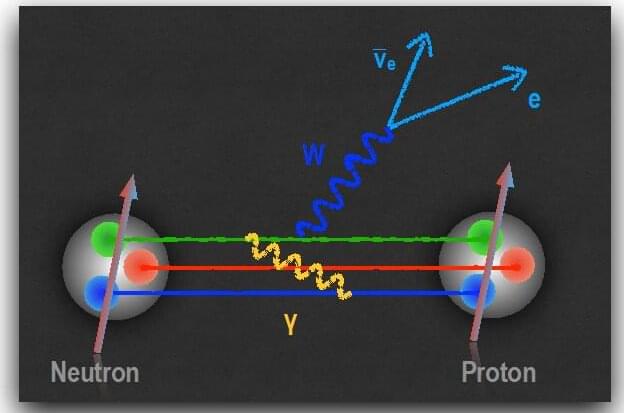
Outside atomic nuclei, neutrons are unstable particles, with a lifetime of about fifteen minutes. The neutron disintegrates due to the weak nuclear force, leaving behind a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The weak nuclear force is one of the four fundamental forces in the universe, along with the strong force, the electromagnetic force, and the gravitational force.
Comparing experimental measurements of neutron decay with theoretical predictions based on the weak nuclear force can reveal as-yet undiscovered interactions. To do so, researchers must achieve extremely high levels of precision. A team of nuclear theorists has uncovered a new, relatively large effect in neutron decay that arises from the interplay of the weak and electromagnetic forces.
This research identified a shift in the strength with which a spinning neutron experiences the weak nuclear force. This has two major implications. First, scientists have known since 1956 that due to the weak force, a system and one built like its mirror image do not behave in the same way. In other words, mirror reflection symmetry is broken. This research affects the search for new interactions, technically known as “right-handed currents,” that, at very short distances of less than one hundred quadrillionths of a centimeter, restore the universe’s mirror-reflection symmetry. Second, this research points to the need to compute electromagnetic effects with higher precision. Doing so will require the use of future high-performance computers.