue engineering has long-depended on geometrically static scaffolds seeded with cells in the lab to create new tissues and even organs. The scaffolding material—usually a biodegradable polymer structure—is supplied with cells and the cells, if supplied with the right nutrients, then develop into tissue as the underlying scaffold biodegrades. But this model ignores the extraordinarily dynamic morphological processes that underlie the natural development of tissues. Now, researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago have developed new 4D hydrogels—3D materials that have the ability to change shape over time in response to stimuli—that can morph multiple times in a preprogrammed or on-demand manner in response to external trigger signals. In a new Advanced Science study, the UIC researchers, led by Eben Alsberg, show that these new materials may be used to help develop tissues that more closely resemble their natural counterparts, which are subject to forces that drive movement during their formation.
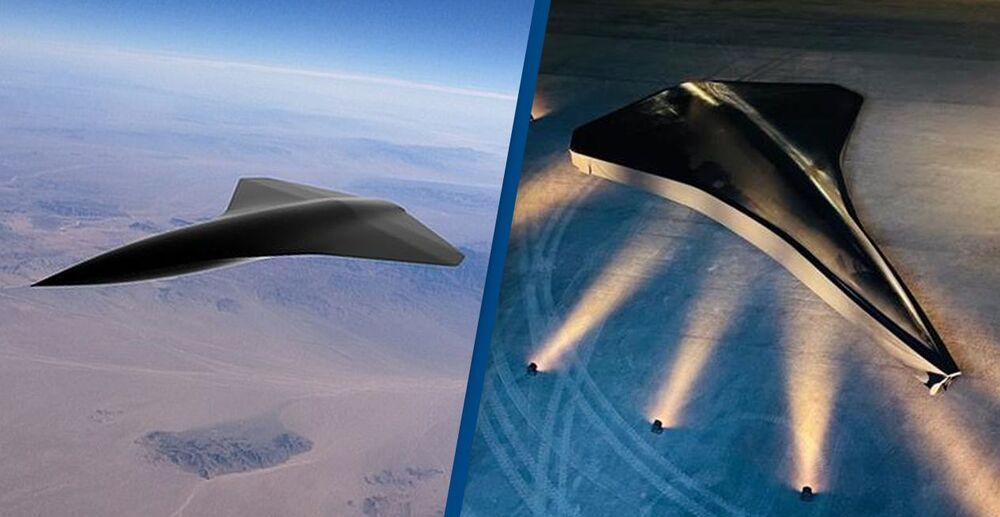

It can exceed the speed of sound, hitting an astonishing Mach 2.1! 😲🤯
A new combat drone has been created that can hit speeds of more than 1500mph.
The drone is much bigger than the ones you’ll have seen floating around your local parks, however, and looks more like a small spaceship.
Created by Kelley Aerospace, the supersonic drone is made up of carbon fibre and is completely unmanned; it can exceed the speed of sound, hitting an astonishing Mach 2.
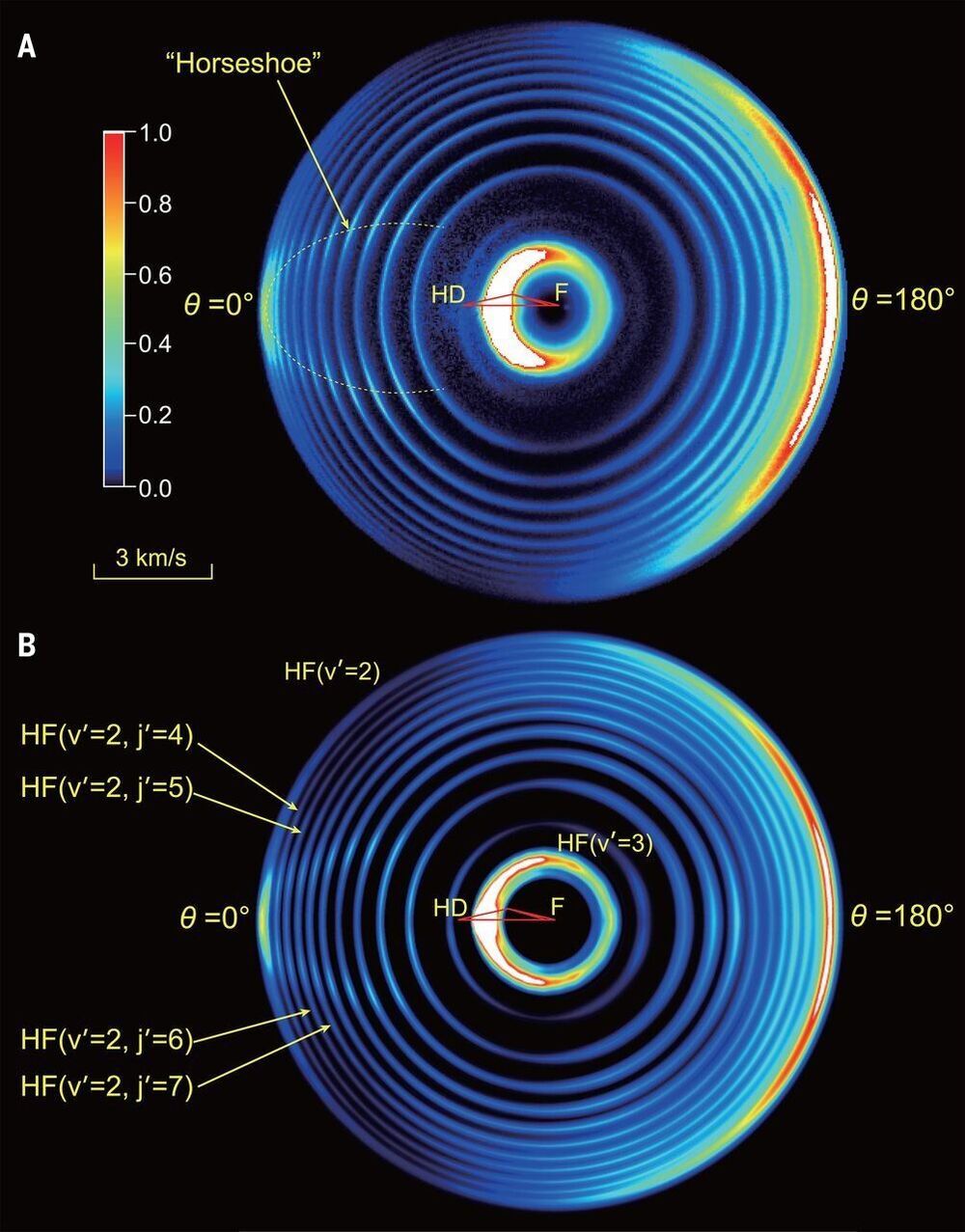
A team of researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Southern University of Science and Technology, has discovered a thought-provoking pattern in cross-sections observed in an F + HD → HF + D reaction. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes their double-pronged approach to learning more about the role of relativistic spin-orbit interactions in chemical reactions. T. Peter Rakitzis, with the University of Crete, and IESL-FORTH, has published a Perspectives piece in the same journal issue outlining the difficulty of studying chemical reactions at the quantum level and the work done by the team in China.