Powered by Linux, this will be an open-source initiative.
PressureUA/iStock.
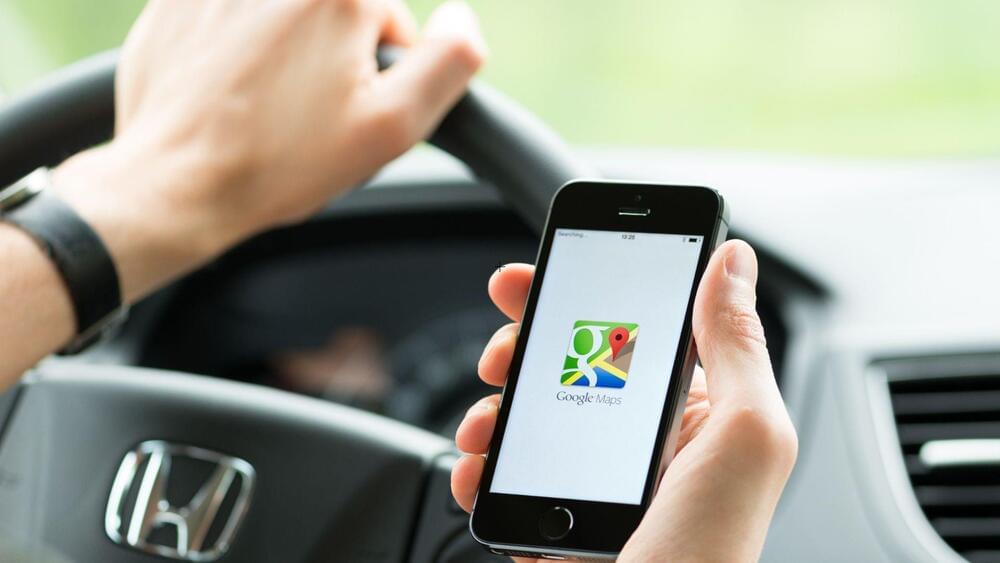
Other tech companies, such as Microsoft as well as Apple, have attempted to break this dominance but have fallen exceedingly short of user expectations. Even though Google Maps are not 100 percent accurate, it is the best available product out there, and now major technology companies want to take on the beast together.