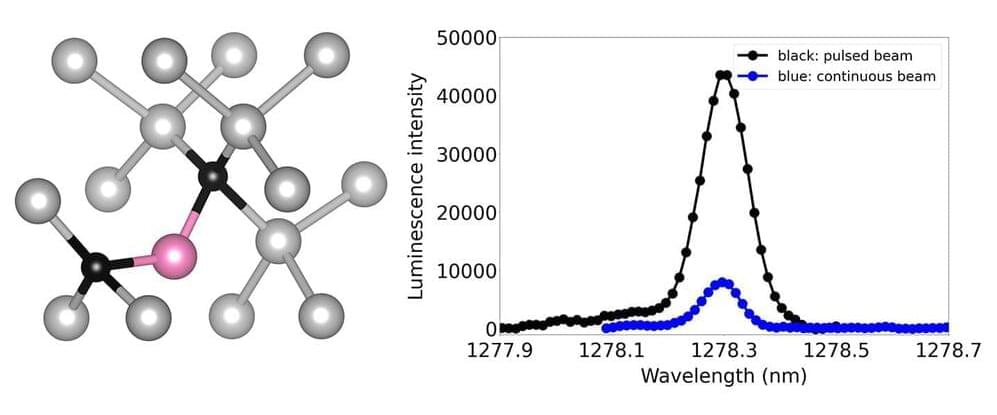
The prospect of a quantum internet, connecting quantum computers and capable of highly secure data transmission, is enticing, but making it poses a formidable challenge. Transporting quantum information requires working with individual photons rather than the light sources used in conventional fiber optic networks.
To produce and manipulate individual photons, scientists are turning to quantum light emitters, also known as color centers. These atomic-scale defects in semiconductor materials can emit single photons of fixed wavelength or color and allow photons to interact with electron spin properties in controlled ways.
A team of researchers has recently demonstrated a more effective technique for creating quantum emitters using pulsed ion beams, deepening our understanding of how quantum emitters are formed. The work was led by Department of Energy Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) researchers Thomas Schenkel, Liang Tan, and Boubacar Kanté who is also an associate professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences at the University of California, Berkeley.