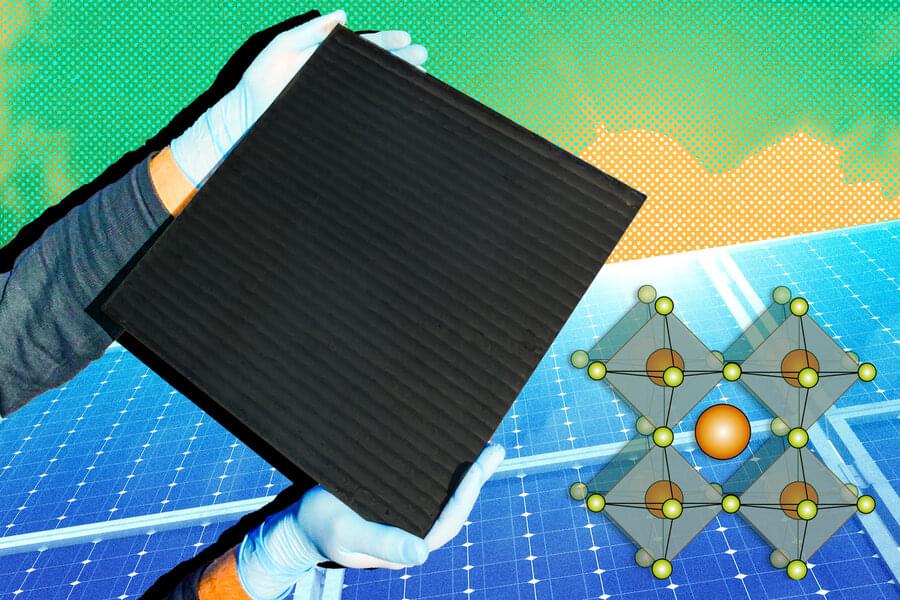
Perovskites are a family of materials that are currently the leading contender to potentially replace today’s silicon-based solar photovoltaics. They hold the promise of panels that are far thinner and lighter, that could be made with ultra-high throughput at room temperature instead of at hundreds of degrees, and that are cheaper and easier to transport and install. But bringing these materials from controlled laboratory experiments into a product that can be manufactured competitively has been a long struggle.
Manufacturing perovskite-based solar cells involves optimizing at least a dozen or so variables at once, even within one particular manufacturing approach among many possibilities. But a new system based on a novel approach to machine learning could speed up the development of optimized production methods and help make the next generation of solar power a reality.
The system, developed by researchers at MIT and Stanford University over the last few years, makes it possible to integrate data from prior experiments, and information based on personal observations by experienced workers, into the machine learning process. This makes the outcomes more accurate and has already led to the manufacturing of perovskite cells with an energy conversion efficiency of 18.5 percent, a competitive level for today’s market.