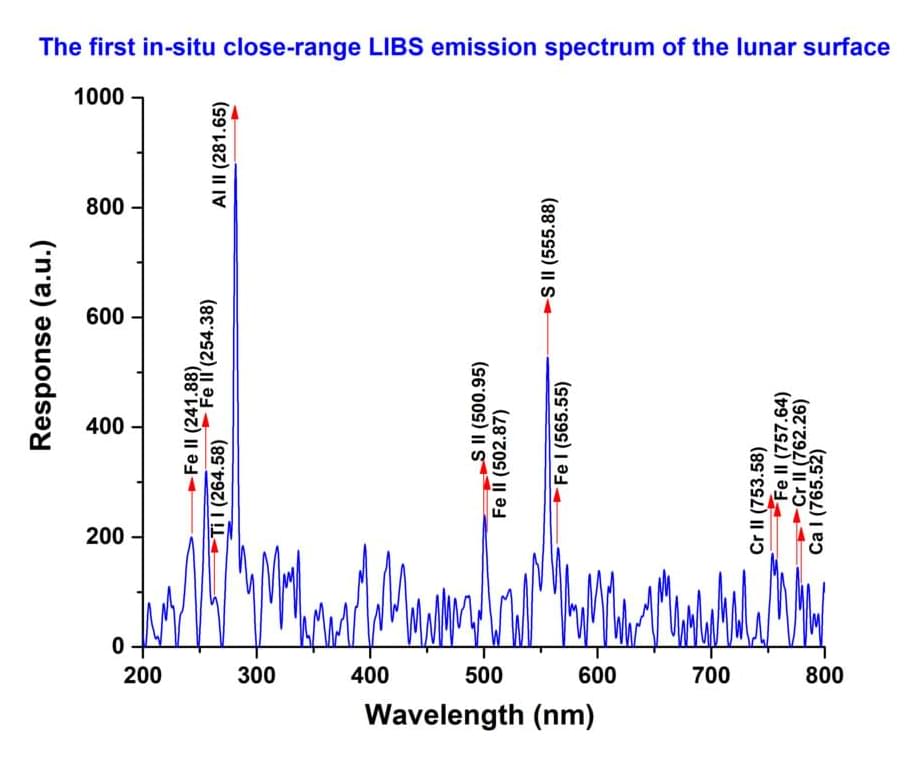
The Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) instrument onboard Chandrayaan-3 Rover has made the first-ever in-situ measurements on the elemental composition of the lunar surface near the south pole. These in-situ measurements confirm the presence of Sulphur (S) in the region unambiguously, something that was not feasible by the instruments onboard the orbiters.
LIBS is a scientific technique that analyzes the composition of materials by exposing them to intense laser pulses. A high-energy laser pulse is focused onto the surface of a material, such as a rock or soil. The laser pulse generates an extremely hot and localized plasma. The collected plasma light is spectrally resolved and detected by detectors such as Charge Coupled Devices. Since each element emits a characteristic set of wavelengths of light when it’s in a plasma state, the elemental composition of the material is determined.
Preliminary analyses, graphically represented, have unveiled the presence of Aluminum (Al), Sulphur (S), Calcium (Ca), Iron (Fe), Chromium (Cr), and Titanium (Ti) on the lunar surface. Further measurements have revealed the presence of manganese (Mn), silicon (Si), and oxygen (O). Thorough investigation regarding the presence of Hydrogen is underway.