This is the first time a Tatre neutron has been observed.


In 2009, a computer scientist then at Princeton University named Fei-Fei Li invented a data set that would change the history of artificial intelligence. Known as ImageNet, the data set included millions of labeled images that could train sophisticated machine-learning models to recognize something in a picture. The machines surpassed human recognition abilities in 2015. Soon after, Li began looking for what she called another of the “North Stars” that would give AI a different push toward true intelligence.
She found inspiration by looking back in time over 530 million years to the Cambrian explosion, when numerous land-dwelling animal species appeared for the first time. An influential theory posits that the burst of new species was driven in part by the emergence of eyes that could see the world around them for the first time. Li realized that vision in animals never occurs by itself but instead is “deeply embedded in a holistic body that needs to move, navigate, survive, manipulate and change in the rapidly changing environment,” she said. “That’s why it was very natural for me to pivot towards a more active vision [for AI].”
Today, Li’s work focuses on AI agents that don’t simply accept static images from a data set but can move around and interact with their environments in simulations of three-dimensional virtual worlds.

One of the godfathers of deep learning pulls together old ideas to sketch out a fresh path for AI, but raises as many questions as he answers.
Now, after months figuring out what was missing, he has a bold new vision for the next generation of AI. In a draft document shared with MIT Technology Review, LeCun sketches out an approach that he thinks will one day give machines the common sense they need to navigate the world. For LeCun, the proposals could be the first steps on a path to building machines with the ability to reason and plan like humans—what many call artificial general intelligence, or AGI. He also steps away from today’s hottest trends in machine learning, resurrecting some old ideas that have gone out of fashion.
But his vision is far from comprehensive; indeed, it may raise more questions than it answers. The biggest question mark, as LeCun points out himself, is that he does not know how to build what he describes.
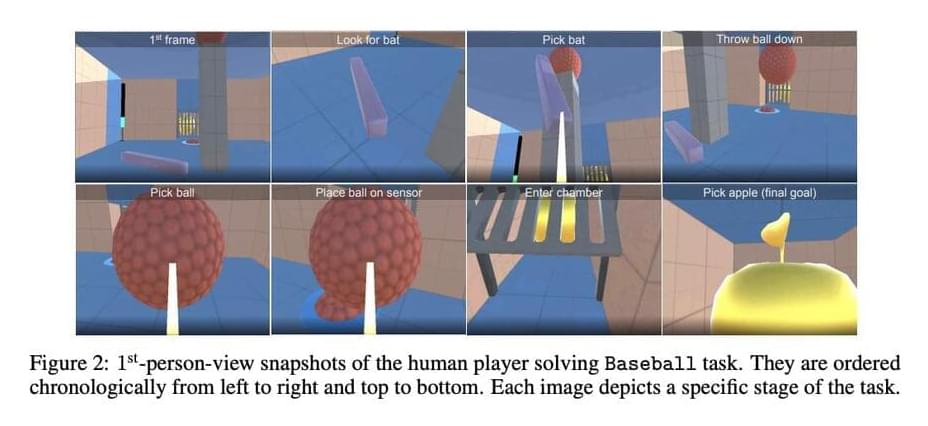
DeepMind Researchers Develop ‘BYOL-Explore’, A Curiosity-Driven Exploration Algorithm That Harnesses The Power Of Self-Supervised Learning To Solve Sparse-Reward Partially-Observable Tasks
Reinforcement learning (RL) requires exploration of the environment. Exploration is even more critical when extrinsic incentives are few or difficult to obtain. Due to the massive size of the environment, it is impractical to visit every location in rich settings due to the range of helpful exploration paths. Consequently, the question is: how can an agent decide which areas of the environment are worth exploring? Curiosity-driven exploration is a viable approach to tackle this problem. It entails learning a world model, a predictive model of specific knowledge about the world, and (ii) exploiting disparities between the world model’s predictions and experience to create intrinsic rewards.
An RL agent that maximizes these intrinsic incentives steers itself toward situations where the world model is unreliable or unsatisfactory, creating new paths for the world model. In other words, the quality of the exploration policy is influenced by the characteristics of the world model, which in turn helps the world model by collecting new data. Therefore, it might be crucial to approach learning the world model and learning the exploratory policy as one cohesive problem to be solved rather than two separate tasks. Deepmind researchers keeping this in mind, introduced a curiosity-driven exploration algorithm BYOL-Explore. Its attraction stems from its conceptual simplicity, generality, and excellent performance.
The strategy is based on Bootstrap Your Own Latent (BYOL), a self-supervised latent-predictive method that forecasts an earlier version of its latent representation. In order to handle the problems of creating the representation of the world model and the curiosity-driven policy, BYOL-Explore learns a world model with a self-supervised prediction loss and trains a curiosity-driven policy using the same loss. Computer vision, learning about graph representations, and RL representation learning have all successfully used this bootstrapping approach. In contrast, BYOL-Explore goes one step further and not only learns a flexible world model but also exploits the world model’s loss to motivate exploration.

Alex Hern reports on recent developments in artificial intelligence and how a Google employee became convinced an AI chatbot was sentient.
How to listen to podcasts: everything you need to know
Google software engineer Blake Lemoine was put on leave by his employer after claiming that the company had produced a sentient artificial intelligence and posting its thoughts online. Google said it suspended him for breaching confidentiality policies.
Lauded for its compelling action sequences and exhilarating portrayal of next-gen aerial dogfighting, Top Gun: Maverick has quickly become a monumental success at the box office. But the producers couldn’t have done it without leveraging the expertise of some of the world’s foremost experts in all things aerospace, and that includes tapping into the minds of Lockheed Martin Skunk Works engineers to craft their physics-bending Darkstar hypersonic jet.
Without wanting to give away any of the plot’s specifics, the Darkstar aircraft features early in the film as Pete “Maverick” Mitchell (played by Tom Cruise) carries out his duties as a test pilot for the US Navy. The futuristic fighter jet is a jaw-dropping introduction to the hyperreal aesthetics of the film, but may also strike a familiar chord with aviation enthusiasts due to a likeness to one of history’s most revered aerial vehicles, the SR-71 Blackbird.
When looking for some expert assistance in creating the Darkstar aircraft, the film’s producers were pointed in the direction of Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works division, responsible for the SR-71, its forthcoming successor the SR-72 and the U-2 spy plane. This collaboration created a new outlet for expression for Skunk Works clandestine conceptual designers, in the sense that this particular aircraft design was one they could share with the world – as conceptual designer “Jim” explains in this video.
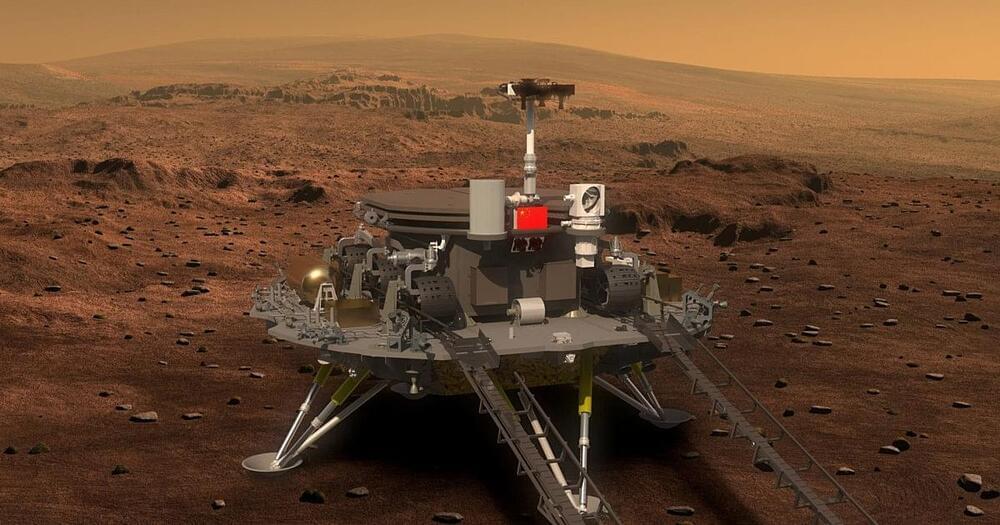

China’s first Mars mission will search for pockets of water beneath the surface that could host life.
As China’s first Mars mission, is uniquely ambitious. No nation had ever attempted to send an orbiter and rover to Mars on the first try. But China succeeded, making a historic victory.
Tianwen-1 arrived in Mars orbit as a single spacecraft. Once on Mars, the landing platform extended a ramp, allowing the Zhurong rover to roll gently onto the surface—similar to the way China’s Chang’e Moon rovers are deployed.
When did the Zhurong rover land on Mars?
Zhurong successfully landed on the Red Planet on May 14. The rover touched down on Utopia Planitia—the vast Martian plain where NASA’s Viking 2 spacecraft landed in the 1970s, and the site of a shipbuilding yard in the Star Trek universe.

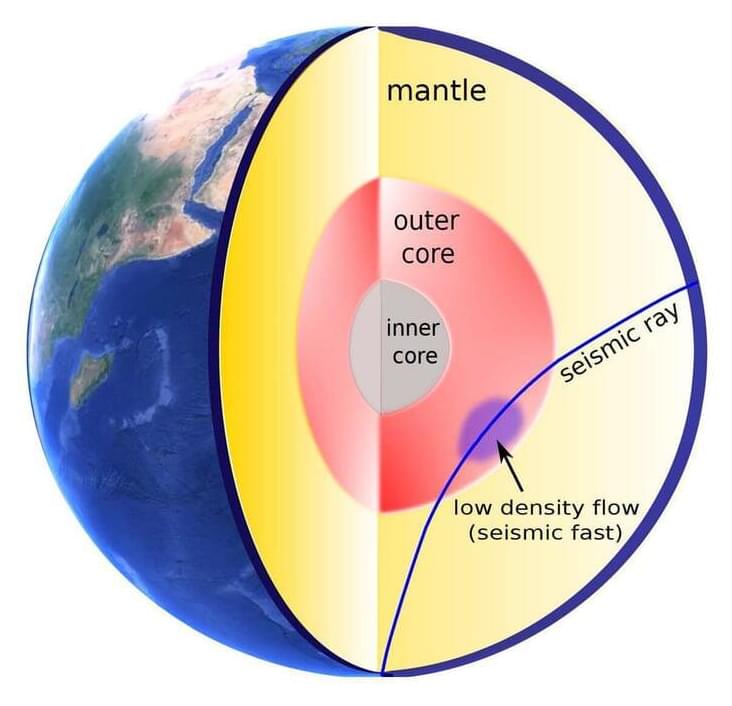
In May 1997, a large earthquake shook the Kermadec Islands region in the South Pacific Ocean. A little over 20 years later, in September 2018, a second big earthquake hit the same location, its waves of seismic energy emanating from the same region.
Though the earthquakes occurred two decades apart, because they occurred in the same region, they’d be expected to send seismic waves through the Earth’s layers at the same speed, said Ying Zhou, a geoscientist with the Department of Geosciences in the Virginia Tech College of Science.
But in data recorded at four of more than 150 Global Seismographic Network stations that log seismic vibrations in real time, Zhou found an anomaly among the twin events: During the 2018 earthquake, a set of seismic waves known as SKS waves traveled about one second faster than their counterparts had in 1997.
