New cost of California’s plan to bring high-speed rail to the state is now $105 billion. It started 14 years ago at $40 billion.
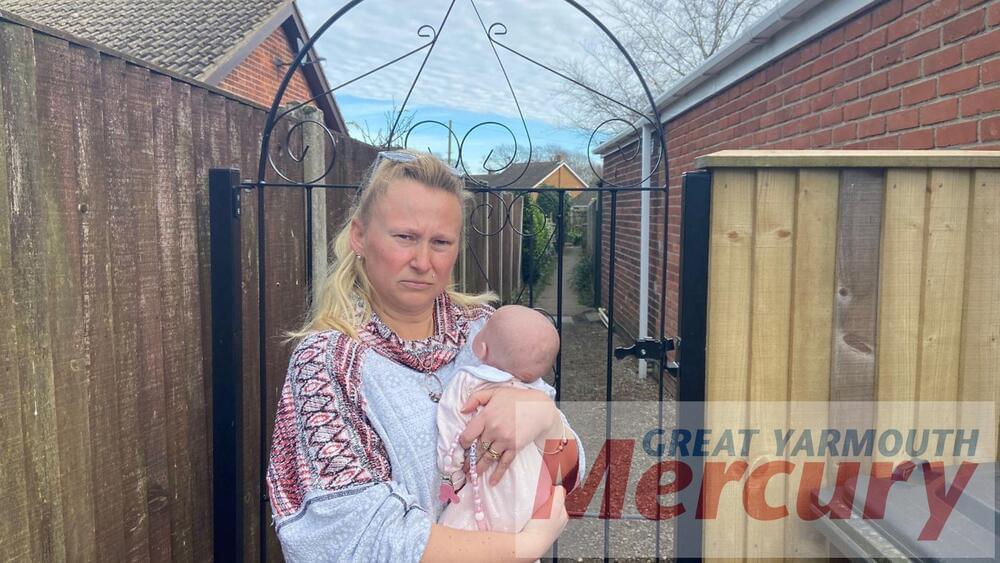



A homeowner has shared her upset after a gas company started laying pipes under her private walkway claiming a narrow passageway was actually a street.
Liesel Symonds has been locked in conflict with gas company Cadent for months.
Cadent says it has legal duty to connect homes and has done nothing wrong.
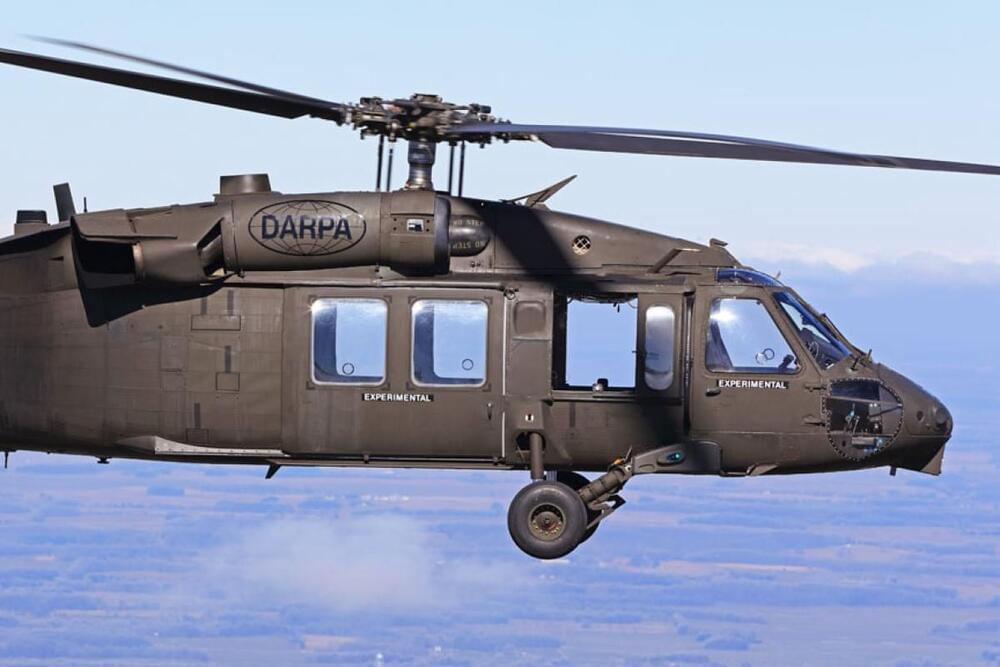


FORT CAMPBELL, KY (AP) — A helicopter flew unmanned around Fort Campbell recently in what is the Army’s first automated flight of an empty Black Hawk, officials said.
The 14,000-pound UH-60A Black Hawk successfully navigated around the post as if it were downtown Manhattan, engineers told reporters Tuesday.
The DARPA Aircrew Labor In-Cockpit Automation System (ALIAS) program took the helicopter on 30-minute flight on Feb. 5. It was the first time the system known as ALIAS flew completely by itself. The system is being tested with 14 military aircraft.

Today’s latest news, Abu Dhabi, Dubai and the Emirates | The National”,” site_title”:null},” social”:{“twitter”:null,” rss”:null,” instagram”:null,” facebook”:null},” site_topper”:{“site_logo_image”:” https://cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/the…WTPZAY.jpg”},” navigation”:{“nav_title”:null},”_admin”:{“alias_ids”:[”/uae”]},” dfp_path”:”“,” usesmallmobileheadersize”:” false”,” useparentheader”:” false”,”_website”:” the-national”,” name”:” UAE”,” order”:{“UK-edition”:1003,” US-edition”:1003,” Gulf-edition”:1003,” MiddleEastandAfricaEdition-edition”:1004,” Middleeastandnorthafrica-edition”:1003,” Middleeastnorthafrica-edition”:1003,” MENA-edition”:1002,” default”:1001,” us-edition”:1003,” JSON-Feed-Sections”:1001,” footer”:1001},” parent”:{“default”:”/”,” Footer”:null,” International”:”/”,” UK-edition”:”/”,” US-edition”:”/”,” Gulf-edition”:”/”,” MiddleEastandAfricaEdition-edition”:”/”,” Middleeastandnorthafrica-edition”:”/”,” International-edition”:”/”,” Middleeastnorthafrica-edition”:”/”,” international-edition”:”/”,” MENA-edition”:”/”,” us-edition”:”/”,” JSON-Feed-Sections”:”/”,” footer”:”/”},” ancestors”:{“default”:[],” Footer”:[],” International”:[],” UK-edition”:[”/”],” US-edition”:[],” Gulf-edition”:[],” MiddleEastandAfricaEdition-edition”:[],” Middleeastandnorthafrica-edition”:[],” International-edition”:[],” Middleeastnorthafrica-edition”:[”/”],” international-edition”:[],” MENA-edition”:[],” us-edition”:[],” JSON-Feed-Sections”:[],” footer”:[]},” inactive”:false,” node_type”:” section”,” children”:[{“_id”:”/uae/expo-2020”,” site”:{“site_url”:” https://www.thenationalnews.com/uae/expo-2020/”,” site_about”:null,” pagebuilder_path_for_native_apps”:null,” site
When the next generations are fewer and less wealthy than the previous generations(who are living longer), problems can arise.
| Invest in blue-chip art for the very first time by signing up for Masterworks: https://masterworks.art/wallstreet.
See important disclosures: https://mw-art.co/37WwvbD
This video is sponsored by Masterworks.
In this video we look at the structure of the US Social Security system and how it closely resembles aa Ponzi Scheme. Current retirees are paid from payroll taxes collected from existing workers. In recent years the demographic trends in the US have deteriorated significantly and Social Security expected to become insolvent by 2033.
0:00 — 1:39 Intro.
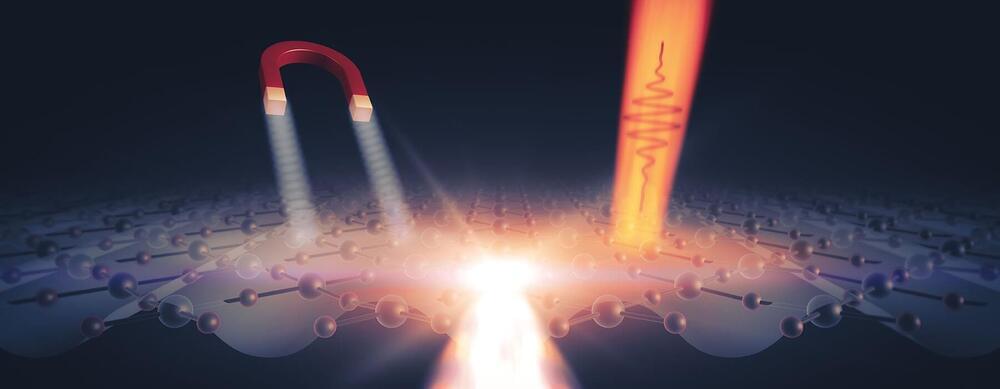
Much like people can learn more about themselves by stepping outside of their comfort zones, researchers can learn more about a system by giving it a jolt that makes it a little unstable—scientists call this “out of equilibrium”—and watching what happens as it settles back down into a more stable state.
In the case of a superconducting material known as yttrium barium copper oxide, or YBCO, experiments have shown that under certain conditions, knocking it out of equilibrium with a laser pulse allows it to superconduct—conduct electrical current with no loss—at much closer to room temperature than researchers expected. This could be a big deal, given that scientists have been pursuing room-temperature superconductors for more than three decades.
But do observations of this unstable state have any bearing on how high-temperature superconductors would work in the real world, where applications like power lines, maglev trains, particle accelerators and medical equipment require them to be stable?


The endless parade of bad news for Israeli malware merchant NSO Group continues. While it appears someone might be willing to bail out the beleaguered company, it still has to do business as the poster boy for the furtherance of human rights violations around the world. That the Israeli government may have played a significant part in NSO’s sales to known human rights violators may ultimately be mitigating, but for now, NSO is stuck playing defense with each passing news cycle.
Late last month, the New York Times revealed some very interesting things about NSO Group. First, it revealed the company was able to undo its built-in ban on searching US phone numbers… provided it was asked to by a US government agency. The FBI took NSO’s powerful Pegasus malware for a spin in 2019, but under an assumed name: Phantom. With the permission of NSO and the Israeli government, the malware was able to target US numbers, albeit ones linked to dummy phones purchased by the FBI.
The report noted the FBI liked what it saw, but found the zero-click exploit provided by NSO’s bespoke “Phantom” (Pegasus, but able to target US numbers) might pose constitutional problems the agency couldn’t surmount. So, it walked away from NSO. But not before running some attack attempts through US servers — something that was inadvertently exposed by Facebook and WhatsApp in their lawsuit against NSO over the targeting of WhatsApp users. An exhibit declared NSO was using US servers to deliver malware, something that suggested NSO didn’t care about its self-imposed restrictions on US targeting. In reality, it was the FBI and NSO running some tests on local applications of zero-click malware that happened to be caught by Facebook techies.