Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.



Customer retention challenges? This company can help with ‘multidimensional’ data listening
California-based StepFunction, which helps enterprises improve customer retention rate, has raised $5 million.
Were you unable to attend Transform 2022? Check out all of the summit sessions in our on-demand library now! Watch here.
Modern-day software-as-a-service (SaaS) enterprises are racing to acquire new users and convert them into paying customers. The rush is great for the industry, but it has also left many organizations looking at only half of the picture.
Case in point: The extensive focus on gaining new paying customers but not so much on post-sale constructs — including customer success, customer care and professional services — could not only improve customer retention but also help grow the business at the same time.
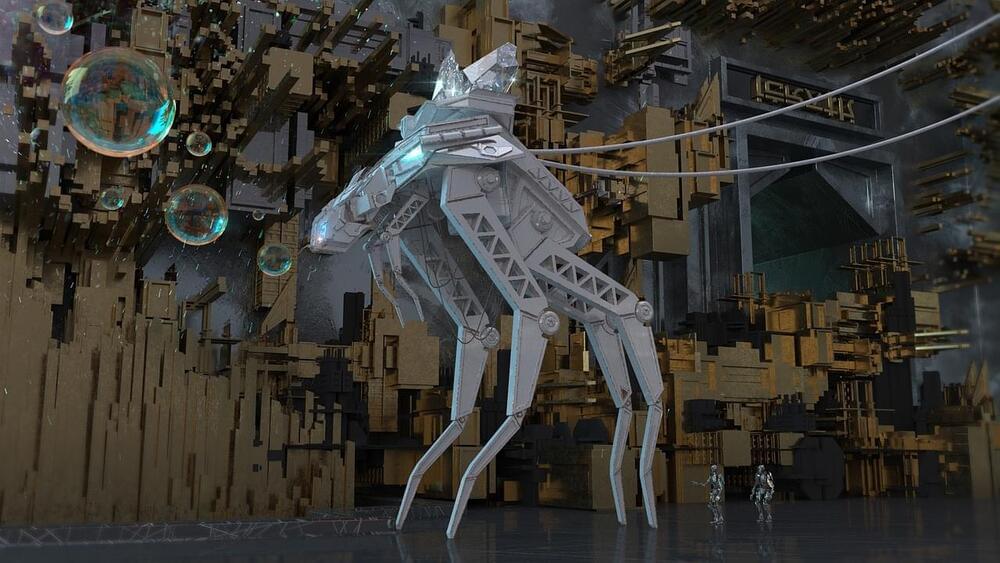
Meet China’s Cyber Dog — The Future Of Robotics
This post is also available in:  עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
China has developed the world’s largest electric-powered quadruped bionic robot, which is expected to join logistics delivery and reconnaissance missions in complex environments that have proven too challenging for human soldiers, including remote border regions and highly risky combat zones, analysts said.
In December, China announced that it would work to become a leading global player in robotics by 2025 under a five-year plan.
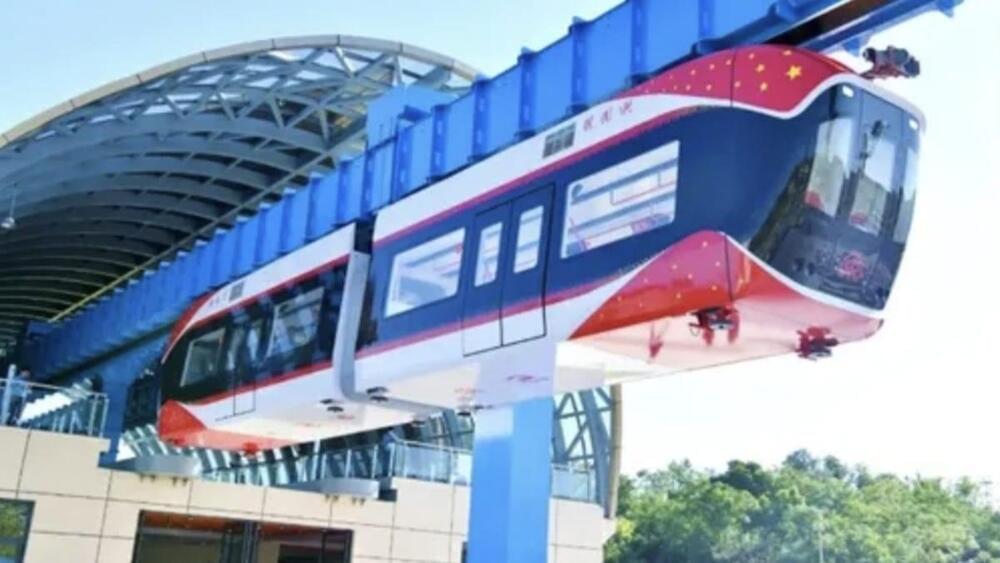

China’s new “sky train” floats under an elevated track, using magnets and AI
The 2,600-foot-long experimental rail is located in Southern China. A typical maglev train glides above its track, supported by magnetic repulsion and propelled by a linear motor. This one, however, moves underneath its track at a speed of 50 mph. It operates about 32 feet above the ground and makes no physical contact with the rail.
SEE: São Paulo subway ordered to suspend use of facial recognition
After some test runs, local authorities said the line could even increase to 4.7 miles and its top operational speed can reach 75 mph.
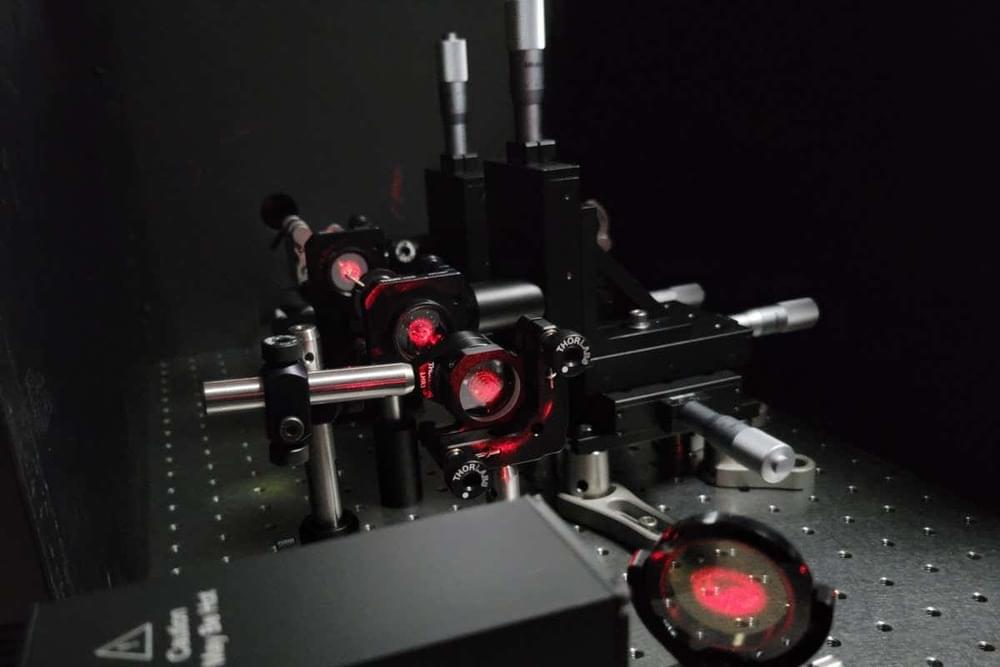
Anti-laser can make any object suck in light
Inserting any material into a special maze of mirrors and lenses can make it absorb light perfectly. This approach could be used to detect faint starlight or for charging faraway devices with lasers.
Ori Katz at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem in Israel and his colleagues created an almost perfect absorber of light by building an “anti-laser”.
In a laser, light bounces between mirrors until it becomes amplified enough to exit the device in a concentrated beam. In an “anti-laser”, says co-author Stefan Rotter at Vienna University of Technology in Austria, light enters the device then gets stuck in an inescapable series of bounces within it.
