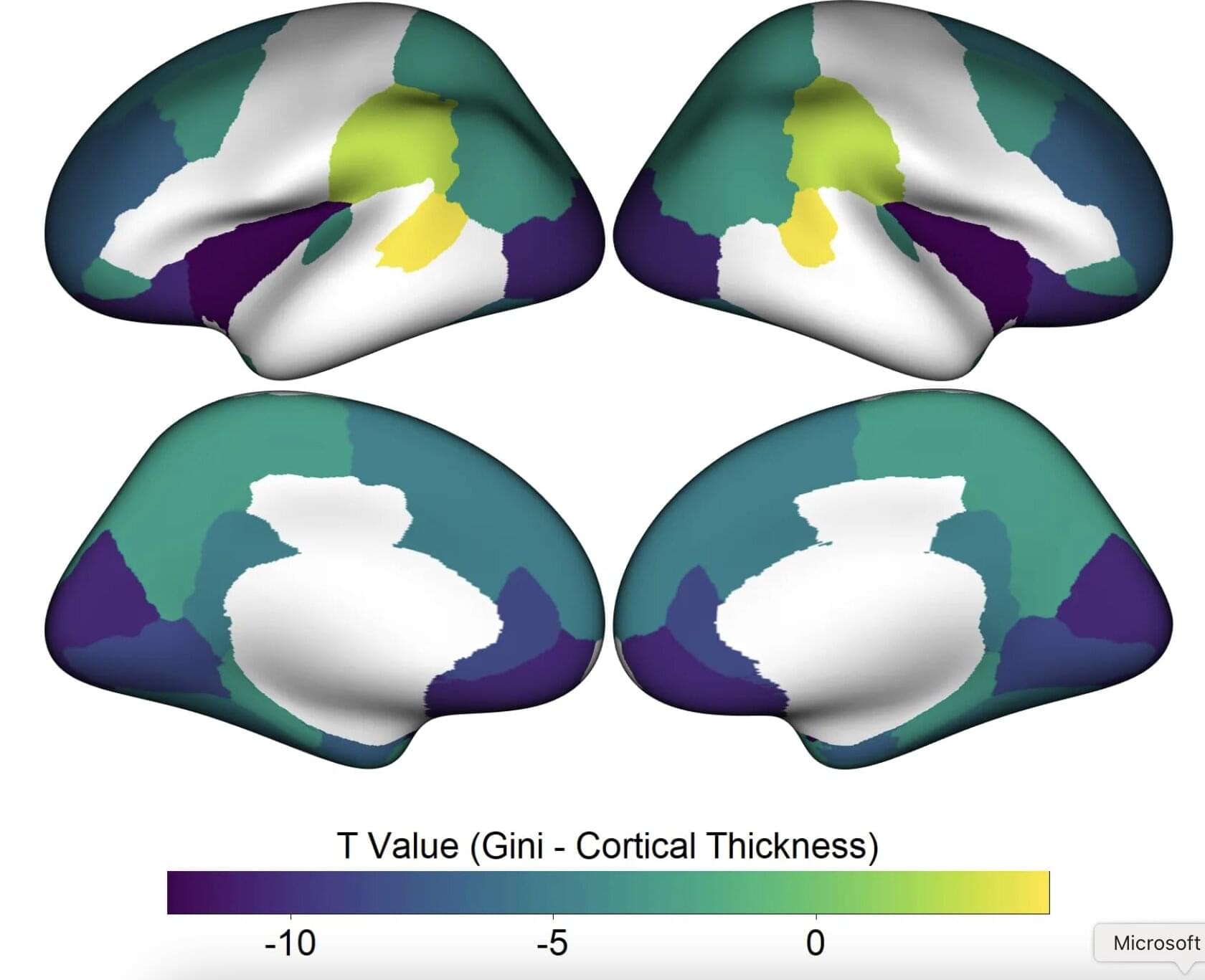
The distribution of wealth between different people living in specific geographical regions has changed substantially over the past decades, with some segments of the population benefiting most from economic growth than others. In some parts of the United States, the United Kingdom and various European countries, the distribution of wealth has become increasingly uneven.
An uneven wealth distribution essentially means that there is significant disparity in the income and resources of the general population, with some people earning good salaries and others living in the same place struggling to meet their basic needs. This inequality is typically measured with a value ranging from 0 to 1, known as the Gini coefficient, where 0 represents perfect equality and 1 extreme inequality.
Researchers at King’s College London, Harvard University and the University of York recently carried out a study aimed at exploring the possible impact of living in a society where wealth is unevenly distributed on the brain’s development in late childhood and pre-adolescence. Their findings, published in Nature Mental Health, suggest that living in places with a high income inequality is associated with differences in the structure of some brain regions, which could in turn predict the emergence of mental health disorders.