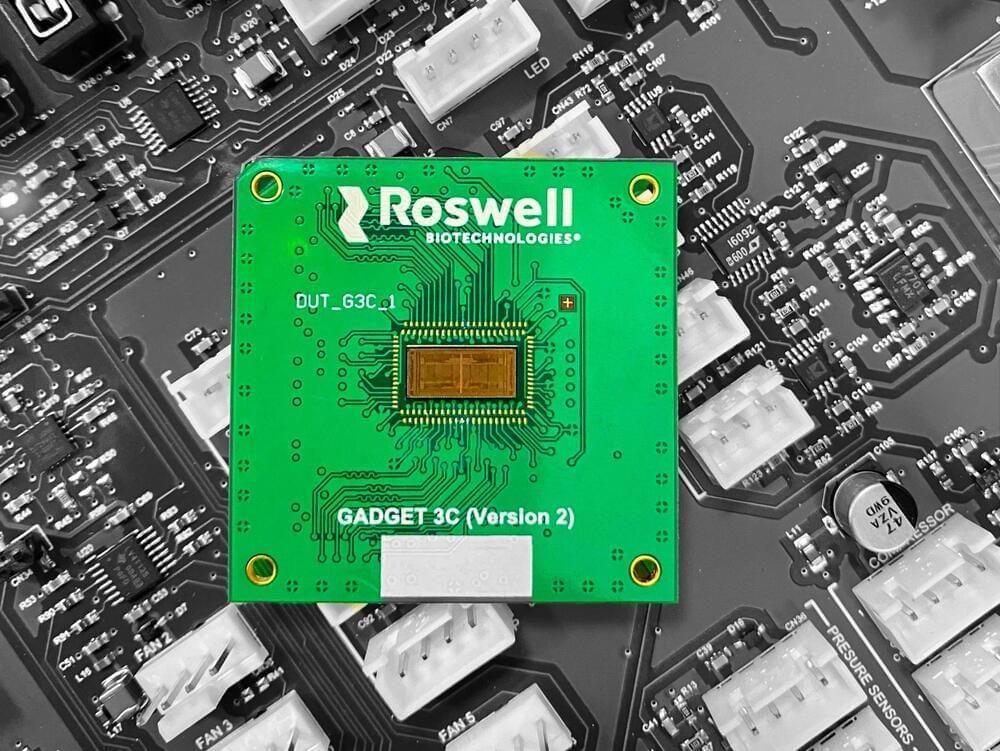
A platform for single-molecule measurement of binding kinetics & enzyme activity.
The first molecular electronics chip has been developed, realizing a 50-year-old goal of integrating single molecules into circuits to achieve the ultimate scaling limits of Moore’s Law. Developed by Roswell Biotechnologies and a multi-disciplinary team of leading academic scientists, the chip uses single molecules as universal sensor elements in a circuit to create a programmable biosensor with real-time, single-molecule sensitivity and unlimited scalability in sensor pixel density. This innovation, appearing this week in a peer-reviewed article in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), will power advances in diverse fields that are fundamentally based on observing molecular interactions, including drug discovery, diagnostics, DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two long strands of nucleotides that coil around each other to form a double helix. It is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms that carries genetic instructions for development, functioning, growth, and reproduction. Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).