Software from Brave and DuckDuckGo will automatically bypass Google AMP.
Brave and DuckDuckGo have rolled out updates to help users bypass a divisive web initiative from Google.

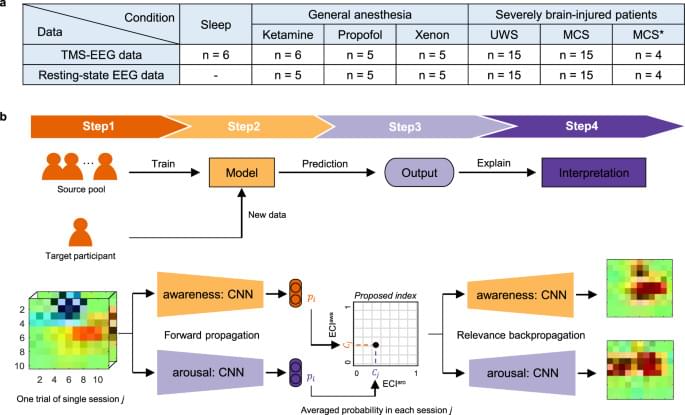
The classical neurophysiological approach for calculating PCI, power spectral density, and spectral exponent relies on many epochs to improve the reliability of statistical estimates of these indices21. However, these methods are only suitable for investigating the averaged brain states and they can only clarify general neurophysiological aspects. Machine learning (ML) allows decoding and identifying specific brain states and discriminating them from unrelated brain signals, even in a single trial in real-time22. This can potentially transform statistical results at the group level into individual predictions9. A deep neural network, which is a popular approach in ML, has been employed to classify or predict brain states using EEG data23. Particularly, a convolutional neural network (CNN) is the most extensively used technique in deep learning and has proven to be effective in the classification of EEG data24. However, a CNN has the drawback that it cannot provide information on why it made a particular prediction25. Recently, layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP) has successfully demonstrated why classifiers such as CNNs have made a specific decision26. Specifically, the relevance score resulting from the LRP indicates the contribution of each input variable to the classification or prediction decision. Thus, a high score in a particular area of an input variable implies that the classifier has made the classification or prediction using this feature. For example, neurophysiological data suggest that the left motor region is activated during right-hand motor imagery27. The LRP indicates that the neural network classifies EEG data as right-hand motor imagery because of the activity of the left motor region28. Therefore, the relevance score was higher in the left motor region than in other regions. Thus, it is possible to interpret the neurophysiological phenomena underlying the decisions of CNNs using LRP.
In this work, we develop a metric, called the explainable consciousness indicator (ECI), to simultaneously quantify the two components of consciousness—arousal and awareness—using CNN. The processed time-series EEG data were used as an input of the CNN. Unlike PCI, which relies on source modeling and permutation-based statistical analysis, ECI used event-related potentials at the sensor level for spatiotemporal dynamics and ML approaches. For a generalized model, we used the leave-one-participant-out (LOPO) approach for transfer learning, which is a type of ML that transfers information to a new participant not included in the training phase24,27. The proposed indicator is a 2D value consisting of indicators of arousal (ECIaro) and awareness (ECIawa). First, we used TMS–EEG data collected from healthy participants during NREM sleep with no subjective experience, REM sleep with subjective experience, and healthy wakefulness to consider each component of consciousness (i.e., low/high arousal and low/high awareness) with the aim to analyze correlations between the proposed ECI and the three states, namely NREM, REM, and wakefulness. Next, we measured ECI using TMS–EEG data collected under general anesthesia with ketamine, propofol, and xenon, again with the aim to measure correlation with these three anesthetics. Before anesthesia, TMS–EEG data were also recorded during healthy wakefulness. Upon awakening, healthy participants reported conscious experience during ketamine-induced anesthesia and no conscious experience during propofol-and xenon-induced anesthesia. Finally, TMS–EEG data were collected from patients with disorders of consciousness (DoC), which includes patients diagnosed as UWS and MCS patients. We hypothesized that our proposed ECI can clearly distinguish between the two components of consciousness under physiological, pharmacological, and pathological conditions.
To verify the proposed indicator, we next compared ECIawa with PCI, which is a reliable index for consciousness. Then, we applied ECI to additional resting-state EEG data acquired in the anesthetized participants and patients with DoC. We hypothesize that if CNN can learn characteristics related to consciousness, it could calculate ECI accurately even without TMS in the proposed framework. In terms of clinical applicability, it is important to use the classifier from the previous LOPO training of the old data to classify the new data (without additional training). Therefore, we computed ECI in patients with DoC using a hold-out approach29, where training data and evaluation data are arbitrarily divided, instead of cross-validation. Finally, we investigated why the classifier generated these decisions using LRP to interpret ECI30.


The first detection of gravitational waves in 2016 provided decisive confirmation of Einstein’s general theory of relativity. But another astounding prediction remains unconfirmed: According to general relativity, every gravitational wave should leave an indelible imprint on the structure of space-time. It should permanently strain space, displacing the mirrors of a gravitational wave detector even after the wave has passed.
Since that first detection almost six years ago, physicists have been trying to figure out how to measure this so-called “memory effect.”
“The memory effect is absolutely a strange, strange phenomenon,” said Paul Lasky, an astrophysicist at Monash University in Australia. “It’s really deep stuff.”
But then some have to write these AL programs.it will create more job opportunities for programmers.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), has been transforming multiple sectors of industries and impacting several aspects of our daily life. Mostly AI has acted prominently in the fields of automating manual processes. And therefore, we will be investigating how AI has affected the realm of software testing, automated testing in particular.
Software testing is the process of assessing the performance of a program developed to check whether it is developed as per the client’s requirements and to find out whether there are faults and improve them before it is deemed ready for use.
Each time developers add new code, new tests must be carried out and it is the responsibility of the QAs to spend significant time on ensuring that new code does not break the existing codebase. Regression testing cycles are extremely time-consuming when undertaken manually and can burden QAs to a large extent.

A large team of researchers at the University of Washington, working with colleagues from Université Montpellier and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, has taken a major step toward the creation of an axle-rotor nanomachine. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes how they used DNA coding to customize E. coli to push them into creating proteins that assembled into rotors and axles.
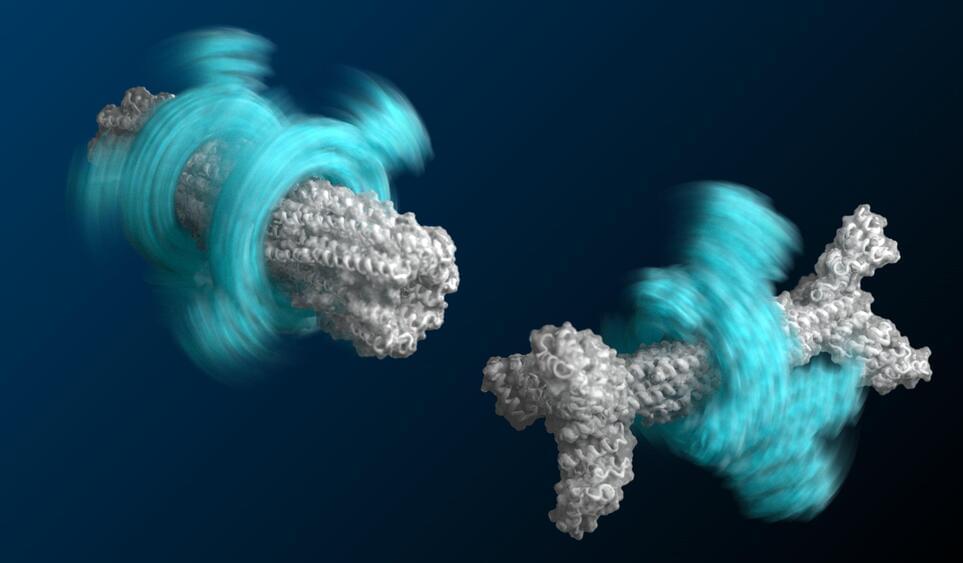
A large team of researchers at the University of Washington, working with colleagues from Université Montpellier and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, has taken a major step toward the creation of an axle-rotor nanomachine. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes how they used DNA coding to customize E. coli to push them into creating proteins that assembled into rotors and axles.
As the researchers note, molecular engines are abundant in nature, from the tails of flagellum on some bacteria to the F1 motor of ATPase. And while such examples have served as good models, attempts to harness them in nature or to create new ones in the lab have been mostly unsuccessful. This is due to the single purpose features of natural engines and the unpredictability of protein folding in synthetic attempts. In this new effort, the researchers have overcome some of the hurdles that others have faced and have taken a major step toward the creation of a molecular engine by creating two of the main parts necessary for such a device—an axle and a rotor—and even managed to connect them to each other.
To create their engine parts, the researchers first used a software program called Rosetta that allowed them to design ring-like proteins with specified diameters. They then used the data from the program to add DNA coding to amino acids in E. coli bacteria that make up proteins. Such proteins are made of chains of the amino acids—it is the sequence of them that defines the shape they will take when they spontaneously fold. The team was able to coax some of the proteins into folding into rotor shapes and others into axle shapes. They then went further by coaxing multiple proteins to fold together into rotor-axle combinations—the rudimentary parts necessary for a molecular engine.
