TIME’s list of the most influential people in artificial intelligence.



Video games could give ophthalmologists an easy window not into the soul, but into eye health and the eye-brain-body connection — the three-way reciprocal communication that influences our actions.
“Infusing science into games is like sneaking broccoli into ice cream,” said Khizer Khaderi, MD, a clinical associate professor of ophthalmology. “It removes the resistance to do something that may not be viewed as fun, such as eating vegetables.” Or in this case, evaluating your vision health.
In a Stanford Medicine-led study, researchers employed video games to evaluate participants’ field of vision and visual stamina, their ability to distinguish contrast, and other factors that can indicate common eye diseases.

The world’s largest democracy is poised to transform itself and the world, embracing AI on an enormous scale.
Speaking with the press Friday in Bengaluru, in the context of announcements from two of India’s largest conglomerates, Reliance Industries Limited and Tata Group, NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang detailed plans to bring AI technology and skills to address the world’s most populous nation’s greatest challenges.
“I think this is going to be one of the largest AI markets in the world,” said Huang, who was wrapping up a week of high-level meetings across the nation, including with Prime Minister Narendra Modi, leading AI researchers, top business leaders, members of the press and the country’s 4,000-some NVIDIA employees.
In a major breakthrough, scientists in Israel have created ‘artificial embryos’. They mimic all the features of a real human embryo. Will these embryos be used to create human life? Here’s what Priyanka Sharma has to say.
#artificialembroy #science #gravitas.
About Channel:
WION The World is One News examines global issues with in-depth analysis. We provide much more than the news of the day. Our aim is to empower people to explore their world. With our Global headquarters in New Delhi, we bring you news on the hour, by the hour. We deliver information that is not biased. We are journalists who are neutral to the core and non-partisan when it comes to world politics. People are tired of biased reportage and we stand for a globalized united world. So for us, the World is truly One.
Please keep discussions on this channel clean and respectful and refrain from using racist or sexist slurs and personal insults.
Check out our website: http://www.wionews.com.
NEW YORK—(BUSINESS WIRE)— Paige, a technology disruptor in healthcare, has joined forces with Microsoft in the fight against cancer, making headway in their collaboration to transform cancer diagnosis and patient care by building the world’s largest image-based artificial intelligence (AI) models for digital pathology and oncology.
“Unleashing the power of AI is a game changer in advancing healthcare to improve lives.” Tweet this
Paige, a global leader in end-to-end digital pathology solutions and clinical AI, developed the first Large Foundation Model using over one billion images from half a million pathology slides across multiple cancer types. Paige is developing with Microsoft a new AI model that is orders-of-magnitude larger than any other image-based AI model existing today, configured with billions of parameters. This model assists in capturing the subtle complexities of cancer and serves as the cornerstone for the next generation of clinical applications and computational biomarkers that push the boundaries of oncology and pathology.
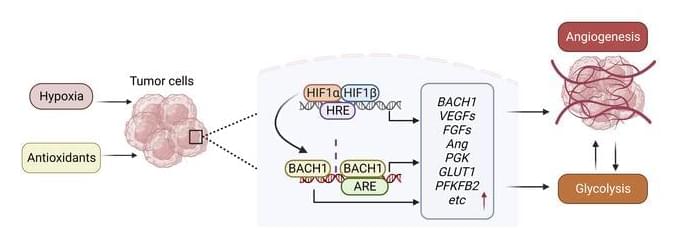
Which is a response to hypoxia typically coordinated by hypoxia-inducible transcription factors (HIFs); but growing evidence indicate that transcriptional programs beyond HIFs control tumor angiogenesis. Here we show that the redox-sensitive transcription factor BTB and CNC homology 1 (BACH1) controls the transcription of a broad range of angiogenesis genes. BACH1 is stabilized by lowering reactive oxygen species levels; consequently, angiogenesis gene expression in lung cancer cells, tumor organoids, and xenograft tumors increased substantially following vitamin C and E and N-acetylcysteine administration in a BACH1-dependent fashion under normoxia. Moreover, angiogenesis gene expression increased in endogenous BACH1–overexpressing cells and decreased in BACH1-knockouts in the absence of antioxidants.
What do you think? China is doing it. The West is going to have to keep up. Have you seen the Netflix series Altered Carbon? It’s like that.
A U.S. Army video shows its concept of the soldier of the future. At first glance, it looks like it will only be a better-equipped soldier.
But the video mentions “neural enhancement.” That can mean a brain implant that connects a human to computers. The defense agency DARPA has been working on an advanced implant that would essentially put the human brain “online.” There could also be eye and ear implants and other circuitry under the skin to make the optimal fighting machine.
Americans will have to decide whether this is ethical because some in our military clearly want it.
FULL REPORT: https://www1.cbn.com/cbnnews/national-security/2021/april/ne…-soldiers.

Citizen Lab says two zero-days fixed by Apple today in emergency security updates were actively abused as part of a zero-click exploit chain (dubbed BLASTPASS) to deploy NSO Group’s Pegasus commercial spyware onto fully patched iPhones.
The two bugs, tracked as CVE-2023–41064 and CVE-2023–41061, allowed the attackers to infect a fully-patched iPhone running iOS 16.6 and belonging to a Washington DC-based civil society organization via PassKit attachments containing malicious images.
“We refer to the exploit chain as BLASTPASS. The exploit chain was capable of compromising iPhones running the latest version of iOS (16.6) without any interaction from the victim,” Citizen Lab said.

ROCHESTER, Minn. — In a randomized trial, published in The Lancet Oncology, Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers uncover evidence supporting a shorter treatment time for breast cancer patients. The study compared two separate dosing schedules of pencil-beam scanning proton therapy, the most advanced type of proton therapy known for its precision in targeting cancer cells while preserving healthy tissue to reduce the risk of side effects.
Survival rates for breast cancer continue to improve due to advances in diagnosis and treatment, leading to increasing emphasis on reducing the long-term toxicity of cancer treatment, including radiotherapy.
Prior to this study, all patients treated with proton postmastectomy radiotherapy (PMRT) had received a conventional 25-to 30-day course delivered five days per week over five to six weeks. The researchers hoped to demonstrate that condensing the course of proton beam therapy, a form of particle therapy that could spare the heart and lungs from radiation damage, may result in a similar side effect profile.
