For about two hours, a bubble of extremely hot electrons whirled around the Milky Way’s supermassive black hole at 30 per cent of the speed of light, and then it was destroyed.
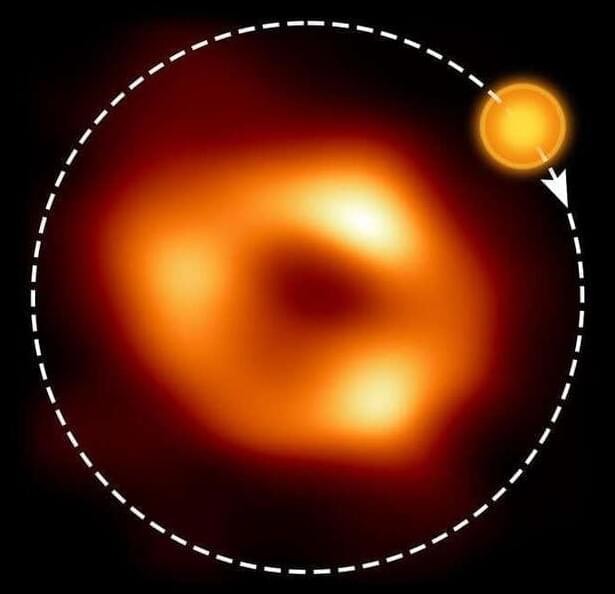

This bubble takes just about an hour to whip around a black hole.
This bubble that circles the event horizon of Sgr A takes just 70 minutes to whip around the black hole. It was observed by the Event Horizon Telescope.
That was Aubrey de Grey, this is Aubrey de White. New foundation, new therapy tests.
Co-founder of the SENS Foundation, Dr Aubrey de Grey is the co-organiser of this week’s Longevity Summit Dublin 2022; he was keynote speaker at this week’s summit, speaking on Robust Mouse Rejuvenation: real soon now? and featuring on the panel discussion Blank Cheque, which also enjoyed contributions from our own Phil Newman, Michael West, Tom Weldon, Greg Grinberg and Evelyne Bischof.
But most excitingly, Dr de Grey used the platform of Longevity Summit Dublin to launch his new foundation; its Board of Directors already boasts Greg Grinberg as Executive Chair, Daria Khaltourina, Martin O’Dea (also Events Director), Gennady Stolyarov and David Wood.
Dr de Grey has always been a passionate advocate of longevity research and biotechnology, so it’s no surprise his energy and enthusiasm has driven him to create a new foundation.
Visit Longevity. Technology — https://bit.ly/3PwtH8Y
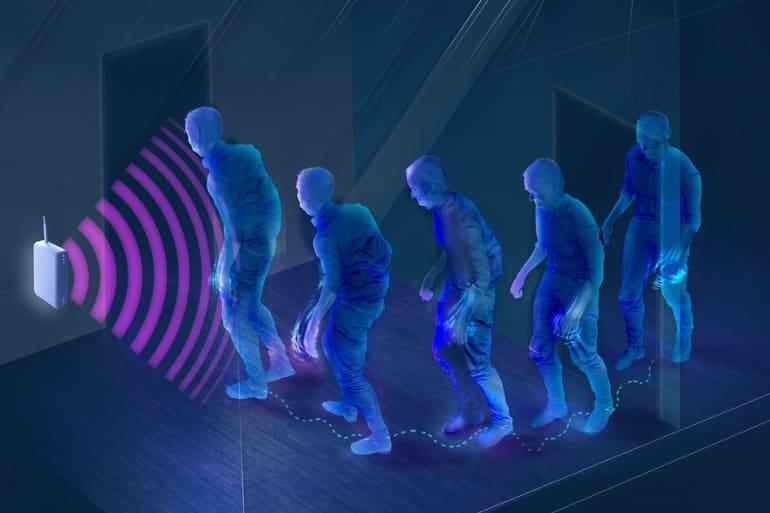



Summary: A new in-home device that monitors movement and gait speed can evaluate Parkinson’s disease severity, progression, and a patient’s response to medication.
Source: MIT
Parkinson’s disease is the fastest-growing neurological disease, now affecting more than 10 million people worldwide, yet clinicians still face huge challenges in tracking its severity and progression.
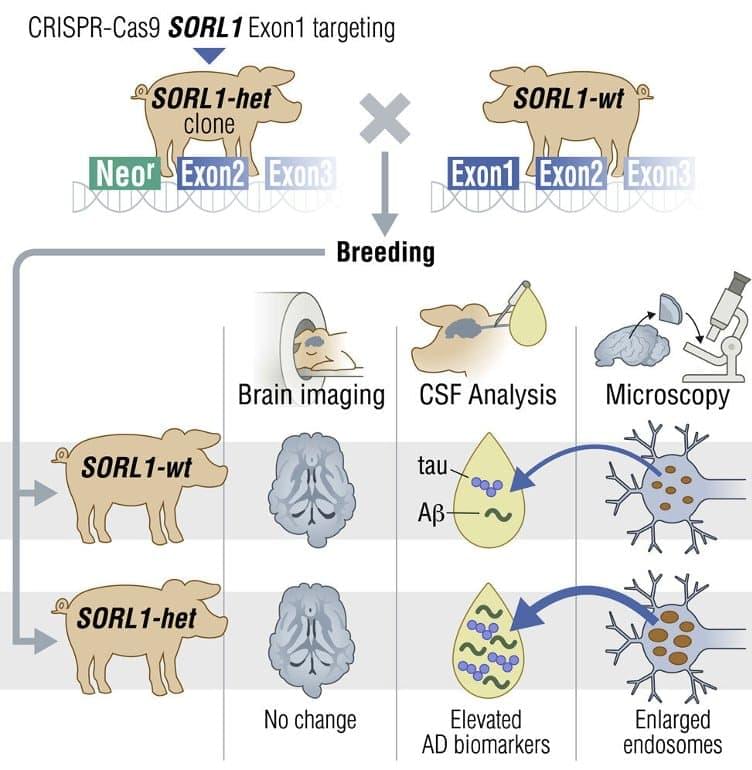
Summary: New research in cloned pigs with a mutation of the SORL1 sheds light on Alzheimer’s development. The findings could pave the way for new treatments for the neurodegenerative disorder.
Source: Aarhus University.
For decades, researchers from all over the world have been working hard to understand Alzheimer’s disease. Now, a collaboration between the Department of Biomedicine and the Department of Clinical Medicine at Aarhus University has resulted in a flock of minipigs that could lead to a major step forward in the research and treatment of Alzheimer’s.

Using artificial intelligence and editing software, photographer Alper Yesiltas has resurrected stars who died when they were young.
The Turkey-based photographer, who created the portraits for a project titled ‘As If Nothing Happened,’ said ‘’With the development of AI technology, I’ve been excited for a while, thinking that anything imaginable can be shown in reality.’’
Sharing the haunting and realistic images on his Instagram handle, Yesiltas said ‘’When I started tinkering with technology, I saw what I could do and thought about what would make me the happiest. I wanted to see some of the people I missed again in front of me and that’s how this project emerged.’‘.

Summary: The Allen Institute is launching a new global collaboration to map approximately 200 billion cells in the human brain by type and function.
Source: Allen Institute.
Scientists at the Allen Institute are launching the brain equivalent of the Human Genome Project, leading a new global collaboration to map the approximately 200 billion cells in the human brain by their type and function.
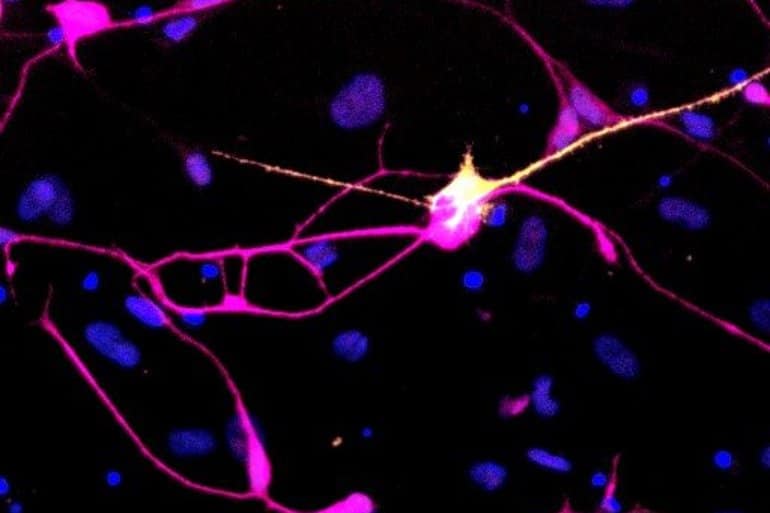
Summary: Researchers successfully turned skin cells from Parkinson’s patients into dopaminergic neurons by introducing a combination of neural-inducing genes into the skin cells.
Source: international society for stem cell research.
The possibility to make virtually all cell types of the human body from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which are embryonic-like cells generated from a patient’s skin, in a process called reprogramming, has opened new avenues for disease modeling in the lab.