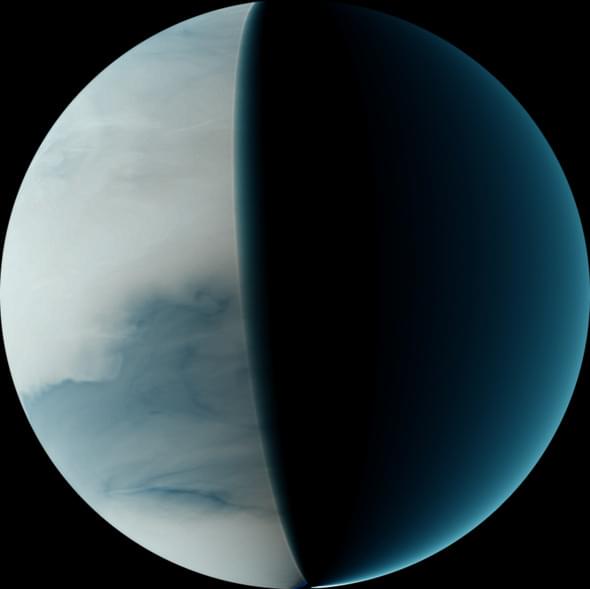
There are many strange things happening on Venus. Among them is a recognizable weather pattern that scientists now realize has persisted in the atmosphere for at least 30 years.




Pioneering mouse study offers new therapeutic avenues for reducing visceral fat stores, which have been associated with cardiovascular disease and multiple types of cancer.
Obesity has been linked to no less than 13 cancers, including the two most prevalent (breast and colorectal), as well as to cardiovascular disease, which remains a leading cause of death worldwide.
The most harmful type of obesity is caused by the excessive accumulation of so-called “deep” fat. Contrary to fat stores located directly under the skin, deep, or “visceral,” fat stores reside inside our abdominal cavity, where they envelop vital organs. In normal amounts, visceral fat supports various fundamental functions, such as reproduction. However, when it is too abundant, it produces unhealthy levels of proteins and hormones that negatively affect neighboring tissues and organs.
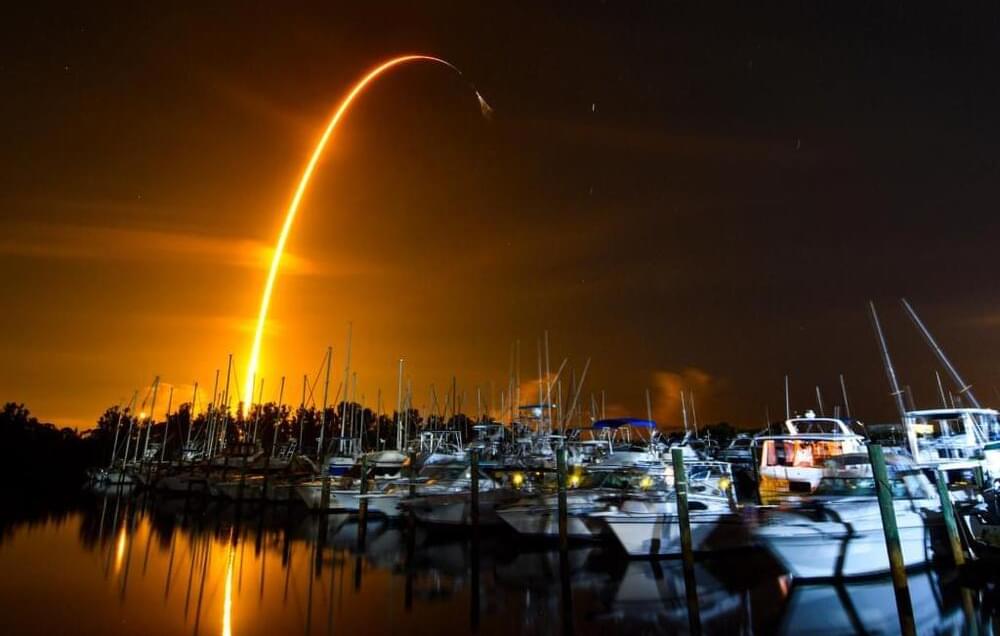

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. — A SpaceX shipment of ants, avocados, and a human-sized robotic arm rocketed toward the International Space Station on Sunday.
The delivery — due to arrive Monday — is the company’s 23rd for NASA in just under a decade.
A recycled Falcon rocket blasted into the predawn sky from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. After hoisting the Dragon capsule, the first-stage booster landed upright on SpaceX’s newest ocean platform, named “A Shortfall of Gravitas.” SpaceX founder Elon Musk continued his tradition of naming the booster-recovery vessels in tribute to the late science fiction writer Iain Banks and his Culture series.

WASHINGTON — SpaceX performed its first Falcon 9 launch in two months Aug. 29 sending a cargo Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station.
The Falcon 9 lifted off from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center at 3:14 a.m. Eastern after a one-day delay because of weather. The Dragon spacecraft separated from the rocket’s upper stage about 12 minutes after liftoff and is scheduled to dock with the station at about 11 a.m. Eastern Aug. 30 for an approximately one-month stay.
The launch was the first for a Falcon 9 since the June 30 launch of the Transporter-2 rideshare mission, the longest pause since a three-month gap between launches from August to November 2019. One reason for the hiatus was a delay in Starlink launches to equip those satellites with laser inter-satellite links; the majority of the Falcon 9 launches this year have been Starlink missions.

Complementarity relation of wave-particle duality is analyzed quantitatively with entangled photons as path detectors.
The twenty-first century has undoubtedly been the era of quantum science. Quantum mechanics was born in the early twentieth century and has been used to develop unprecedented technologies which include quantum information, quantum communication, quantum metrology, quantum imaging, and quantum sensing. However, in quantum science, there are still unresolved and even inapprehensible issues like wave-particle duality and complementarity, superposition of wave functions, wave function collapse after quantum measurement, wave function entanglement of the composite wave function, etc.
To test the fundamental principle of wave-particle duality and complementarity quantitatively, a quantum composite system that can be controlled by experimental parameters is needed. So far, there have been several theoretical proposals after Neils Bohr introduced the concept of “complementarity” in 1,928 but only a few ideas have been tested experimentally, with them detecting interference patterns with low visibility. Thus, the concept of complementarity and wave-particle duality still remains elusive and has not been fully confirmed experimentally yet.

It’s his personal mission to make it to 200.
Sergey Young has made it his personal mission to live to 200. Seriously: The longevity expert, founder of the Longevity Vision Fund, and author of The Science and Technology of Growing Young, has dedicated his entire career to helping at least 1 billion people live long, healthy lives—and make these technological advances affordable and accessible for all.
Through his work, he has identified what he calls lifestyle “longevity buckets” to increase your lifespan and healthspan (because who wants to live to 200 with a low quality of life?). “By implementing them, we can add 10 20 healthy and happy years to our life,” he says on this episode of the mindbodygreen podcast. “We can easily live 200 years.”

Physicists may have just detected a cloud of dark matter particles! It could also be primordial black holes, but either would be a major breakthrough.