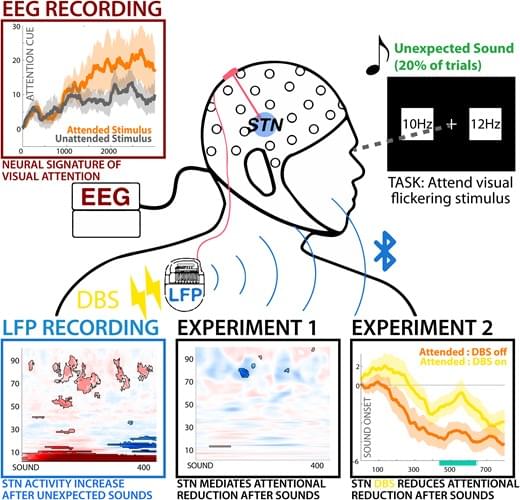
Using a novel technique to wirelessly record neural signals from already-implanted deep-brain stimulators in patients with Parkinson’s disease in an outpat


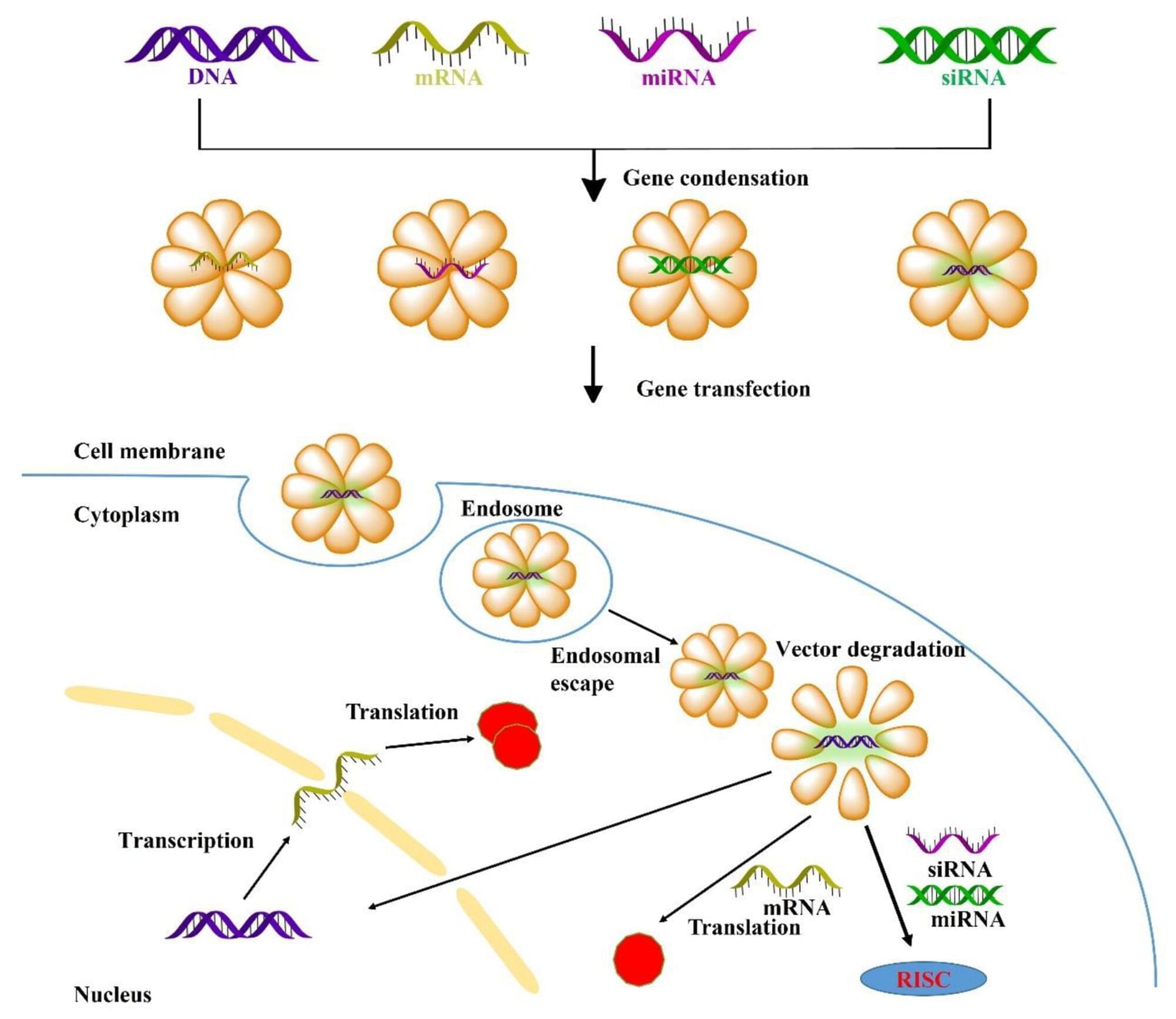
The development of COVID-19 vaccines has sparked widespread interest. mRNA-based therapies are rapidly gaining attention owing to their unique advantages in quickly developing vaccines and immunotherapy for various ailments [1, 2]. Given that most human diseases stem from genetic factors, gene therapy represents a promising modality for addressing various inherited or acquired disorders by replacing faulty genes or silencing genes [3]. Gene therapy encompasses the targeted exploitation of genetic material, which includes gene replacement through DNA or mRNA [4, 5]; gene silencing utilizing siRNA or miRNA [6], and CRISPR-Cas9 based gene editing [7].
However, achieving safe and efficient gene delivery to specific cells requires overcoming multiple biological barriers, including extracellular obstacles such as enzyme degradation, serum protein interactions, electrostatic repulsion of genes and cell membranes, and innate immune system, as well as intracellular obstacles such as endosomal escape, transport barriers, precise release [8]. Therefore, gene vectors require several characteristics such as high gene condensation; favorable serum stability to avoid non-specific serum protein interactions, endonuclease degradation, and renal clearance; achieved specific targeting cell or tissues; effective transport into the cytoplasm thereby facilitating gene transfection (mRNA, siRNA and miRNA); precise gene release and scheduling, and nuclear localization that enables DNA transcription. Comprehensive exploration of transfection mechanisms can aid in the development of high-performance gene vectors [9, 10].
Gene vectors generally include viral vectors and non-viral vectors. Presently, approximately 70% of clinical gene therapy trials employ viral vectors, which include retroviruses, lentiviruses, adenoviruses, and adeno-associated viruses. Due to their exceptional infectivity, virus-based vectors typically exhibit excellent gene transfection capabilities. However, the clinical safety of viral vectors has been questioned due to their propensity to stimulate immunogenic reactions and induce transgene insertion mutations. Moreover, viral vectors possess several limitations, including low gene loading capacity, inability to deliver large-sized genes, complicated preparation procedures, and the patient cannot be repeatedly administered [4]. In contrast, non-viral vectors, particularly lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) and cationic polymers, have demonstrated robust gene loading capacity, heigh safety and practicability, simplicity preparation [10, 11]. Consequently, non-viral vectors are exhibiting tremendous potential for further clinical development and application. Our review primarily highlights the significant potential of non-viral vectors, particularly lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), highly branched poly(β-amino ester) (HPAE), single-chain cyclic polymer (SCKP), poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers, and polyethyleneimine (PEI). We intend to provide a detailed examination of the latest research progress and existing limitations of non-viral gene vectors over recent years.
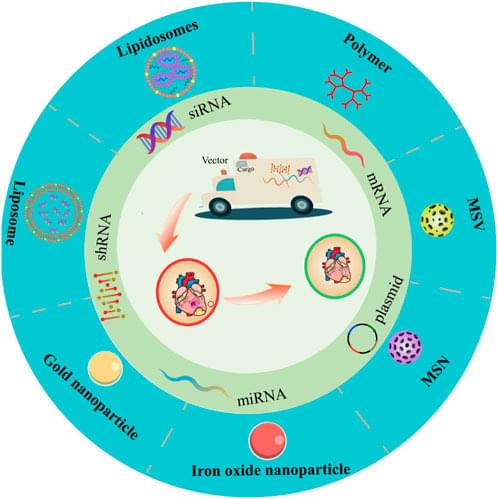
Gene therapy is a technique that rectifies defective or abnormal genes by introducing exogenous genes into target cells to cure the disease. Although gene therapy has gained some accomplishment for the diagnosis and therapy of inherited or acquired cardiovascular diseases, how to efficiently and specifically deliver targeted genes to the lesion sites without being cleared by the blood system remains challenging. Based on nanotechnology development, the non-viral vectors provide a promising strategy for overcoming the difficulties in gene therapy. At present, according to the physicochemical properties, nanotechnology-based non-viral vectors include polymers, liposomes, lipid nanoparticles, and inorganic nanoparticles. Non-viral vectors have an advantage in safety, efficiency, and easy production, possessing potential clinical application value when compared with viral vectors. Therefore, we summarized recent research progress of gene therapy for cardiovascular diseases based on commonly used non-viral vectors, hopefully providing guidance and orientation for future relevant research.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) leads to almost a third of all deaths worldwide, resulting from atherosclerotic plaque leading to hemadostenosis and blood flow restriction (Park et al., 2020; Tsao et al., 2022). Despite progress in medical technology, CVD is still a major cause of death (Yang et al., 2023). Conventional treatment strategies for CVD include anticoagulation, antiplatelet, thrombolytics, hypolipidemic drugs, and invasive therapies like vascular bypass grafting and stent transplantation (Zhu et al., 2021). However, small molecule drug therapy in conventional treatment strategies is characterized by short half-life and low bioavailability, and long-term use of certain drugs may also lead to side effects such as drug resistance and potential hematological toxicity (Missri, 1979; Fu et al., 2014). Surgical treatment, on the other hand, is more pro-traumatic, requires a longer recovery time, and has a high risk of postoperative complications.
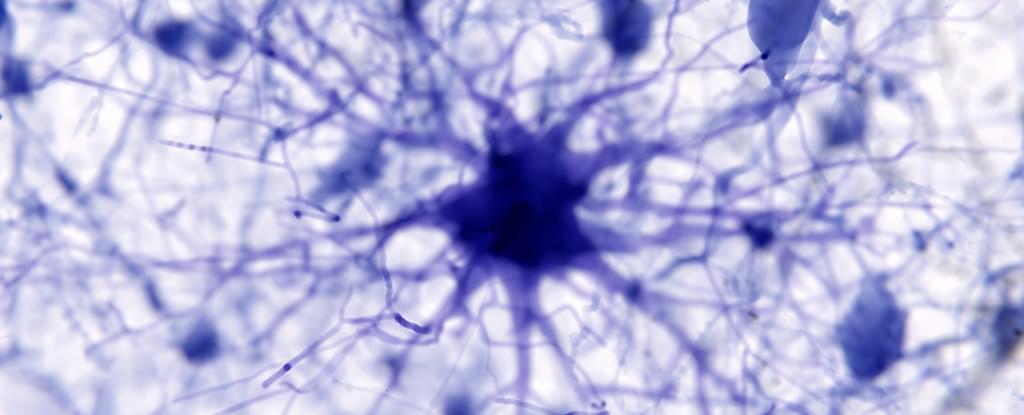
“To date, there was little understanding of how the estrous cycle affects neurons in living mice,” said Nora Wolcott, the paper’s lead author. Now, thanks to advanced microscopy techniques, Goard’s team was able to measure the structure and activity of neurons across multiple estrous cycles, thereby gaining insight into sex hormones’ role in brain plasticity and memory. Other authors on the paper include William Redman, Marie Karpinska, and Emily Jacobs.
Researchers observe how fluctuations in ovarian hormones shape the structure and function in the mouse hippocampus, with implications for neural plasticity in humans.
Discover Lockheed Martin’s vision for how a water-based lunar architecture will help us settle permanently and sustainably on the Moon.
Researchers in Singapore have achieved a breakthrough in rechargeable battery technology by solving one of the most persistent challenges in zinc-ion batteries, with the help of artificial intelligence.
Dendrites, tiny needle-like structures that form during charging and cause short circuits, have long posed an issue in zinc-ion (Zn-ion) battery technology by compromising battery safety and shortening their lifespan.