“Our study may be as good as it will ever get for finding neural signatures of near-death consciousness,” said the study’s senior author.



Aviation punches above its weight when it comes to greenhouse emissions — it is by far the highest emission form of transportation. Our modern mega planes may be the most efficient they’ve ever been, but in 2019, they still churned out over 915 million tonnes of carbon dioxide.
To make matters worse, one of our best zero-emission alternatives — hydrogen — is far too heavy and bulky to build a usable airplane. Or at least that is what we thought.
The California startup HyPoint recently announced their plan to make a hydrogen-powered aircraft with nearly three times the range of a turboprop commuter jet.
Upon removal of ventilator support, two of the patients showed an increase in heart rate along with a surge of gamma wave activity, considered the fastest brain activity and associated with consciousness.
Furthermore, the activity was detected in the so-called hot zone of neural correlates of consciousness in the brain, the junction between the temporal, parietal and occipital lobes in the back of the brain. This area has been correlated with dreaming, visual hallucinations in epilepsy, and altered states of consciousness in other brain studies.
In this video, the YouTube channel Dark Footage explains and demonstrates how the small-caliber guided bullet was developed and how accurate it is. As explained in the description box, this system combines a movable bullet with a guidance framework that can alter the bullet’s path after it has been fired. This guarantees the bullet reaches its target no matter what. Yes, this means both experienced and inexperienced shooters can hit a moving target using the technology.
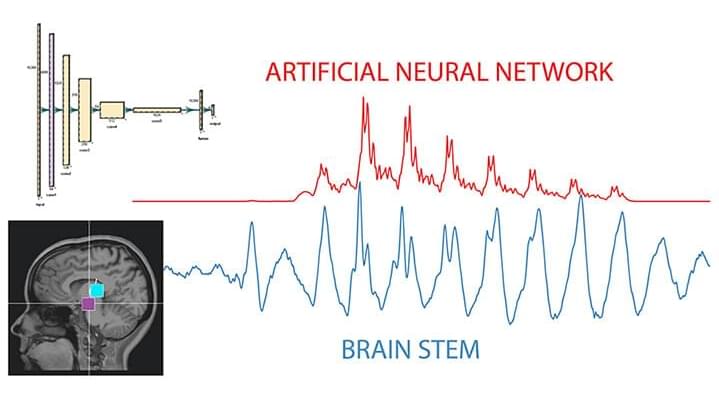
New research from the University of California, Berkeley, shows that artificial intelligence (AI) systems can process signals in a way that is remarkably similar to how the brain interprets speech, a finding scientists say might help explain the black box of how AI systems operate.
Using a system of electrodes placed on participants’ heads, scientists with the Berkeley Speech and Computation Lab measured brain waves as participants listened to a single syllable— bah. They then compared that brain activity to the signals produced by an AI system trained to learn English.
“The shapes are remarkably similar,” said Gasper Begus, assistant professor of linguistics at UC Berkeley and lead author on the study published recently in the journal Scientific Reports. “That tells you similar things get encoded, that processing is similar.”
iSpace, a private space company based in Japan, lost contact with its Hakuto-R spacecraft as it attempted to become the first private mission to land on the moon this morning. “We have to assume that we could not complete the landing on the lunar surface,” iSpace CEO and founder Takeshi Hakamada said during a livestream. “Our engineers will continue to investigate the situation, and we will update you with further information when we finish the investigation.”
Hakuto-R launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket last December. It took a long but efficient route, looping way out past the moon before using several orbital adjustments and the gravity of the Earth, moon, and sun to enter lunar orbit last month. On April 13, after a few more final adjustments, it locked into a circular orbit 100 kilometers above the lunar surface.
Early in its landing attempt, the spacecraft dipped behind the moon making communications impossible. The team reestablished contact as it rounded the lunar horizon and began its descent. During the livestream, iSpace showed a simulation of the landing. The ride to the surface began with a deceleration burn and a series of attitude adjustments, bending the spacecraft’s trajectory toward the surface and flipping its orientation.
The “La Moto Volante” – the Flying Motorcycle is based on his Lazareth LM 847 with a 350kW, 4.7-litre Maserati V8 that was unveiled at the Geneva Motor Show in March 2016. At the center of each wheel hub is a powerful jet turbine, exhaust facing downward, similar to a quadcopter drone, but with much more power.
Source/image(PrtSc): Lazareth Auto-Moto


He thinks about Robert Oppenheimer and the Manhattan Project that led to the atomic bomb, Hiroshima, and Nagasaki, and the current state of mutually assured destruction (MAD). It started with a science experiment to split the atom and soon the genie was released from the bottle.
I think of the arrival of generalized AI like ChatGPT as being equivalent to the revolution brought on by the invention of movable type and the printing press. Would the Reformation in Europe have happened without it? Would Europe’s rise to world dominance in the 18th and 19th centuries have resulted? The printing press genie uncorked led to a generalized knowledge revolution with both good and bad consequences.
The future uncorked AI genie with no guidance from us could, in answering the question I asked at the beginning of this posting, see humanity as the greatest threat to life on the planet and act accordingly if we don’t gain control over it.