A college in the US has announced it will be closing its doors very soon following the impact of a cyberattack in December 2021.


Zack Mannheimer, the CEO of Alquist, predicts more US homes will be 3D printed than built “traditionally” within the next five years.
Imagine moving through airport security without having to take off your shoes or belt or getting pulled aside while your flight boards—while keeping all the precautions that ensure the safety of passengers and flight crews.

Imagine moving through airport security without having to take off your shoes or belt or getting pulled aside while your flight boards—while keeping all the precautions that ensure the safety of passengers and flight crews.
This is the challenge tackled by a team including researchers from Sandia National Laboratories—a challenge that led to development of the Open Threat Assessment Platform, which allows the Transportation Security Administration to respond more quickly and easily to threats to air travel safety.
“When we wanted to change how we screen in response to new threats,” said Andrew Cox, a Sandia R&D systems analyst who leads the OTAP project. “The technology was too rigid. TSA compensated by adding procedures. There’s a shoe bomber and you have to take your shoes off; liquid explosives arrived, and TSA had to limit liquids and gels.”

* Astrocytes play a variety of roles with neurons, but until now, scientists did not know that these cells carry electrical impulses.
* Applying new technology, Tufts University scientists recently discovered in mice that astrocytes are electrically active like neurons. Astrocytes play a variety of roles with neurons, but until now, scientists did not know that these cells carry electrical impulses.
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate the transfer of electrical signals between neurons and support the blood-brain barrier. Scientists have long understood that astrocytes control these substances to support neuronal health.
This study breaks ground in showing that neurons release potassium ions, which change the astrocytes’ electrical activity. This modulation affects how the astrocytes control neurotransmitters.
Until now, scientists could not image potassium activity in the brain.

Pharmaceutical intervention of aging requires targeting multiple pathways, thus there is rationale to test combinations of drugs targeting different but overlapping processes. In order to determine if combining drugs shown to extend lifespan and healthy aging in mice would have greater impact than any individual drug, a cocktail diet containing 14 ppm rapamycin, 1,000 ppm acarbose, and 1,000 ppm phenylbutyrate was fed to 20-month-old C57BL/6 and HET3 4-way cross mice of both sexes for three months. Mice treated with the cocktail showed a sex and strain-dependent phenotype consistent with healthy aging including decreased body fat, improved cognition, increased strength and endurance, and decreased age-related pathology compared to mice treated with individual drugs or control. The severity of age-related lesions in heart, lungs, liver, and kidney was consistently decreased in mice treated with the cocktail compared to mice treated with individual drugs or control, suggesting an interactive advantage of the three drugs. This study shows that a combination of three drugs, each previously shown to enhance lifespan and health span in mice, is able to delay aging phenotypes in middle-aged mice more effectively than any individual drug in the cocktail over a 3-month treatment period.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement.
A technological demonstration from China recently presented the power of super drones that track objects and people with high precision. The remote-powered vehicles, developed by scholars from Zhejiang University, were deployed into a thick bamboo forest to test their capabilities.
A video released by the researchers shows that the drones maneuvered effectively over the complex obstacles of the forest. The demonstration of the machines creeped out many audiences, as the precision and navigation of the drones exceeded far more than those of the technologies we see today.
Engineers from China developed what might be the most advanced drone swarm to date. Learn more about the autonomous machines and how they performed in tests.
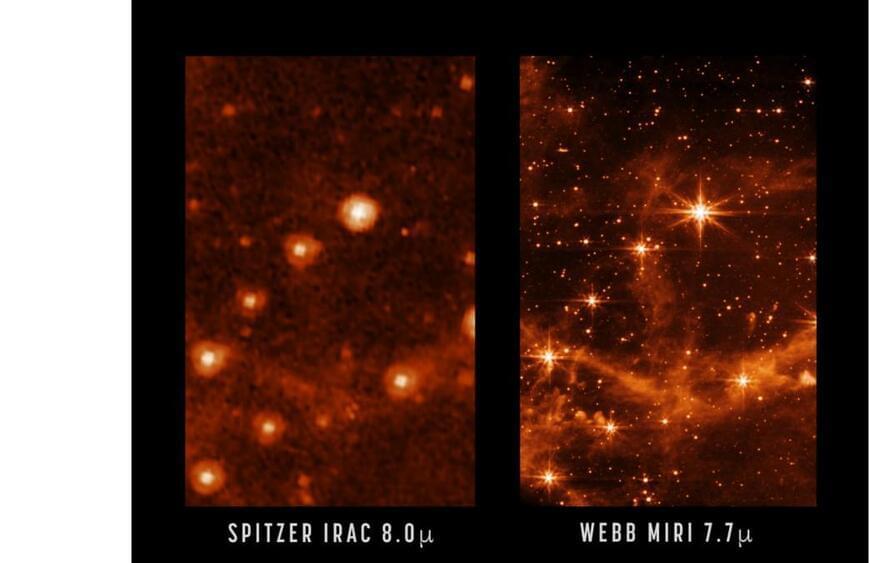

We’ve never seen a neighboring galaxy like this before.
The Large Magellanic Cloud is sharper than ever in the infrared eyes of the James Webb Space Telescope.
As the $10 billion observatory enters the “homestretch” of its commissioning work, according to officials, Webb’s latest image showed off the telescope’s literally stellar performance using its coldest instrument, the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI).
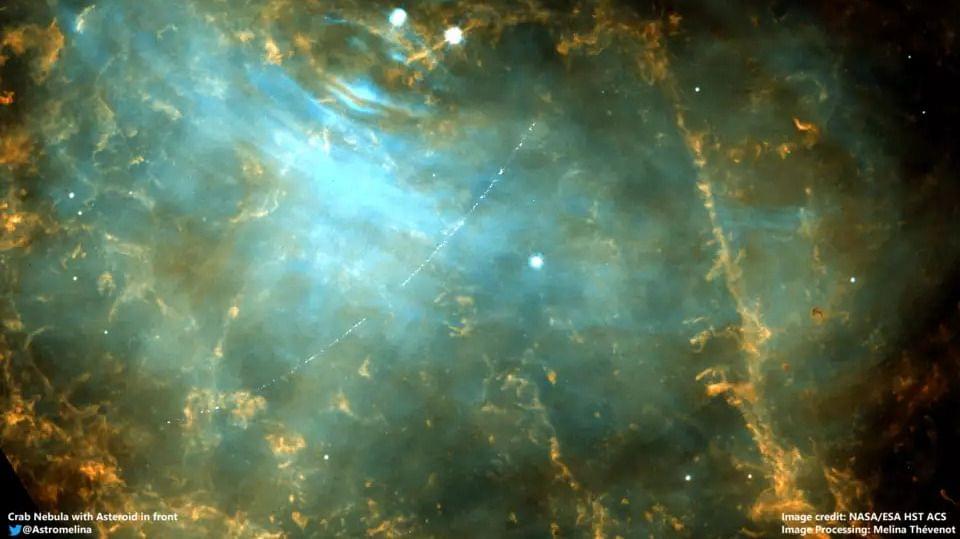

Astronomers have revealed the trails of nearly 1,500 new asteroids hidden in data gathered by NASA’s most venerable space telescope.
In a new study, astronomers and a team of amateur scientists have worked together to comb through archival data from the Hubble Space Telescope. The project began on International Asteroid Day in 2019, when a team of astronomers launched the “Hubble Asteroid Hunter” project on Zooniverse, a popular platform for crowdsourcing science. The project’s aim was to identify asteroids in old data from Hubble; signals that, in other studies, might have just been filtered out as noise.
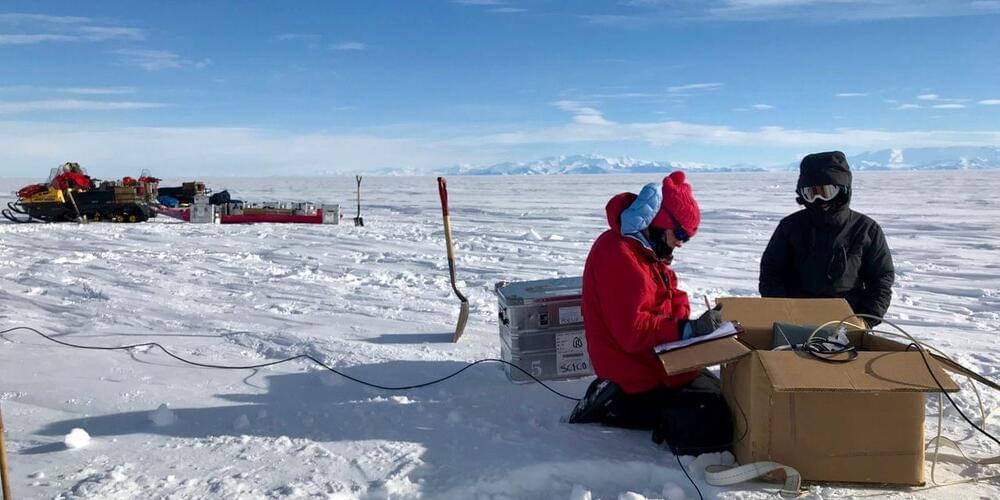

A vast reservoir of ancient water has been found thousands of feet under the ice in western Antarctica, scientists said in a paper published Thursday in the journal Science.
Researchers had long suspected but never before established the existence of such hidden pockets of Antarctic groundwater, which they believe act to lessen friction between ice sheets and underlying bedrock to make the ice more prone to slide from the continent’s interior toward the surrounding ocean.
