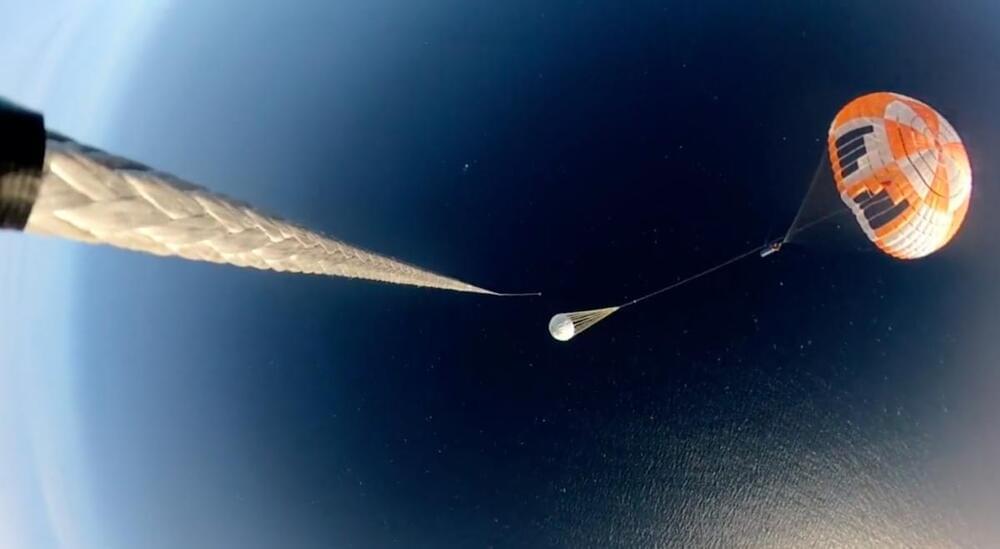
Rocket Lab aims to catch a falling booster with a helicopter for the first time ever this week, and a new video shows us how the action is supposed to go down.




Summary: New findings reveal how anesthesia-induced unconsciousness differs from normal sleep in relation to delta wave activity in the brain.
Source: picower institute for learning and memory.
Imagine the conscious brain as a sea roiling with the collisions and dispersals of waves of different sizes and shapes, swirling around and flowing across in many different directions. Now imagine that an ocean liner lumbers through, flattening everything that trails behind with its powerful, parting wake.
Have you ever made a mistake that you wish you could undo? Correcting past mistakes is one of the reasons we find the concept of time travel so fascinating. As often portrayed in science fiction, with a time machine, nothing is permanent anymore – you can always go back and change it. But is time travel really possible in our universe, or is it just science fiction?
Our modern understanding of time and causality comes from general relativity. Theoretical physicist Albert Einstein’s theory combines space and time into a single entity – “spacetime” – and provides a remarkably intricate explanation of how they both work, at a level unmatched by any other established theory.
This theory has existed for more than 100 years, and has been experimentally verified to extremely high precision, so physicists are fairly certain it provides an accurate description of the causal structure of our Universe.
By exchanging a classical material for one with unique quantum properties, scientists have made a superconducting circuit that’s capable of feats long thought to be impossible.
The discovery, made by researchers from Germany, the Netherlands, and the US, overturns a century of thought on the nature of superconducting circuits, and how their currents can be tamed and put to practical use.
Low-waste, high-speed circuits based on the physics of superconductivity present a golden opportunity to take supercomputing technology to a whole new level.