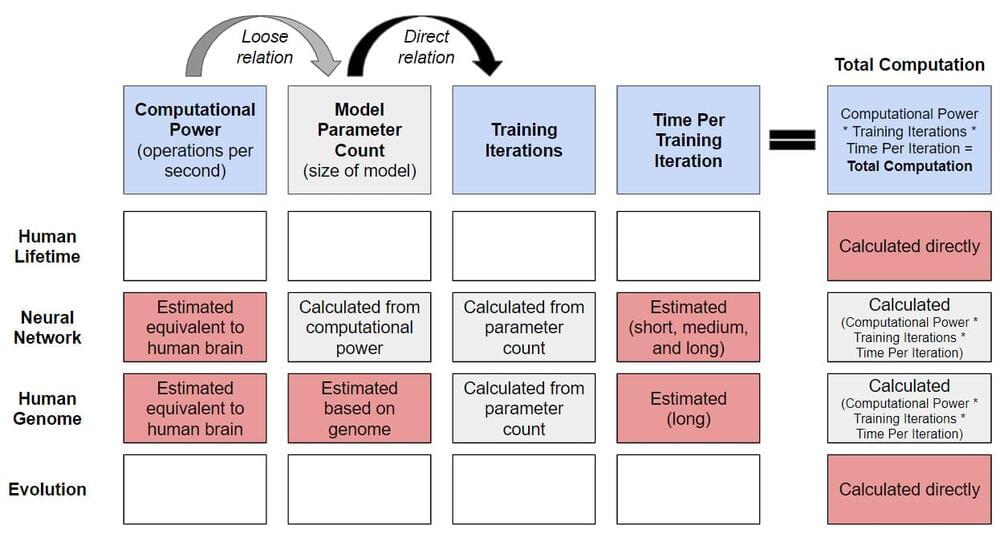
April, 2022
Sean Carroll (Caltech and Santa Fe Institute)
https://simons.berkeley.edu/events/causality-program-externa…-institute.
Causality.
Abstract:
A macroscopic arrow of time can be derived from reversible and time-symmetric fundamental laws if we assume an appropriate notion of coarse-graining and a Past Hypothesis of low entropy at early times. It is an ongoing project to show how familiar aspects of time’s arrow, such as the fact that causes precede effects, can be derived from such a formalism. I will argue that the causal arrow arises naturally when we describe macroscopic systems in terms of a causal network, and make some suggestions about how to fit prediction and memory into this framework.
Sean Carroll is a Research Professor of theoretical physics at the California Institute of Technology, and Fractal Faculty at the Santa Fe Institute. He received his Ph.D. in 1993 from Harvard University. His research focuses on foundational questions in quantum mechanics, spacetime, cosmology, emergence, entropy, and complexity, occasionally touching on issues of dark matter, dark energy, symmetry, and the origin of the universe. Carroll is the author of Something Deeply Hidden, The Big Picture, The Particle at the End of the Universe, From Eternity to Here, and Spacetime and Geometry: An Introduction to General Relativity. He has been awarded prizes and fellowships by the National Science Foundation, NASA, the Sloan Foundation, the Packard Foundation, the American Physical Society, the American Institute of Physics, the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the Freedom From Religion Foundation, the Royal Society of London, and the Guggenheim Foundation. Carroll has appeared on TV shows such as The Colbert Report, PBS’s NOVA, and Through the Wormhole with Morgan Freeman, and frequently serves as a science consultant for film and television. He is host of the weekly Mindscape podcast. He lives in Los Angeles with his wife, writer Jennifer Ouellette.