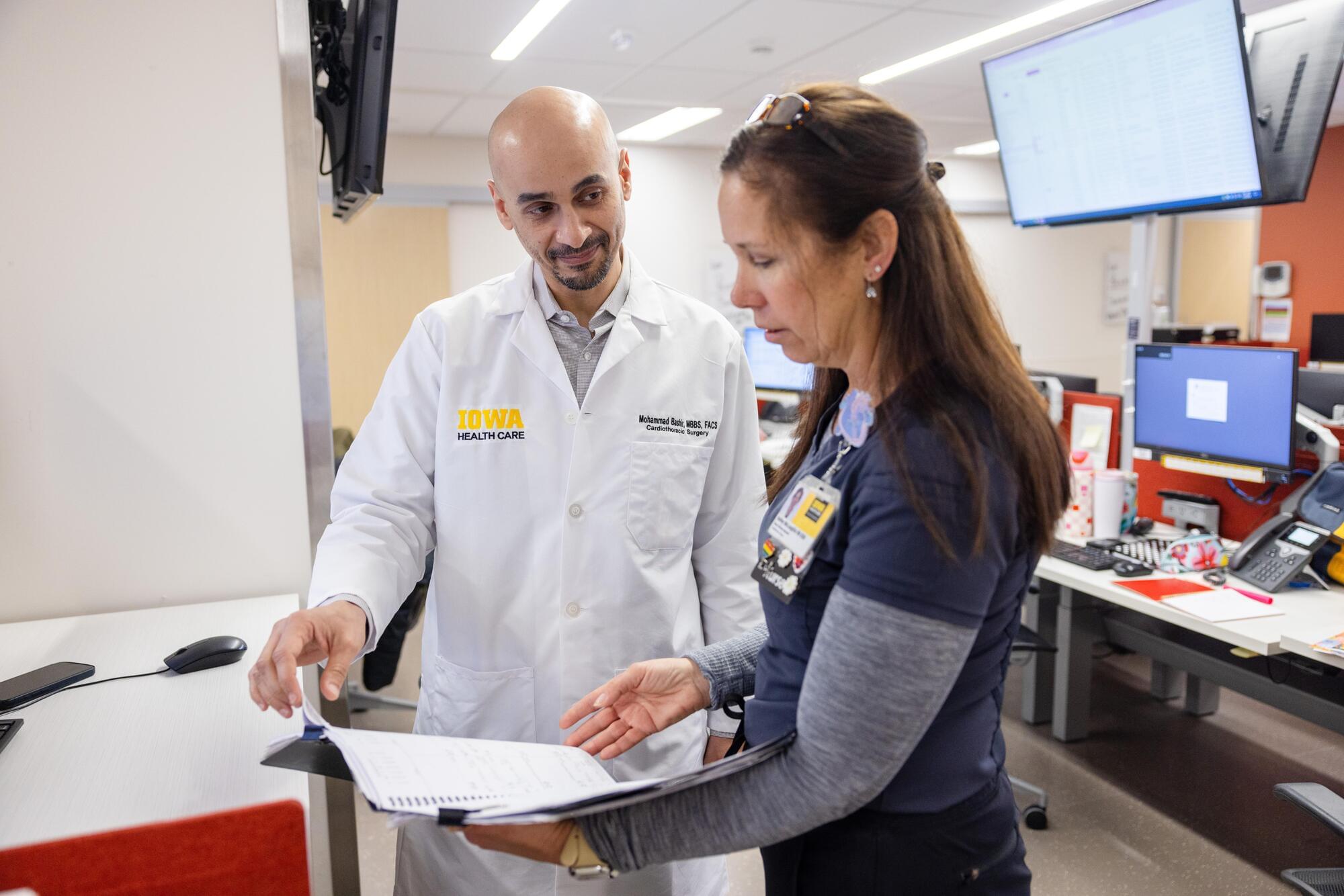
King George, Albert Einstein, John Ritter, Richard Holbrooke, George C Scott, Lucille Ball, Betty Garrett, Walter Huston, Humphrey Lyttleton, Marilyn Chambers, and Michael Rennie all died from the same thing, Aortic dissection however the FDA recently approved AMDS Hybrid Prosthesis is helping change that by greatly inproving survival and recovery rates. UI Health Care is the first in Iowa to implant a patient with the recently approved AMDS Hybrid Prosthesis.
Patients who experience a specific type of aortic tear now have a new treatment option available at UI Health Care. The AMDS Hybrid Prosthesis, the world’s first aortic arch remodeling device, was recently approved for DeBakey Type 1 aortic dissection patients.
DeBakey Type 1 aortic dissection is a tear in the inner layer of the wall of the aorta—the main artery that carries oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body. An aortic dissection causes blood to flow between the wall layers, which slows or stops normal blood flow and can lead to a complete rupture of the aorta. The condition is emergent, life-threatening, and requires immediate surgical repair.
The current treatment option involves removing a portion of the damaged aorta and grafting a synthetic tube in its place. These procedures are successful but often fail to treat the remainder of the diseased aorta, which can result in complications and the need for additional procedures in the future.