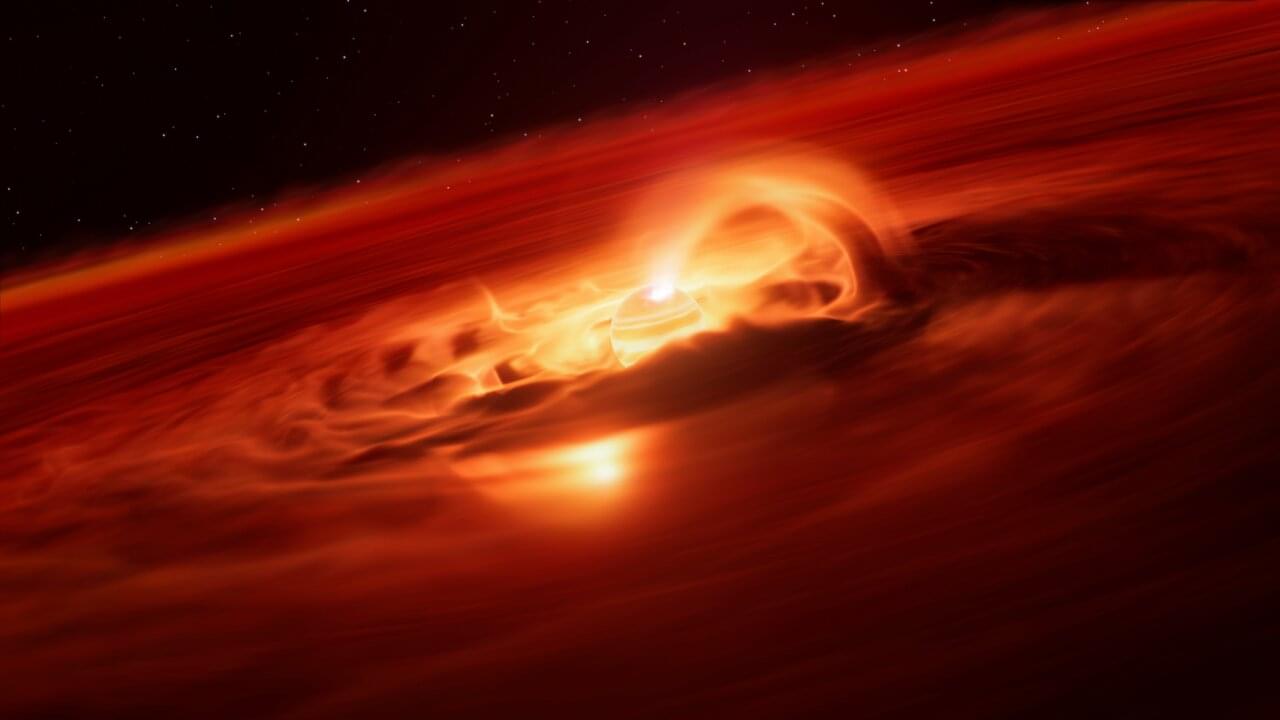
Astronomers have identified an enormous ‘growth spurt’ in a so-called rogue planet. Unlike the planets in our Solar System, these objects do not orbit stars, free-floating on their own instead. The new observations, made with the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT), reveal that this free-floating planet is eating up gas and dust from its surroundings at a rate of six billion tonnes a second. This is the strongest growth rate ever recorded for a rogue planet, or a planet of any kind, providing valuable insights into how they form and grow.
“People may think of planets as quiet and stable worlds, but with this discovery we see that planetary-mass objects freely floating in space can be exciting places,” says Víctor Almendros-Abad, an astronomer at the Astronomical Observatory of Palermo, National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF), Italy and lead author of the new study.
The newly studied object, which has a mass five to 10 times the mass of Jupiter, is located about 620 light-years away in the constellation Chamaeleon. Officially named Cha 1107–7626, this rogue planet is still forming and is fed by a surrounding disc of gas and dust. This material constantly falls onto the free-floating planet, a process known as accretion. However, the team led by Almendros-Abad has now found that the rate at which the young planet is accreting is not steady.