For science.



If in space, no one can hear you scream, then what happens when DNA silently breaks in microgravity? Spoiler alert: it heals itself.
This is what a CRISPR experiment that won the Genes in Space 6 contest — SYFY WIRE was at the recent launch of the Genes in Space 8 experiment to the ISS — found out. DNA damage or breakage can mean the potential for degenerative diseases such as cancer, but the fact that it can also self-repair (and in microgravity!) has enormous implications for medical treatments above and below Earth’s atmosphere.
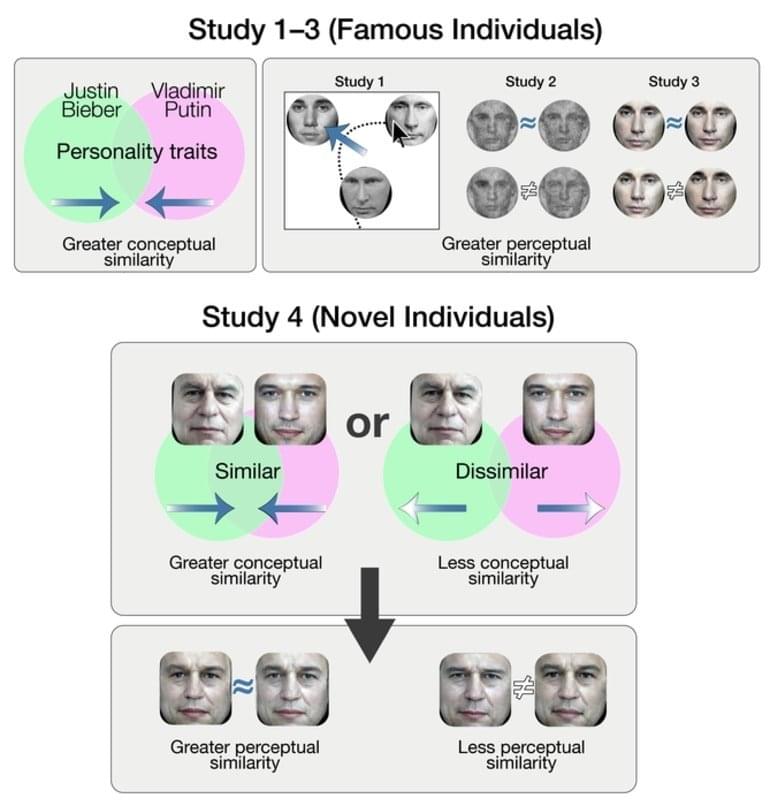
The authors add that the research informs fundamental scientific understanding of how face recognition works in the brain, suggesting that not only a face’s visual cues but also prior social knowledge plays an active role in perceiving faces.
Summary: Knowledge of an individual’s personality can influence the perception of a face’s identity and bias it toward unrelated people or identities, researchers report.
Source: NYU
Do Vladimir Putin and Justin Bieber look alike? They do if you think they have similar personalities, shows a new study by a team of psychologists.
Its findings, which appear in the journal Cognition, reveal that knowledge of a person’s personality can influence the perception of a face’s identity and bias it toward unrelated identities. For example, if Vladimir Putin and Justin Bieber, a pair of faces among many tested in the research, have more similar personalities in your mind, then they visually appear more similar to you as well, even if they lack any physical resemblance.
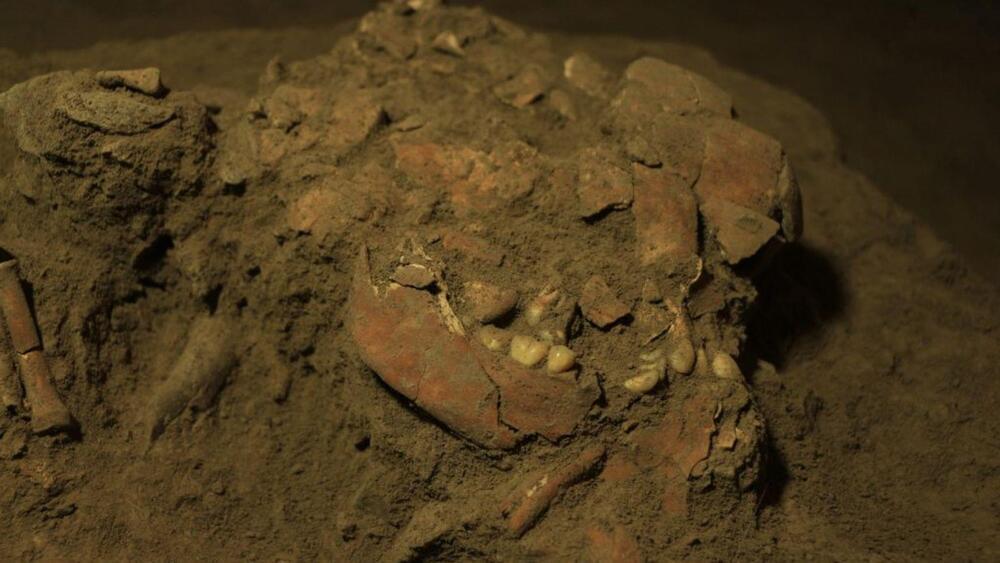


Archaeologists have analysed DNA found in the remains of a woman who died 7,200 years ago in Indonesia — challenging previous theories around the migration of early humans.
The remains of the teenager, nicknamed Besse, were discovered in the Leang Panninge cave on Sulawesi in 2015.
It is believed to be the first time ancient human DNA has been discovered in Wallacea, a group of islands between mainland Asia and Australia.


In a discovery published in the journal Nature, an international team of researchers has described a novel molecular device with exceptional computing prowess.
Reminiscent of the plasticity of connections in the human brain, the device can be reconfigured on the fly for different computational tasks by simply changing applied voltages. Furthermore, like nerve cells can store memories, the same device can also retain information for future retrieval and processing.
“The brain has the remarkable ability to change its wiring around by making and breaking connections between nerve cells. Achieving something comparable in a physical system has been extremely challenging,” said Dr. R. Stanley Williams, professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Texas A&M University. “We have now created a molecular device with dramatic reconfigurability, which is achieved not by changing physical connections like in the brain, but by reprogramming its logic.”
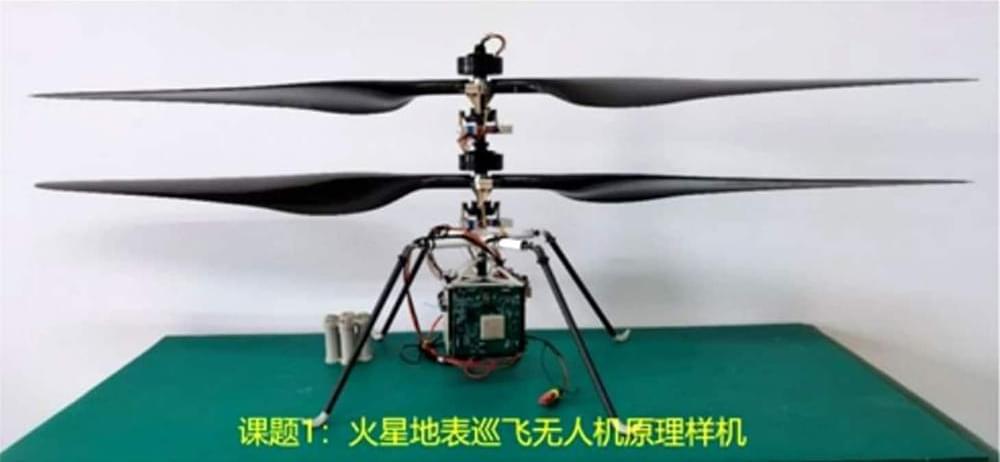

China has shown off the prototype of its “Mars cruise drone” designed for surveillance work on future Mars missions, following the historic landing of a robotic rover on the Red Planet a few months ago.
The prototype of the miniature helicopter successfully passed the final acceptance, China’s National Space Science Center (CNNSC) announced on Wednesday. In the images shared by the science center, the prototype looks similar in appearance to NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter, developed for its Perseverance mission this year.
The Chinese prototype sports two rotor blades, a sensor-and-camera base, and four thin legs, but there is no solar panel at the top like Ingenuity.

Two senior leaders in the US Food and Drug Administration’s vaccine review office are stepping down, even as the agency works toward high-profile decisions around Covid-19 vaccine approvals, authorizations for younger children and booster shots.
The retirements of Dr. Marion Gruber, director of the Office of Vaccines Research and Review at FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, and Dr. Philip Krause, deputy director of the office, were announced in an internal agency email sent on Tuesday and shared with CNN by the FDA.
In the email, CBER Director Dr. Peter Marks said Gruber will retire on October 31 and Krause is leaving in November. Marks thanked Gruber for her leadership throughout efforts to authorize and approve Covid-19 vaccines, and Krause for serving in a “key role in our interactions to address critical vaccine-related issues with our public health counterparts around the world.”
Brent Nally interviews Dr Katcher about E5 plasma filtering. “What’s the purpose of anything if you’re gonna die?” E5 human trials perhaps by the end of 2022. All treated rats so far are still alive. “The question is how many times can we do this?” So far with rats it’s 3 times. He has not given out the specific E5 formula. Right now there is another party attempting to repeat his rat experiments.
Harold earned his PhD in Biology, is Chief Science Officer of Yuvan Research and is one of the discoverers of the breast cancer gene (BRCA1). Harold describes in his book, The Illusion of Knowledge, his personal story and journey developing E5 which may be extremely promising for the field of rejuvenation/biological age reversal. Read this May2020paper.
Sign up for free: https://LongevityPlan.com https://Twitter.com/BrentNally https://Patreon.com/BrentNally https://Linkedin.com/in/BrentNally https://Instagram.com/Brent.Nally https://Facebook.com/Brent.Nally https://Reddit.com/user/BrentNally Discord Brent Nally#0616 TikTok @brentnally Telegram https://t.me/brentnally https://medium.com/@BrentNally https://BrentNally.tumblr.com Snapchat BrentNally.
- My mission is to solve the human aging problem ASAP.
- I NEED YOUR SUPPORT: