Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


Welp, Now We Have Robo-Dogs With Sniper Rifles
The “Special Purpose Unmanned Rifle” has materialized from your Black Mirror nightmares.
Science fiction has seeped into science reality this week, as a robotics company showed off its sniper rifle-equipped robo-dog at the Association of the U.S. Army’s annual convention in Washington, D.C.
✈︎ Don’t miss our best-in-class military news. Join our squadron.
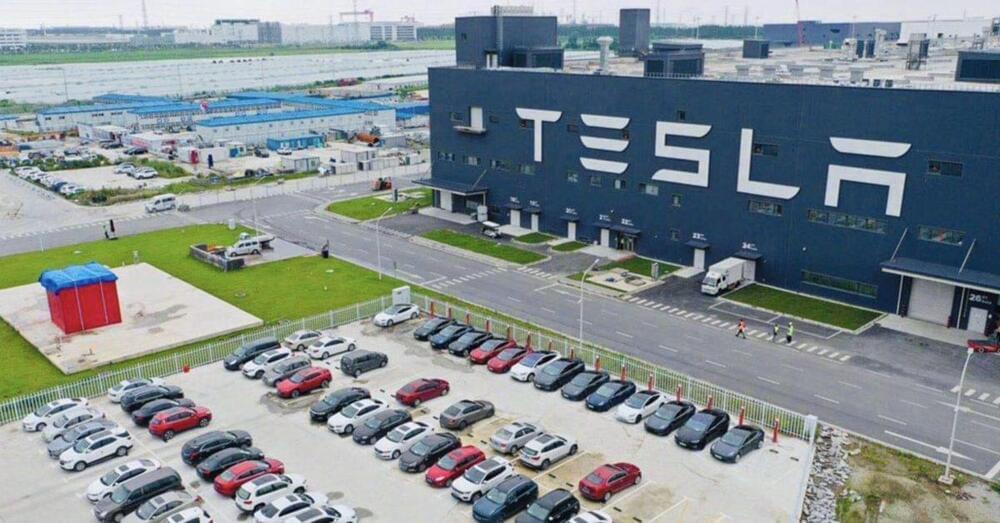

Tesla is rumored to be building new factory adjacent to Gigafactory Shanghai to double production to two million cars
A new report claims that Tesla is starting work on building a new factory adjacent to Gigafactory Shanghai in order to double production capacity to two million cars annually.
Tesla currently operates two main factories, Tesla Fremont and Gigafactory Shanghai, and it has Gigafactory Texas and Gigafactory Berlin slowly starting to ramp up production.
Those four projects alone should push Tesla’s production capacity beyond three million vehicles annually by the end of next year, but the automaker has much greater ambitions for this decade that will require several more factories. The company recently confirmed that it plans to announce a new location for a factory by the end of this year.
Scientists Have Discovered an Exotic Magnetic State of Matter
Scientists identify a long-sought magnetic state predicted nearly 60 years ago.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered a long-predicted magnetic state of matter called an “antiferromagnetic excitonic insulator.”
“Broadly speaking, this is a novel type of magnet,” said Brookhaven Lab physicist Mark Dean, senior author on a paper describing the research just published in Nature Communications. “Since magnetic materials lie at the heart of much of the technology around us, new types of magnets are both fundamentally fascinating and promising for future applications.”

Colossal Black Holes Locked in an Epic Cosmic Dance at Heart of Galaxy
Astronomers find evidence for the tightest-knit supermassive black hole duo observed to date.
Locked in an epic cosmic waltz 9 billion light years away, two supermassive black holes appear to be orbiting around each other every two years. The two giant bodies each have masses that are hundreds of millions of times larger than that of our sun, and the objects are separated by a distance roughly 50 times that which separates our sun and Pluto. When the pair merge in roughly 10,000 years, the titanic collision is expected to shake space and time itself, sending gravitational waves across the universe.
A Caltech-led team of astronomers has discovered evidence for this scenario taking place within a fiercely energetic object known as a quasar. Quasars are active cores of galaxies in which a supermassive black hole is siphoning material from a disk encircling it. In some quasars, the supermassive black hole creates a jet that shoots out at near the speed of light. The quasar observed in the new study, PKS 2131-021, belongs to a subclass of quasars called blazars in which the jet is pointing toward the Earth. Astronomers already knew quasars could possess two orbiting supermassive black holes, but finding direct evidence for this has proved difficult.
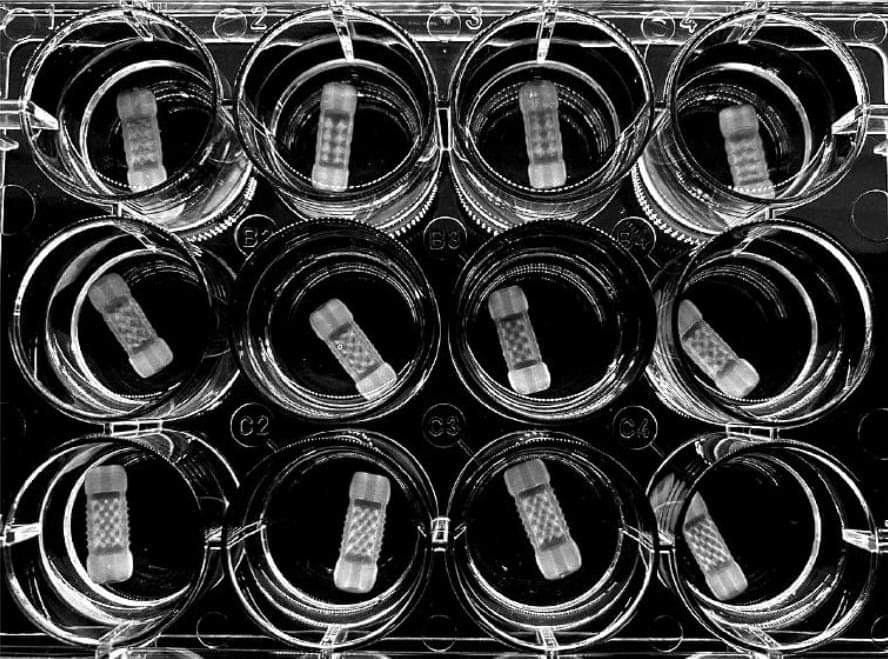


Researchers make regenerative medicine breakthrough with volumetric 3D bioprinted livers
A research team from Utrecht University has successfully fabricated working livers using a newly developed ultrafast volumetric 3D bioprinting method.
By means of visible light tomography, the volumetric bioprinting method enabled the successful printing of miniature stem cell units by making the cells “transparent”, which meant they retained their resolution and ability to perform biological processes.
Printed in less than 20 seconds, the liver units were able to perform key toxin elimination processes mimicking those that natural livers perform in our bodies, and could open new opportunities for regenerative medicine and personalized drug testing.