Experiments with programmable electroacoustic cavities reveal that a multistable system can be steered into states that are unreachable with conventional control methods.
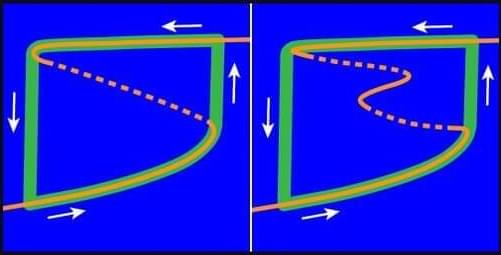
Many physical systems can be in more than one stable state: A laser can be on or off, and a magnetic bit up or down. This multistability can appear in nonlinear resonators—such as ferromagnets and genetic toggle switches in cells—that are driven into different steady states, or “branches,” by ramping up and down the driving parameter [1]. This behavior is often pictured using a familiar hysteresis loop that traces the system’s trajectory between a lower branch and higher branch (Fig. 1). It is easy to imagine that additional steady states might coexist with those sampled, but experiments have largely ignored that possibility, assuming instead that slow, quasistatic parameter sweeps reveal all “physically relevant” behavior.
In a new acoustic experiment, Kun Zhang from the Wuhan University in China and colleagues challenge that assumption [2]. They show that a pair of coupled acoustic cavities can host a fully “folded” steady state that is perfectly stable yet invisible to conventional sweeps. This hidden branch can, however, be reached with carefully designed sound pulses, the team shows. These results—combined with those from another recent study [3]—turn the abstract idea of hidden multistability into a concrete and controllable feature of nonlinear resonator networks, which might one day be used to securely store sensitive information.