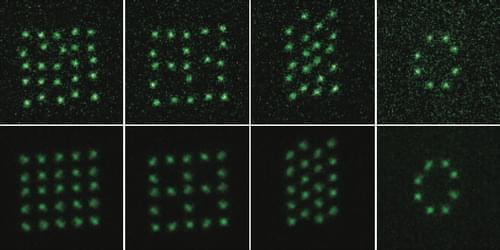
An optical tweezer array is a staple tool for trapping and controlling the positions of atoms in quantum research applications. Interfering, counterpropagating lasers can perform a similar function by creating “optical lattices.” The former tool suffers from having a potential that varies from site to site, limiting the ability of the atoms to move around. The latter tool creates uniform potentials but restricts the shape to some predefined geometry. Now Zoe Yan of Princeton University and her colleagues show that they can create arbitrarily shaped, reconfigurable 2D atom lattices with uniform potentials [1]. Such traps are desirable for simulating quantum spin interactions in electronic models and exploring the behaviors of atoms in systems with complex topologies.
Yan and her colleagues create their atom arrays by sequentially adding lines of atoms until the lattice is complete. They load up to 50 cold lithium atoms into an optical tweezer. They then generate the first line of their array using a vibrating transducer, which can break up and deflect a single laser beam such that it turns into a line of light spots. Subsequent lines of the array are made with another transducer, programmed to flash on and off like a strobe light, with each line illuminated for a fraction of the strobe cycle. The result is a time-averaged 2D trap potential, where each site is independently controlled, overcoming the nonuniformity problem that previous experiments with optical tweezer arrays experienced.
Using their technique, the team has created rectangular, triangular, and octagonal-ring-shaped arrays of atoms, which they say could be used to explore the behaviors of exotic states of matter, such as chiral spin liquids.