Each potential flight will last more than a month.
With that out of the way, Artemis I should be able to fly in late August or early September.
Each potential flight will last more than a month.
With that out of the way, Artemis I should be able to fly in late August or early September.

The automotive industry has a ‘million-mile’ dream for electric vehicles, but it’s a boring one. They want to build a battery capable of being recharged over and over as many times as it takes to reach a million miles without losing its ability to retain a charge. Yawn.
We’re more interested in the cutting-edge quantum physics version of a million-mile battery: one that can last a million miles between charges.
This would effectively eliminate the need for the bulk of vehicle operators to ever charge their batteries. Even heavy-use owners could just pop into the shop for routine maintenance every couple of years to top their batteries off.

Circa 2016
Take advantage of the next clear night and drop in on a quasar that’s currently undergoing its brightest outburst in more than 40 years.

Circa 2019
Yuri Oganessian relates the story of the formation and decay of a doubly odd moscovium nucleus.
Element 115 was the first superheavy element with an odd atomic number (Z) that we synthesized in nuclear reactions using a beam of accelerated 48 Ca ions. These experiments were carried out in 2003, on the heels of the first results obtained for even elements 114 and 116. We had no doubts that their odd neighbour could also be produced in a similar manner; its decay properties however would be very different.
Circa 2021
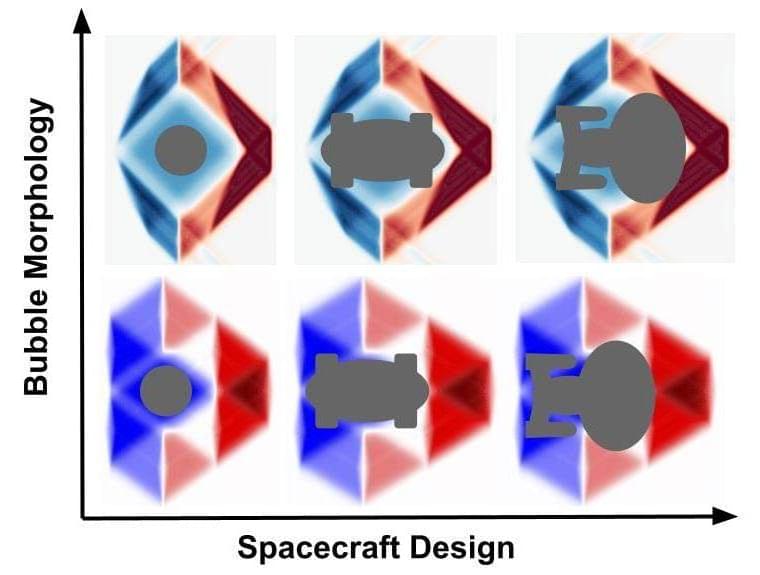
Astrophysicist at Göttingen University discovers new theoretical hyper-fast soliton solutions.
If travel to distant stars within an individual’s lifetime is going to be possible, a means of faster-than-light propulsion will have to be found. To date, even recent research about superluminal (faster-than-light) transport based on Einstein’s theory of general relativity would require vast amounts of hypothetical particles and states of matter that have “exotic” physical properties such as negative energy density. This type of matter either cannot currently be found or cannot be manufactured in viable quantities. In contrast, new research carried out at the University of Göttingen gets around this problem by constructing a new class of hyper-fast ‘solitons’ using sources with only positive energies that can enable travel at any speed. This reignites debate about the possibility of faster-than-light travel based on conventional physics. The research is published in the journal Classical and Quantum Gravity.
The author of the paper, Dr. Erik Lentz, analyzed existing research and discovered gaps in previous ‘warp drive’ studies. Lentz noticed that there existed yet-to-be explored configurations of space-time curvature organized into ‘solitons’ that have the potential to solve the puzzle while being physically viable. A soliton – in this context also informally referred to as a ‘warp bubble’ – is a compact wave that maintains its shape and moves at constant velocity. Lentz derived the Einstein equations for unexplored soliton configurations (where the space-time metric’s shift vector components obey a hyperbolic relation), finding that the altered space-time geometries could be formed in a way that worked even with conventional energy sources. In essence, the new method uses the very structure of space and time arranged in a soliton to provide a solution to faster-than-light travel, which – unlike other research – would only need sources with positive energy densities.
Else Labs, the company behind the countertop home cooking robot called Oliver, announced today the launch of Oliver Fleet, a commercial kitchen reimagining of its original core product.
The new Fleet solution is a respin of its original standalone Oliver home cooking robot into a solution that allows multiple units to be used and managed simultaneously in professional kitchen environments to automate cooking tasks. According to company CEO Khalid Aboujassoum, while the Oliver Fleet units look the same from the outside as the original consumer unit, they’ve been built to withstand the more rugged requirements of the professional kitchen.
“It might look like the household unit from the outside, but the guts of the Oliver Fleet are different,” Aboujassoum said. “The Fleet units are designed for back-to-back cooking, for that harsh environment in the commercial kitchen compared to the household.”

LONDON (AP) — The chief of the World Health Organization said the expanding monkeypox outbreak in more than 70 countries is an “extraordinary” situation that now qualifies as a global emergency, a declaration Saturday that could spur further investment in treating the once-rare disease and worsen the scramble for scarce vaccines.
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus made the decision to issue the declaration despite a lack of consensus among experts serving on the U.N. health agency’s emergency committee. It was the first time the chief of the U.N. health agency has taken such an action.
“We have an outbreak that has spread around the world rapidly through new modes of transmission about which we understand too little and which meets the criteria in the international health regulations,” Tedros said.