𝙎𝙥𝙤𝙣𝙜𝙚 𝙂𝙚𝙣𝙚𝙨 𝙃𝙞𝙣𝙩 𝙖𝙩 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙊𝙧𝙞𝙜𝙞𝙣𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙉𝙚𝙪𝙧𝙤𝙣𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙊𝙩𝙝𝙚𝙧 𝘾𝙚𝙡𝙡𝙨
A new study of gene expression in sponges reveals the complex diversity of their cells as well as some possibly ancient connections between the nervous, immune and digestive systems.

Great video of vital biomolecular processes.
COVID-19 mRNA vaccines deliver directions to make a protein that educates our immune system, so it will neutralize the virus in future encounters. The mRNA-containing lipid particles are taken up by specialized immune system cells. See more: COVIDVaccineAnswers.org
Animation created by and for the Vaccine Makers Project.
Copyright © 2021, Medical History Pictures, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Vaccine Makers Project (VMP) is the classroom-based program of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (VEC at CHOP). The Center’s team is composed of scientists, physicians, mothers and fathers devoted to the study and prevention of infectious diseases. The Center was launched in October 2000 to provide accurate, comprehensive and up-to-date information about vaccines and the diseases they prevent. The VMP program is committed to public education about vaccine science via scientifically supported, historically accurate, and emotionally compelling content.
With the recent COP talks in mind, is this the Eco alternative to rocketry? And are there perhaps others?
I talked about Spinlaunch a few years ago, they wanted to reduce space launch costs by throwing the launch vehicles out of a spinning launcher at hypersonic speeds. I was somewhat skeptical as to the chances of solving the engineering problems inherent in this, but recently they demonstrated a mach 1 launch using their 1/3 scale launcher, so they’re already making progress on developing a viable launch syste.
Follow me on Twitter for more updates:
Tweets by DJSnM
I have a discord server where I regularly turn up:
It’s more likely than you think.
When it comes to interstellar missions, however, there are no plans for crewed missions on the table. While there are proposals for sending robotic missions, sending astronauts to nearby stars and exoplanets simply isn’t feasible yet.
However, according to new research led by the University of California, interstellar missions could be conducted in the near future that would have tardigrades (aka. “Water Bears”) as their crew.
The study, titled “The First Interstellar Astronauts Will Not Be Human,” was conducted by researchers from UC Santa Barbara, the UCLA Health Center, the University of Florida, and Ruhr-University Bochum. It will be published in the January 2022 issue of Acta Astronautica.

Companies like Facebook parent Meta and Google parent Alphabet have all experienced major A.I. bias blunders, sometimes involving computer vision technology misidentifying Black people with primates. Numerous high-profile academic studies, articles in mainstream news outlets, and proposed regulations by lawmakers in the European Union and elsewhere continue to bring the issue to the forefront.
On a personal note, I’ve lost count of the number of times I’ve had to write variations of the phrase “facial recognition software that works better on white males than women and people of color” in articles about A.I. bias.

Many companies are experimenting with AI, often in many different areas of the company. But experimentation is not enough. It’s essential to have a bold corporate strategy driven from the top. The AI strategy needs to be coordinated throughout the company in tight alignment with the overall business strategy.
AI can be scary for employees, and many are worried about their jobs (see another jobs?). The most successful AI-fueled organizations lead with change management to enable AI systems to succeed.
A key factor for successful change management is trust. Companies that focus on relationship-building, collaboration, and training engender trust. Successful companies help employees understand that most AI replaces tasks, not jobs. Those companies are aiming to augment jobs so that AI and employees work together. If AI is going to replace jobs, management needs to be clear about exactly how that will play out for the employees and provide opportunities for them to upskill or reskill.
Full Story:
Deloitte recently published a comprehensive study of the current state of AI, asking the question: “What are today’s most AI-fueled organizations doing differently to drive success?”
In this article, I provide you with a summary of their findings to determine whether or not you need to go deeper to get more value.
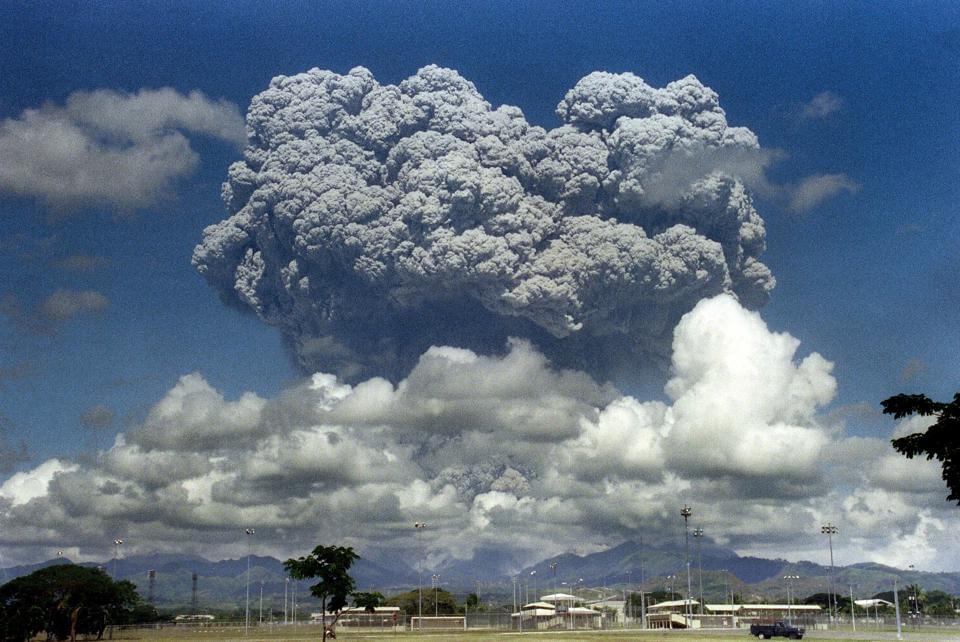

Volcanic eruptions contributed to the collapse of dynasties in China in the last 2,000 years by temporarily cooling the climate and affecting agriculture, according to a news release by Rutgers University.
In a study published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment, scientists reconstructed the magnitude of 156 explosive volcanic eruptions from 1 A.D. to 1915 by examining elevated sulfate levels in ice cores from Greenland and Antarctica. They also analyzed historical documents from China on 68 dynasties and examined warfare there between 850 and 1911.
Scientists found that smaller volcanic “shocks” to the climate may cause dynasties to collapse when political and socioeconomic stress is already high. Larger shocks may lead to collapses without substantial pre-existing stress. Other factors include poor leadership, administrative corruption and demographic pressures.
CoinFlip has the largest network of Bitcoin ATMs in the US. With Market leading low rates, buy using cash, card, or bank transfer. Buying Bitcoin has never been easier.
