It doesn’t have to be all fun and games in the Metaverse, especially when its best use cases are the ones that need a different reality the most. Thanks to a few companies that have large marketing machines, the word “Metaverse” has become muddled in hype and controversy. While the current use of the coined word might be new to our ears, the technologies that empower it have been around for quite some time now. And they aren’t always used for games or entertainment, even if that is what everyone thinks these days. In fact, one of the most frequent early adopters of these technologies come from the medical field, which continuously tests new equipment, theories, and digital experiences to help improve lives. So while mainstream media, carmakers, and social networks continue to shine the light on new ways to experience different worlds, the Metaverse, its concepts, and its applications are already sneaking their way into medical and scientific institutions, ready to take healthcare to the next, augmented reality level.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
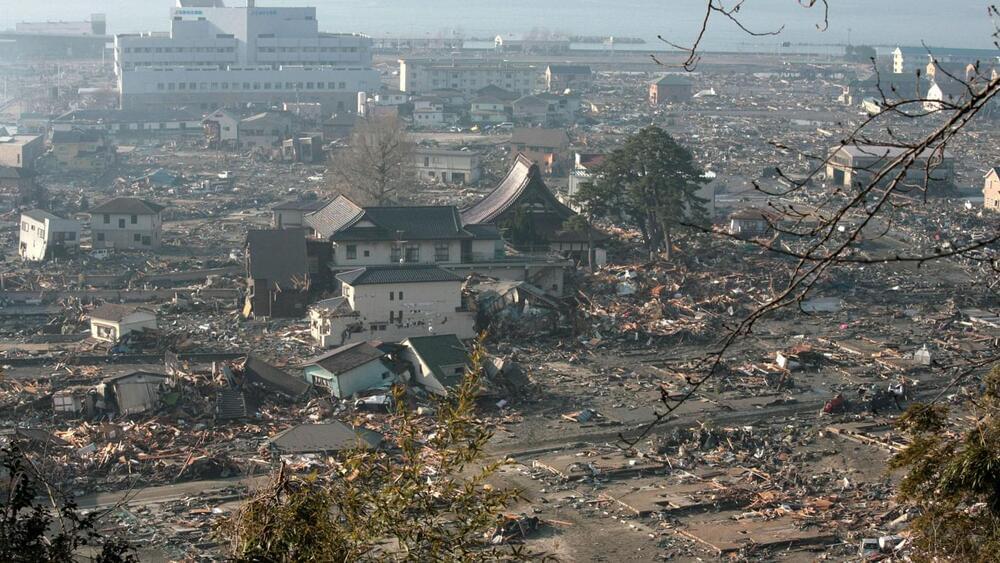

Machine learning and gravity signals could rapidly detect big earthquakes
Massive earthquakes don’t just move the ground — they make speed-of-light adjustments to Earth’s gravitational field. Now, researchers have trained computers to identify these tiny gravitational signals, demonstrating how the signals can be used to mark the location and size of a strong quake almost instantaneously.
It’s a first step to creating a very early warning system for the planet’s most powerful quakes, scientists report May 11 in Nature.
Such a system could help solve a thorny problem in seismology: how to quickly pin down the true magnitude of a massive quake immediately after it happens, says Andrea Licciardi, a geophysicist at the Université Côte d’Azur in Nice, France. Without that ability, it’s much harder to swiftly and effectively issue hazard warnings that could save lives.

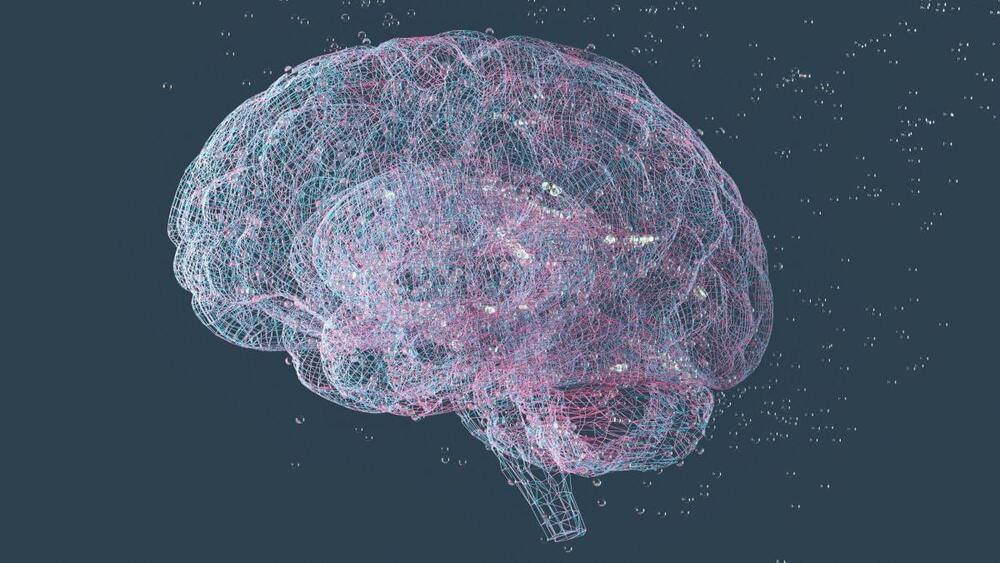
New astronauts have changes in their brains after their first long-duration mission
The findings could have implications for long-duration space missions.
The researchers found that the total PVS volume of novice astronauts increased after their trips to space. The PVS of experienced astronauts, by contrast, did not show this growth — in fact, their total PVS volume actually decreased. This may indicate that their brains “reached some kind of homeostasis,” Piantino said in a statement. In other words, their brains may have adjusted more to microgravity after previous spaceflight.
In fact, the researchers found that the total PVS volume of experienced astronauts before their current flight tended to be higher, and that this baseline volume correlated with previous amount of time spent in space. Though neither of these trends were statistically significant, meaning they could have happened by chance, they fit with previous research suggesting that changes in the brains of astronauts depend on the total time spent in space and the frequency of space missions.
Although PVS volume gradually increases as people age, the members of the Earth-based control group did not experience the kind of PVS changes that the novice astronauts showed. The PVS are part of the glymphatic system, which clears out waste from the brain, mostly during sleep. Other health conditions — such as dementia and hydrocephalus, or the buildup of too much fluid in the brain’s ventricles — can affect these spaces. The results of the new study may help to address the effects on these brain structures that result from health conditions on Earth.

Imperial students find innovative new use for lobster shell waste
The four students are studying Innovation Design Engineering, a course delivered jointly by Imperial College London and the Royal College of Art. They have built a series of machines that extract, form and recycle the material, which they believe could be used as a replacement for various single-use plastics.
The project uses chitin, the world’s second most abundant biopolymer, (a naturally produced plastic). Chitin is found in crustaceans, insects and fungi, but needs to be chemically extracted from the source before it can be turned into the material.
The group of students have developed new manufacturing processes to transform lobster shell waste into biodegradable, recyclable bioplastic.
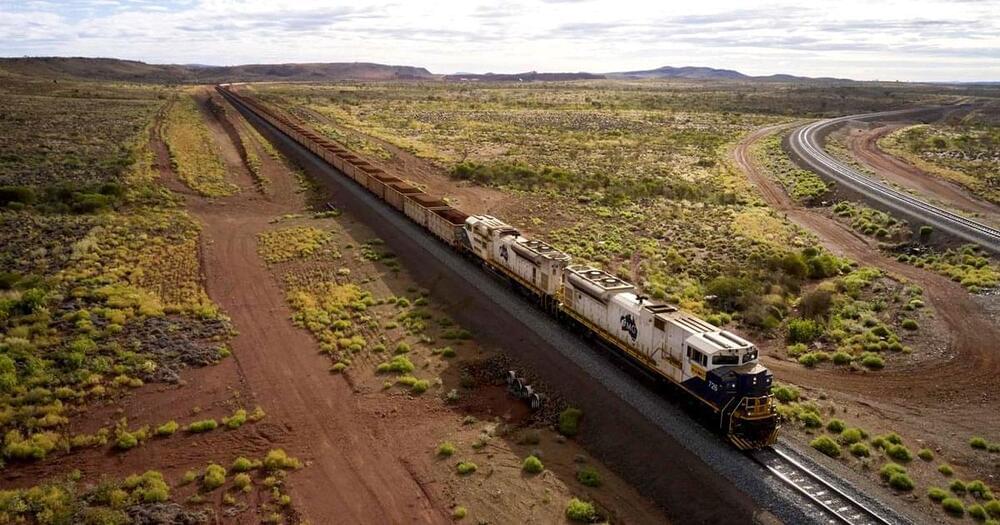

Ingenious Electric Train Fully Charges Itself
Australian mining company Fortescue is looking to reduce the carbon footprint of its operations by allowing a specially designed electric “Infinity Train” to roll down a hill to recharge its massive batteries — without ever relying on an external charging system.
“The Infinity Train has the capacity to be the world’s most efficient battery electric locomotive,” Fortescue CEO Elizabeth Gaines said in a statement. “The regeneration of electricity on the downhill loaded sections will remove the need for the installation of renewable energy generation and recharging infrastructure, making it a capital efficient solution for eliminating diesel and emissions from our rail operations.”
It’s a cleverly designed system: since the train is far lighter on the way up, it will generate enough energy fully loaded with iron ore on the way down to make it back up to the mine. In other words, it might sound like a perpetual motion machine — which is impossible, of course — but in reality it’s just an ingenious exploit of conventional physics.
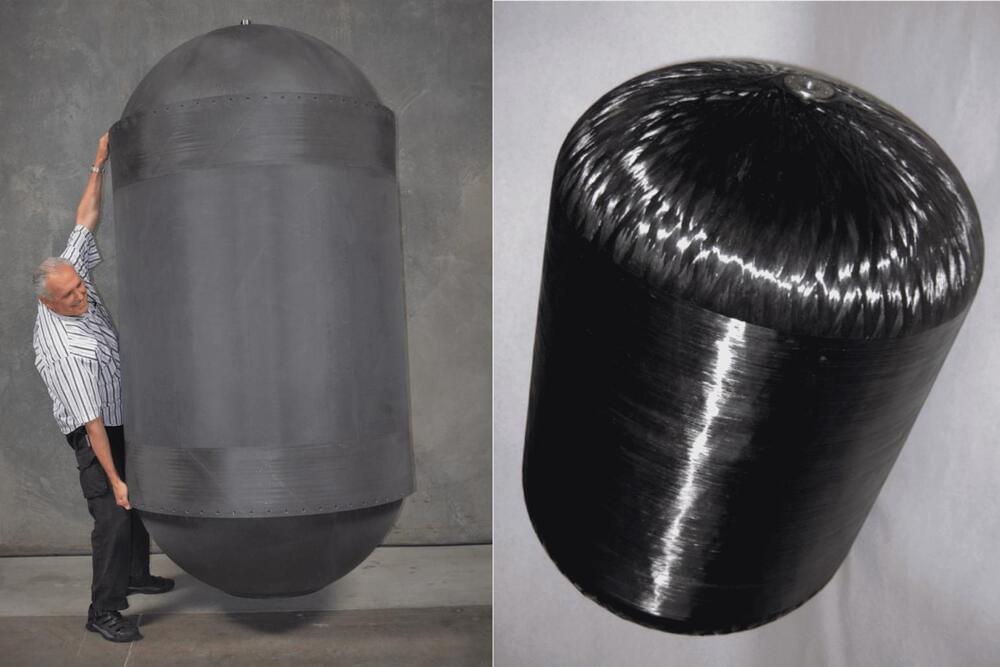


Ultra-light liquid hydrogen tanks promise to make jet fuel obsolete
A revolutionary cryogenic tank design promises to radically boost the range of hydrogen-powered aircraft – to the point where clean, fuel-cell airliners could fly up to four times farther than comparable planes running on today’s dirty jet fuel.
Weight is the enemy of all things aerospace – indeed, hydrogen’s superior energy storage per weight is what makes it such an attractive alternative to lithium batteries in the aviation world. We’ve written before about HyPoint’s turbo air-cooled fuel cell technology, but its key differentiator in the aviation market is its enormous power density compared with traditional fuel cells. For its high power output, it’s extremely lightweight.
Now, it seems HyPoint has found a similarly-minded partner that’s making similar claims on the fuel storage side. Tennessee company Gloyer-Taylor Laboratories (GTL) has been working for many years now on developing ultra-lightweight cryogenic tanks made from graphite fiber composites, among other materials.
Google’s New AI Creates Summaries of Your Documents in Google Docs
Google recently announced a new model for automatically generating summaries using machine learning, released in Google Docs that you can already use.
The model will try to understand the whole document and generate a short summary of the piece—something some movie professionals clearly still can’t do.
The model needs to achieve two things to achieve that, which you will learn in the video below!
