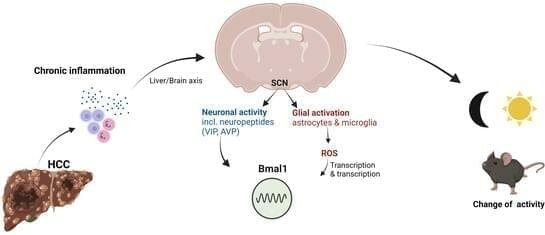
Background: Chronic liver diseases such as hepatic tumors can affect the brain through the liver–brain axis, leading to neurotransmitter dysregulation and behavioral changes. Cancer patients suffer from fatigue, which can be associated with sleep disturbances. Sleep is regulated via two interlocked mechanisms: homeostatic regulation and the circadian system. In mammals, the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) is the key component of the circadian system. It generates circadian rhythms in physiology and behavior and controls their entrainment to the surrounding light/dark cycle. Neuron–glia interactions are crucial for the functional integrity of the SCN. Under pathological conditions, oxidative stress can compromise these interactions and thus circadian timekeeping and entrainment.