“An exciting outcome of this research is that it definitively shows the critical protective element at chromosome ends is the telomere DNA loop,” said Associate Professor Cesare.
“This likely explains why telomere length regulates ageing; cells must need long enough telomeres to make the DNA loops and this becomes difficult as cells age.”
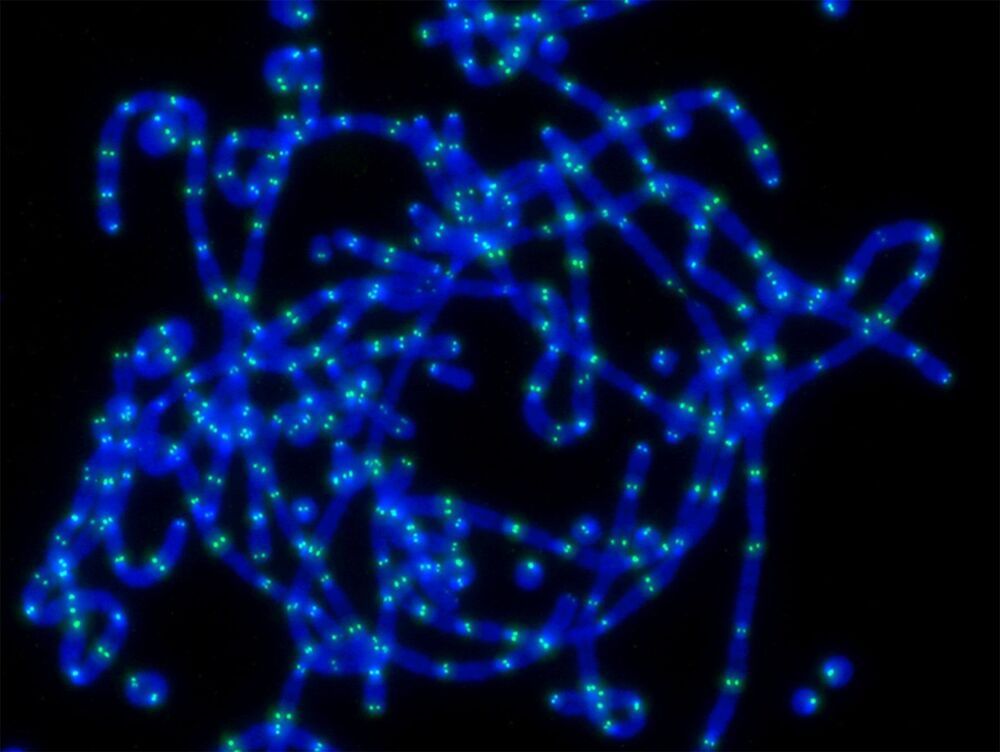
Telomeres are the protective caps at chromosome ends. In adult cells, telomeres shorten each time a cell divides and this contributes to ageing and cancer. Pluripotent stem cells, however, are specialised cells that exist in the earliest days of development. These pluripotent cells do not age and have the ability to turn into any type of adult cell.
The surprise finding, published today in Nature, shows that telomeres in pluripotent stem cells are protected very differently than telomeres in adult tissues.
“This upends 20 years of thinking on how stem cells protect their DNA,” said Associate Professor Tony Cesare, from the University of Sydney’s Faculty of Medicine and Health, who is Head of the Genome Integrity Unit at Children’s Medical Research Institute (CMRI) and co-leader of a research team that collaborated on this research.
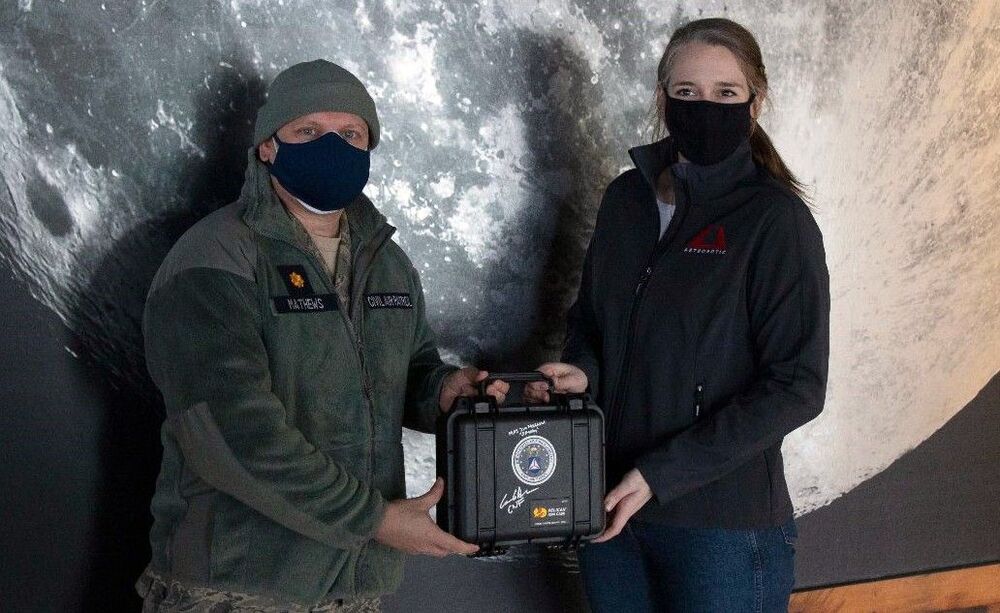








 A microchip carrying more than 27000 Civil Air Patrol names with related messages and images is set to be carried to the moon later this year aboard space robotics company Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander.
A microchip carrying more than 27000 Civil Air Patrol names with related messages and images is set to be carried to the moon later this year aboard space robotics company Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander.