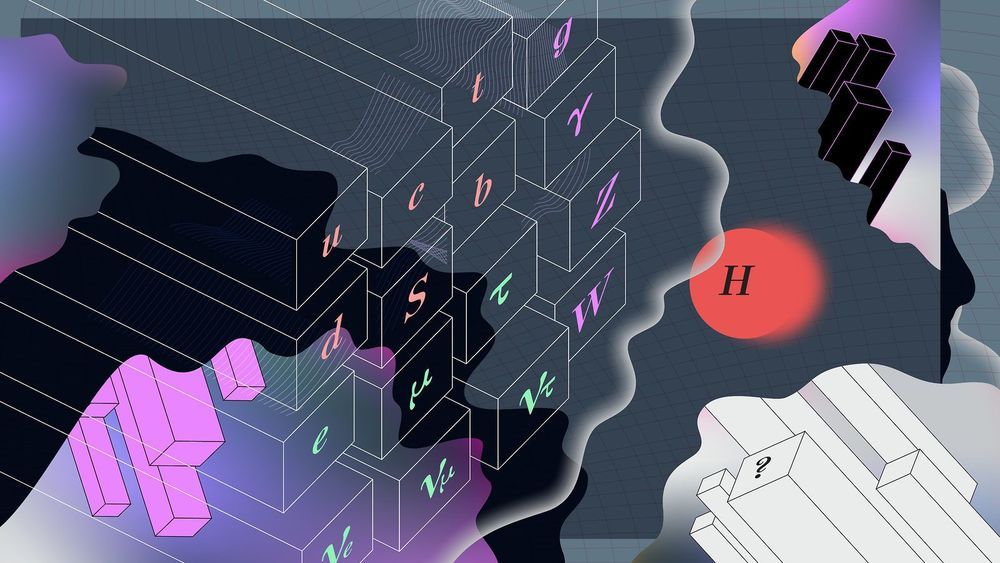
Our best model of particle physics explains only about 5 percent of the universe.
Related: Sikorsky-Boeing’s SB-1 Defiant Helicopter Prototype Impresses Leaders in Demo
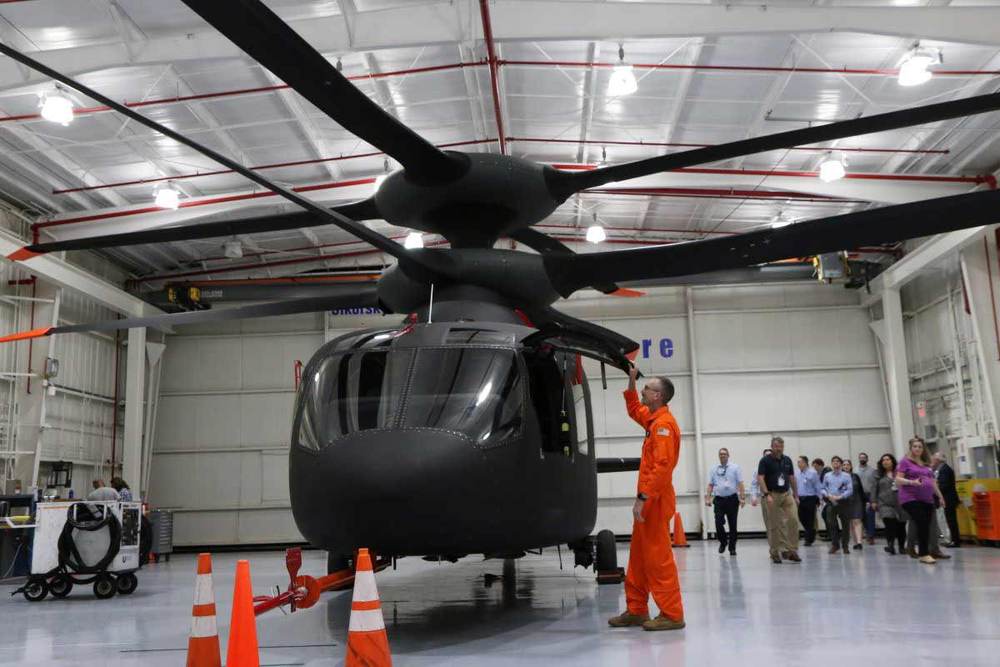
Defiant strikes an intimidating silhouette with its prominent X2 technology, which features a coaxial rotor system and a large rear propeller that replaces the tail rotor found on conventional helicopters.
Sikorsky-Boeing officials said the new aircraft design will be capable of flying at speeds of more than 200 knots, or 230 miles per hour, and maneuvering like a fine-tuned sports car.
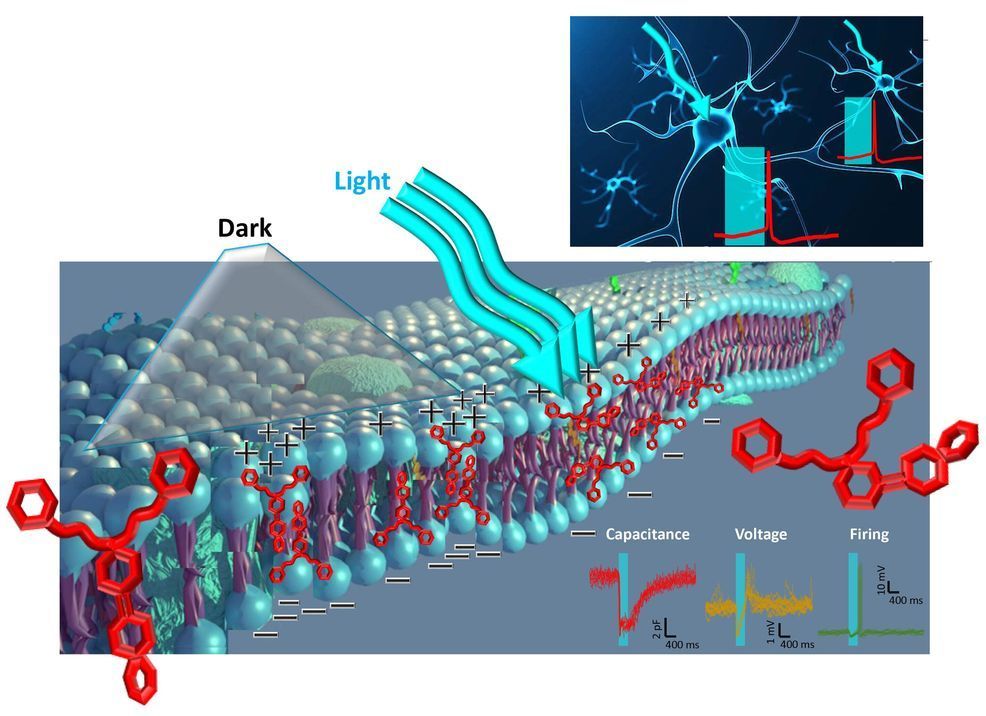
Optical technologies that can be used to modulate neuronal activity are opening up exciting possibilities for research in neuroscience and biology. Optical tools allow neuroscientists to excite and inhibit neurons or areas of the brain at will. They can thus be used to investigate the function of specific brain circuits or regions, as well as to identify new potential treatments for neurological and psychiatric diseases.
The generation of tethered azobenzene photoswitches targeted at membrane bilayers or linked to ion channels is a pioneering optical technique that could further aid the study of the human brain. This technique, however, particularly when implemented at high light intensities, can lead to a considerable increase in temperature and can thus be harmful to neurons when used repeatedly.
To overcome this limitation, researchers at the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT) in collaboration with Politecnico di Milano, have recently created a new light-sensitive azobenzene compound, dubbed Ziapin2, which can be used to build photoswitches that do not increase in temperature when irradiated with visible light. This new compound, introduced in a paper published in Nature Nanotechnology, partitions into the plasma membrane with a high stability, enabling its thinning and an increased capacitance at a steady state.
An experiment by EPFL researchers has confirmed a theory that has been used in mechanics for over half a century—despite never having been fully validated. The team could now use the theory in bolder and more innovative ways in their quest to develop ever better energy systems.
Some theories are widely used even though they have never been experimentally validated. One example is the so-called narrow groove theory, or NGT, which explains how air-lubricated bearings work in mechanical systems.
The theory was proposed in 1965 but, until recently, it had only been tested partially or indirectly. Researchers at EPFL’s Laboratory for Applied Mechanical Design (LAMD), based at Microcity in Neuch tel, have now closed a gap that has persisted in the scientific literature for over 50 years. The team has published its findings in the journal Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing.
Changing a single word can alter the way an AI program judges a job applicant or assesses a medical claim.
CEO Elon Musk congratulated the Tesla team after the Model 3 got 350 miles of range on a single charge in a new test on range mode.
Officially, Tesla Model 3 Long Range had a range of 310 miles on a single charge, but Tesla has found some optimizations in recent months – leading to an increase of EPA-rated range to 322 miles.
Now Consumer Reports conducted its own test of the car – confirming the EPA rating.
Scientists discover a new link between a protein and an eye condition which affects 1.5 million people.
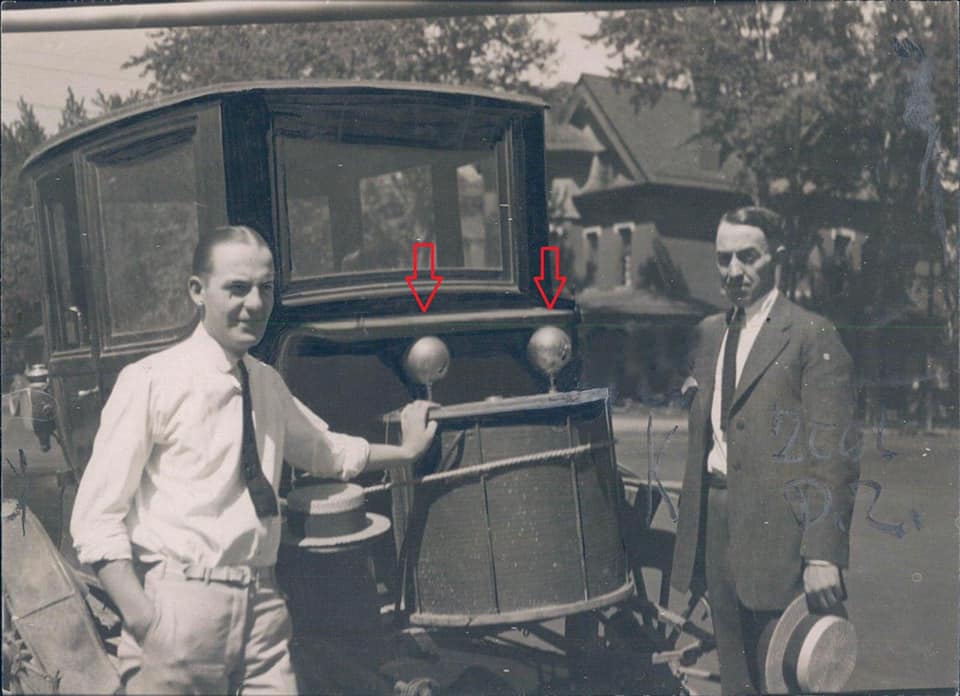
Earl Ammann and his ‘atmospheric generator’ powered car:
Denver Post — Monday, August 8, 1921 Denver Man Invents Generator That Takes Electricity From Air & Propels Automobile Believes He has Apparatus that will Revolutionize Power & Lighting & Gives it a Test on Streets of City.
Has an invention been made that will revolutionize the electrical world? Will the apparatus conceived by a Denver man light buildings, run automobiles, battleships, power plants by the unlimited supply of electricity in the air? Denver electrical experts say “yes”, and the young inventor, C. Earl Ammann, Monday demonstrated his invention by attaching it to an old automobile and running it about the city.
I’ve been reading an excellent book by David Wood, entitled, which was recommended by my pal Steele Hawes. I’ve come to an excellent segment of the book that I will quote now.
“One particular challenge that international trustable monitoring needs to address is the risk of more ever powerful weapon systems being placed under autonomous control by AI systems. New weapons systems, such as swarms of miniature drones, increasingly change their configuration at speeds faster than human reactions can follow. This will lead to increased pressures to transfer control of these systems, at critical moments, from human overseers to AI algorithms. Each individual step along the journey from total human oversight to minimal human oversight might be justified, on grounds of a balance of risk and reward. However, that series of individual decisions adds up to an overall change that is highly dangerous, given the potential for unforeseen defects or design flaws in the AI algorithms being used.”
The fifteen years from 2020 to 2035 could be the most turbulent of human history. Revolutions are gathering pace in four overlapping fields of technology: nanotech, biotech, infotech, and cognotech, or NBIC for short. In combination, these NBIC revolutions offer enormous new possibilities: enormous opportunities and enormous risks.
Department of Homeland Security (DHS) whistleblower Philip Haney was found dead in Amador County, Calif., on Friday, according to local authorities.
Haney, 66, “appeared to have suffered a single, self-inflicted gunshot wound,” the Amador County Sheriff’s Office said in a release. Sheriff and coroner Martin A. Ryan shared the initial details of the case.
“On February 21, 2020 at approximately 1012 hours, deputies and detectives responded to the area of Highway 124 and Highway 16 in Plymouth to the report of a male subject on the ground with a gunshot wound,” the release read.