Artificial intelligence, machine learning, data science.


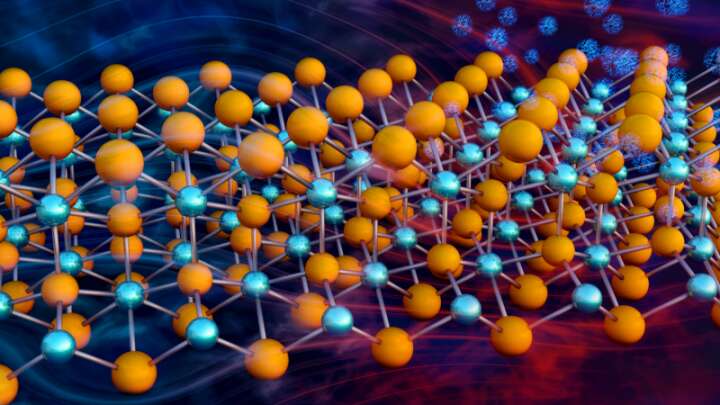
Engineers usually regard heat as “waste energy” since it is hard to efficiently turn into anything useful. However, a new class of thermoelectric materials could change that after researchers opted to try the exact opposite of the usual approach. A paper in Science Advances explains why, speeding the search for even better versions.
As the name suggests, thermoelectric materials turn heat into electricity, skipping the boiling water stage used in most bulk electricity production. However, cost and inefficiency have kept thermoelectric generators restricted to niche applications, such as powering spacecraft like the Mars Perseverance rover where lightweight, reliable energy production matters more than price.
Thermoelectric materials are too expensive and polluting for more widespread use, but new versions that replace heavier elements with magnesium could change that, opening the door to even better options that could find widespread uses.
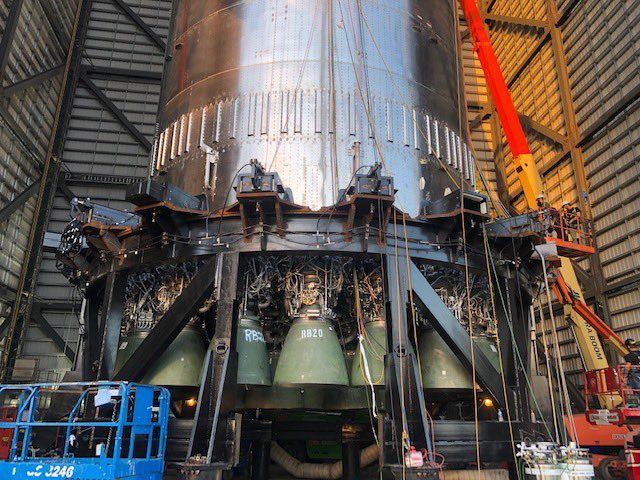


Nanoracks has hired a former NASA official most recently involved with planning for Artemis to lead its efforts to develop commercial space stations.
WASHINGTON — Commercial space services company Nanoracks has hired a former NASA official most recently involved with planning for the Artemis program to lead its efforts to develop commercial space stations.
Nanoracks announced Aug. 2 it hired Marshall Smith to be its senior vice president of commercial space stations. Smith retired from NASA at the end of July after more than 35 years at the agency, most recently as deputy associate administrator for systems engineering and integration in the Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate.
In his new role, Smith will oversee the company’s Outpost program, which seeks to convert upper stages of launch vehicles into modules that can be used for in-space manufacturing or habitats, as well as plans to develop free-flyer commercial space stations. Smith will run the company’s new office in Huntsville, Alabama.

Should you be worried about the massive space rock that could, theoretically, spell disaster if it were to make landfall on terra firma? No, you shouldn’t. But that doesn’t mean you should ignore it either.
The asteroid, called 2016 AJ193, is just under a mile wide and moving at a speed of 58538 miles per hour, according to EarthSky. Its closest encounter with Earth will occur on August 23 at 11:10 a.m. ET, and experts note that anyone trying to spot the asteroid in the wild will have the best chance of doing so before sunrise. If you’re trying to catch a glimpse of it, you’ll have to use a telescope.
Despite the “potentially hazardous” label designated by NASA, EarthSky is quick to allay any fears of impending apocalypse (at least from this particular asteroid) because it won’t hit Earth.



The image shows an elongated galaxy sandwiched, and stretched, between two galaxies. A long tail is visible in the galaxy on the right in this image: Called a “tidal tail,” this can occur when stars and gases are “stripped” from the outside arms of galaxies during a merger, according to Cosmos.
Tweet may have been deleted
The Hubble Space Telescope — the size of a large school bus — is over 30 years old. The solar-powered telescope takes detailed images of far-off cosmic objects, like Arp 195, yet the legendary instrument is wearing down with age, most recently exemplified by a computer problem that sent Hubble offline for weeks. Still, NASA expects “Hubble will last for many more years and will continue making groundbreaking observations, working in tandem with other space observatories including the James Webb Space Telescope to further our knowledge of the cosmos.”
