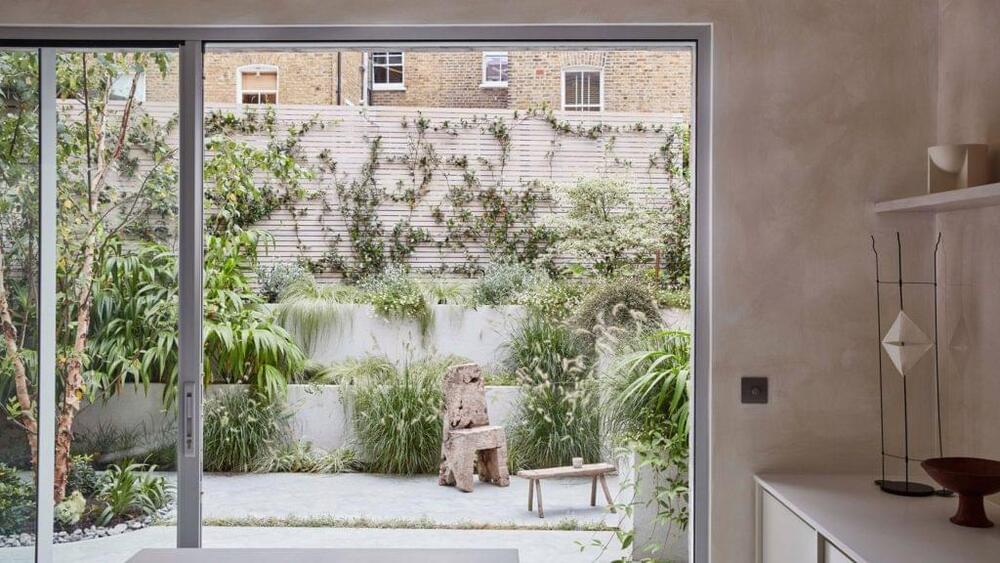
Design studio Daytrip has taken a less-is-more approach to the renovation and extension of this Victorian terrace house in London’s Clapton, which is now home to three separate apartments.
The 250-square-metre Reighton Road development was designed as a “minimalist sanctuary” that could act as a blank canvas for residents’ belongings.
“A good home should be flexible and speak of its owners,” explained Hackney-based Daytrip. “The ability to cultivate and populate it over time with art, objects and personal items makes the home unique.”